Assim como nas versões anteriores, o Android 15 inclui mudanças de comportamento que podem afetar seu app. As mudanças de comportamento a seguir se aplicam exclusivamente a apps destinados ao Android 15 ou versões mais recentes. Caso seu app seja direcionado ao Android 15 ou a versões mais recentes, faça modificações para oferecer suporte a esses comportamentos de forma adequada, quando aplicável.
Consulte também a lista de mudanças de comportamento que afetam todos os apps
executados no Android 15, independente da targetSdkVersion do seu app.
Principal recurso
O Android 15 modifica ou expande vários recursos principais do sistema Android.
Mudanças nos serviços em primeiro plano
我们将对 Android 15 中的前台服务进行以下更改。
数据同步前台服务超时行为
O Android 15 introduz um novo comportamento de tempo limite no dataSync para apps destinados
ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API) ou versões mais recentes. Esse comportamento também se aplica ao novo
tipo de serviço em primeiro plano mediaProcessing.
O sistema permite que os serviços dataSync de um app sejam executados por um total de 6 horas
em um período de 24 horas. Depois disso, o sistema chama o método
Service.onTimeout(int, int) do serviço em execução (introduzido no Android
15). No momento, o serviço tem alguns segundos para chamar
Service.stopSelf(). Quando Service.onTimeout() é chamado, o
serviço não é mais considerado um serviço em primeiro plano. Se o serviço não
chamar Service.stopSelf(), o sistema vai gerar uma exceção interna. A
exceção é registrada no Logcat com a seguinte mensagem:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Para evitar problemas com essa mudança de comportamento, faça uma ou mais das seguintes ações:
- Faça com que o serviço implemente o novo método
Service.onTimeout(int, int). Quando o app receber o callback, chamestopSelf()em alguns segundos. Se você não parar o app imediatamente, o sistema vai gerar uma falha. - Os serviços
dataSyncdo app não podem ser executados por mais de 6 horas em um período de 24 horas (a menos que o usuário interaja com o app, redefinindo o timer). - Só inicie serviços em primeiro plano
dataSynccomo resultado da interação direta do usuário. Como o app está em primeiro plano quando o serviço é iniciado, ele tem seis horas completas após o app ir para o segundo plano. - Em vez de usar um serviço em primeiro plano
dataSync, use uma API alternativa.
Se os serviços em primeiro plano dataSync do app tiverem sido executados por seis horas nas últimas
24 horas, não será possível iniciar outro serviço em primeiro plano dataSync a menos que o usuário
tenha trazido o app para o primeiro plano, o que redefine o timer. Se você tentar
iniciar outro serviço em primeiro plano dataSync, o sistema vai gerar
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
com uma mensagem de erro como "O limite de tempo já foi esgotado para o tipo de serviço em primeiro plano
dataSync".
Teste
Para testar o comportamento do app, ative os timeouts de sincronização de dados mesmo que o app
não esteja segmentado para o Android 15, desde que esteja sendo executado em um dispositivo
Android 15. Para ativar os tempos limite, execute o comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Você também pode ajustar o período de tempo limite para facilitar o teste do comportamento
do app quando o limite for atingido. Para definir um novo período de tempo limite, execute o
seguinte comando adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
新的媒体处理前台服务类型
O Android 15 apresenta um novo tipo de serviço em primeiro plano, mediaProcessing. Esse
tipo de serviço é adequado para operações como transcodificação de arquivos de mídia. Por
exemplo, um app de mídia pode fazer o download de um arquivo de áudio e precisar convertê-lo para um
formato diferente antes de reproduzi-lo. Você pode usar um serviço em primeiro plano
mediaProcessing para garantir que a conversão continue mesmo quando o app estiver em
segundo plano.
O sistema permite que os serviços mediaProcessing de um app sejam executados por um total de 6
horas em um período de 24 horas. Depois disso, o sistema chama o método
Service.onTimeout(int, int) do serviço em execução (introduzido no Android
15). Nesse momento, o serviço tem alguns segundos para chamar
Service.stopSelf(). Se o serviço não
chamar Service.stopSelf(), o sistema vai gerar uma exceção interna. A
exceção é registrada no Logcat com a seguinte mensagem:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
Para evitar a exceção, siga um destes procedimentos:
- Faça com que o serviço implemente o novo método
Service.onTimeout(int, int). Quando o app receber o callback, chamestopSelf()dentro de alguns segundos. Se você não interromper o app imediatamente, o sistema vai gerar uma falha. - Verifique se os serviços
mediaProcessingdo app não são executados por mais de um total de seis horas em qualquer período de 24 horas, a menos que o usuário interaja com o app, redefinindo o timer. - Só inicie serviços em primeiro plano
mediaProcessingcomo resultado da interação direta do usuário. Como o app está em primeiro plano quando o serviço é iniciado, ele tem seis horas completas após o app ir para o segundo plano. - Em vez de usar um serviço em primeiro plano
mediaProcessing, use uma API alternativa, como o WorkManager.
Se os serviços em primeiro plano mediaProcessing do app tiverem sido executados por 6 horas nas
últimas 24 horas, não será possível iniciar outro serviço em primeiro plano mediaProcessing a menos que
o usuário tenha trazido o app para o primeiro plano (o que redefine o timer). Se você
tentar iniciar outro serviço mediaProcessing em primeiro plano, o sistema vai gerar
ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
com uma mensagem de erro como "O limite de tempo já se esgotou para o tipo de serviço em primeiro plano
mediaProcessing".
Para mais informações sobre o tipo de serviço mediaProcessing, consulte Mudanças nos
tipos de serviço em primeiro plano do Android 15: processamento de mídia.
Teste
Para testar o comportamento do app, ative os timeouts de processamento de mídia, mesmo que
o app não seja direcionado ao Android 15 (desde que esteja sendo executado em um
dispositivo Android 15). Para ativar os tempos limite, execute o seguinte comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
Você também pode ajustar o período de tempo limite para facilitar o teste do comportamento
do app quando o limite for atingido. Para definir um novo período de tempo limite, execute o
seguinte comando adb:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
对启动前台服务的 BOOT_COMPLETED 广播接收器的限制
Há novas restrições para inicialização de broadcast receivers BOOT_COMPLETED
serviços em primeiro plano. Receptores BOOT_COMPLETED não têm permissão para iniciar o
seguintes tipos de serviços em primeiro plano:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(esta restrição está em vigor paramicrophonedesde o Android 14)
Se um receptor BOOT_COMPLETED tentar iniciar qualquer um desses tipos de primeiro plano
serviços, o sistema gera ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Teste
Para testar o comportamento do app, ative essas novas restrições mesmo que seu
O app não é destinado ao Android 15, desde que seja executado em um Android 15
dispositivo). Execute o seguinte comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Para enviar uma transmissão BOOT_COMPLETED sem reiniciar o dispositivo:
Execute o seguinte comando adb:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
在应用拥有 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 权限时启动前台服务的限制
Anteriormente, se um app tivesse a permissão SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW, ele poderia iniciar
um serviço em primeiro plano mesmo que estivesse em segundo plano (conforme
discutido em isenção de restrições de início em segundo plano).
Se um app for destinado ao Android 15, essa isenção será mais restrita. Agora o app precisa
ter a permissão SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW e também ter uma janela de sobreposição
visível. Ou seja, o app precisa primeiro abrir uma
janela TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY e a janela
precisa estar visível antes de iniciar um serviço em primeiro plano.
Se o app tentar iniciar um serviço em primeiro plano em segundo plano sem
atender a esses novos requisitos (e não tiver outra isenção), o
sistema vai gerar uma ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Se o app declarar a permissão SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW
e iniciar serviços em primeiro plano em segundo plano, ele poderá ser afetado por essa
mudança. Se o app receber uma ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException, verifique
a ordem das operações e verifique se ele já tem uma janela de sobreposição
ativa antes de tentar iniciar um serviço em primeiro plano em segundo
plano. Você pode conferir se a janela de sobreposição está visível
chamando View.getWindowVisibility() ou
substituir View.onWindowVisibilityChanged()
para receber uma notificação sempre que a visibilidade mudar.
Teste
Para testar o comportamento do app, ative essas novas restrições mesmo que ele
não seja direcionado ao Android 15, desde que esteja sendo executado em um dispositivo
Android 15. Para ativar essas novas restrições na inicialização de serviços em primeiro plano
em segundo plano, execute este comando adb:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
Mudanças em quando os apps podem modificar o estado global do modo Não perturbe
Os apps direcionados ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API) e mais recentes não podem mais mudar o
estado global ou a política de Não perturbe (DND, na sigla em inglês) em um dispositivo, seja modificando
as configurações do usuário ou desativando o modo DND. Em vez disso, os apps precisam contribuir com um
AutomaticZenRule, que o sistema combina em uma política global com o
esquema de política mais restritiva. As chamadas para APIs que
afetam o estado global (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) resultam na criação ou atualização de um
AutomaticZenRule implícito, que é ativado e desativado dependendo do ciclo de chamadas
dessas chamadas de API.
Essa mudança só afeta o comportamento observável se o app estiver chamando
setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) e esperar que essa chamada desative uma AutomaticZenRule que foi ativada anteriormente pelos proprietários.
Mudanças na API OpenJDK
O Android 15 continua o trabalho de atualizar as principais bibliotecas do Android para se alinhar aos recursos das versões mais recentes do LTS do OpenJDK.
Algumas dessas mudanças podem afetar a compatibilidade de apps destinados ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API):
Mudanças nas APIs de formatação de strings: a validação de índice de argumento, flags, largura e precisão agora é mais rigorosa ao usar as seguintes APIs
String.format()eFormatter.format():String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
Por exemplo, a exceção a seguir é gerada quando um índice de argumento 0 é usado (
%0na string de formato):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0Nesse caso, o problema pode ser corrigido usando um índice de argumento de 1 (
%1na string de formato).Mudanças no tipo de componente de
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): ao usarArrays.asList(...).toArray(), o tipo de componente da matriz resultante agora é umObject, não o tipo dos elementos da matriz subjacente. Portanto, o código a seguir gera umClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();Nesse caso, para preservar
Stringcomo o tipo de componente na matriz resultante, useCollection.toArray(Object[]):String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Mudanças no processamento de códigos de idioma: ao usar a API
Locale, os códigos de idioma para hebraico, iídiche e indonésio não são mais convertidos para as formas obsoletas (hebraico:iw, iídiche:jie indonésio:in). Ao especificar o código de idioma para uma dessas localidades, use os códigos do ISO 639-1 (hebraico:he, iídiche:yie indonésio:id).Mudanças nas sequências de números inteiros aleatórios: seguindo as mudanças feitas em https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, os seguintes métodos
Random.ints()agora retornam uma sequência de números diferente dos métodosRandom.nextInt():Em geral, essa mudança não deve resultar em um comportamento que prejudique o app, mas seu código não deve esperar que a sequência gerada pelos métodos
Random.ints()corresponda aRandom.nextInt().
A nova API SequencedCollection pode afetar a compatibilidade do app
depois que você atualizar compileSdk na configuração de build do app para usar
o Android 15 (nível 35 da API):
Colisão com funções de extensão
MutableList.removeFirst()eMutableList.removeLast()emkotlin-stdlibO tipo
Listem Java é mapeado para o tipoMutableListem Kotlin. Como as APIsList.removeFirst()eList.removeLast()foram introduzidas no Android 15 (nível 35 da API), o compilador Kotlin resolve chamadas de função, por exemplo,list.removeFirst(), estaticamente para as novas APIsListem vez das funções de extensão emkotlin-stdlib.Se um app for recompilado com
compileSdkdefinido como35eminSdkdefinido como34ou inferior, e depois o app for executado no Android 14 e versões anteriores, um erro de tempo de execução será gerado:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;A opção
NewApido lint no Plug-in do Android para Gradle pode detectar esses novos usos da API../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()Para corrigir a exceção de execução e os erros de lint, as chamadas de função
removeFirst()eremoveLast()podem ser substituídas porremoveAt(0)eremoveAt(list.lastIndex), respectivamente, em Kotlin. Se você estiver usando o Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 ou mais recente, ele também vai oferecer uma opção de correção rápida para esses erros.Considere remover
@SuppressLint("NewApi")elintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }se a opção de lint estiver desativada.Colisão com outros métodos em Java
Novos métodos foram adicionados aos tipos atuais, por exemplo,
ListeDeque. Esses novos métodos podem não ser compatíveis com os métodos de mesmo nome e tipos de argumentos em outras interfaces e classes. No caso de uma colisão de assinatura de método com incompatibilidade, o compiladorjavacgera um erro de tempo de build. Por exemplo:Exemplo de erro 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListExemplo de erro 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorExemplo de erro 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorPara corrigir esses erros de build, a classe que implementa essas interfaces precisa substituir o método com um tipo de retorno compatível. Exemplo:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
Segurança
O Android 15 inclui mudanças que promovem a segurança do sistema para ajudar a proteger apps e usuários contra apps maliciosos.
Versões TLS restritas
Android 15 限制了对 TLS 版本 1.0 和 1.1 的使用。这些版本之前已在 Android 中被弃用,但现在不允许面向 Android 15 的应用使用。
Início de atividades em segundo plano seguras
O Android 15 protege os usuários contra apps maliciosos e dá mais controle sobre os dispositivos. Isso é feito com mudanças que impedem que apps maliciosos em segundo plano tragam outros apps para o primeiro plano, elevem os privilégios e abusem da interação do usuário. O início de atividades em segundo plano está restrito desde o Android 10 (nível 29 da API).
Outras mudanças
- Mude os criadores de
PendingIntentpara bloquear as atividades em segundo plano por padrão. Isso ajuda a evitar que os apps criem acidentalmente umPendingIntentque possa ser usado indevidamente por agentes maliciosos. - Não coloque um app em primeiro plano, a menos que o remetente
PendingIntentpermita isso. Essa mudança tem como objetivo impedir que apps maliciosos abusem da capacidade de iniciar atividades em segundo plano. Por padrão, os apps não podem trazer a pilha de tarefas para o primeiro plano, a menos que o criador permita privilégios de início de atividade em segundo plano ou o remetente tenha esses privilégios. - Controlar como a atividade principal de uma pilha de tarefas pode concluir a tarefa. Se a atividade principal concluir uma tarefa, o Android voltará para a tarefa que estava ativa por último. Além disso, se uma atividade não principal concluir a tarefa, o Android voltará à tela inicial e não vai bloquear a conclusão dessa atividade não principal.
- Evite iniciar atividades arbitrárias de outros apps na sua tarefa. Essa mudança impede que apps maliciosos façam phishing com os usuários criando atividades que parecem ser de outros apps.
- Impedir que janelas não visíveis sejam consideradas para inicializações de atividades em segundo plano. Isso ajuda a impedir que apps maliciosos abusem de inícios de atividade em segundo plano para mostrar conteúdo indesejado ou malicioso aos usuários.
Intents mais seguras
Agora, o Android 15 tem o StrictMode para intents.
Para conferir registros detalhados sobre violações de uso do Intent, use o seguinte método:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
Experiência do usuário e interface do sistema
O Android 15 inclui algumas mudanças que visam criar uma experiência do usuário mais consistente e intuitiva.
Mudanças no encarte da janela
Há duas mudanças relacionadas aos engastes de janela no Android 15: o engaste de borda a borda é forçado por padrão, e também há mudanças de configuração, como a configuração padrão das barras do sistema.
Aplicação de ponta a ponta
Os apps são de ponta a ponta por padrão em dispositivos com Android 15 se o app for destinado ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API).
Essa é uma mudança incompatível que pode afetar negativamente a interface do seu app. As mudanças afetam as seguintes áreas da interface:
- Barra de navegação com alça de gestos
- Transparente por padrão.
- O deslocamento da parte de baixo está desativado, então o conteúdo é mostrado por trás da barra de navegação do sistema, a menos que encartes sejam aplicados.
setNavigationBarColoreR.attr#navigationBarColorestão descontinuados e não afetam a navegação por gestos.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedeR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedcontinuam sem efeito na navegação por gestos.
- Navegação com três botões
- Opacidade definida como 80% por padrão, com a cor possivelmente correspondendo ao plano de fundo da janela.
- Deslocamento da parte de baixo desativado para que o conteúdo seja mostrado por trás da barra de navegação do sistema, a menos que encartes sejam aplicados.
setNavigationBarColoreR.attr#navigationBarColorsão definidos para corresponder ao plano de fundo da janela por padrão. O plano de fundo da janela precisa ser um drawable de cor para que esse padrão seja aplicado. Essa API está descontinuada, mas continua afetando a navegação com três botões.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedeR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedsão verdadeiros por padrão, o que adiciona um plano de fundo 80% opaco na navegação com três botões.
- Barra de status
- Transparente por padrão.
- O deslocamento da parte de cima é desativado, então o conteúdo é mostrado por trás da barra de status, a menos que encartes sejam aplicados.
setStatusBarColoreR.attr#statusBarColorforam descontinuados e não têm efeito no Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedeR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedforam descontinuados, mas ainda têm um efeito no Android 15.
- Corte da tela
- O
layoutInDisplayCutoutModede janelas não flutuantes precisa serLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVEReDEFAULTsão interpretados comoALWAYSpara que os usuários não vejam uma barra preta causada pelo corte da tela e apareçam de ponta a ponta.
- O
O exemplo a seguir mostra um app antes e depois de ser direcionado ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API) e antes e depois de aplicar encartes. Este exemplo não é abrangente e pode aparecer de maneira diferente no Android Auto.
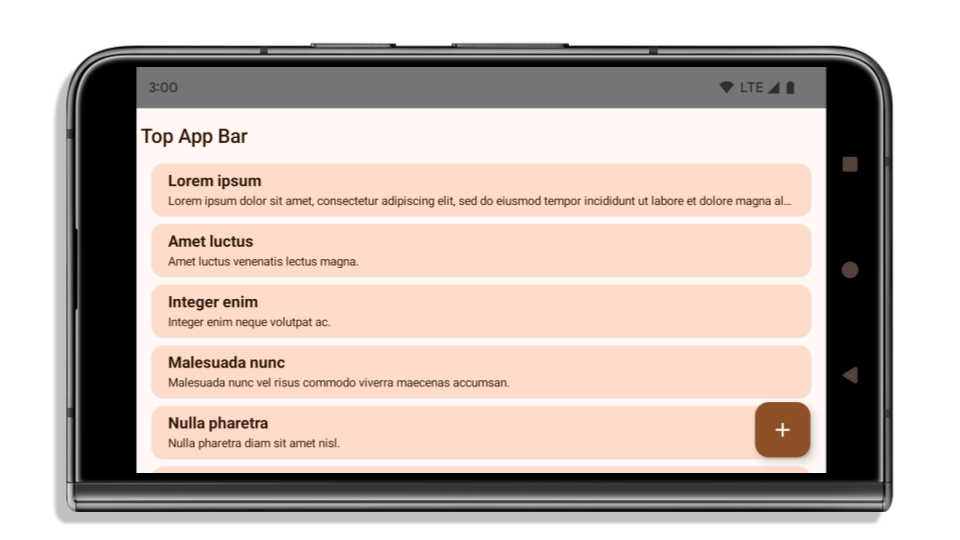

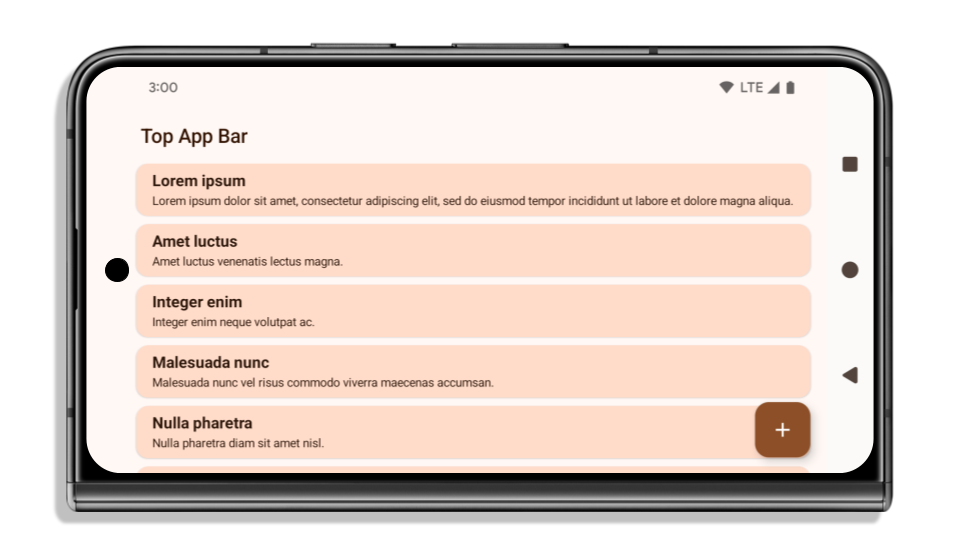
O que verificar se o app já é de ponta a ponta
Se o app já for de ponta a ponta e aplicar encartes, você não será muito afetado, exceto nos seguintes cenários. No entanto, mesmo que você não acredite que seu app foi afetado, recomendamos que você o teste.
- Você tem uma janela não flutuante, como um
Activityque usaSHORT_EDGES,NEVERouDEFAULTem vez deLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. Se o app falhar ao iniciar, o problema pode ser a tela de apresentação. Você pode fazer upgrade da dependência core splashscreen para 1.2.0-alpha01 ou uma versão mais recente ou definirwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - Pode haver telas com menos tráfego e interface obstruída. Verifique se essas telas menos visitadas não têm uma interface obstruída. As telas com menos tráfego incluem:
- Telas de onboarding ou login
- Páginas de configurações
O que verificar se o app ainda não é de ponta a ponta
Se o app ainda não estiver de ponta a ponta, é provável que você seja afetado. Além dos cenários para apps que já são de ponta a ponta, considere o seguinte:
- Se o app usar componentes do Material 3 (
androidx.compose.material3) no Compose, comoTopAppBar,BottomAppBareNavigationBar, é provável que esses componentes não sejam afetados porque processam encartes automaticamente. - Se o app estiver usando componentes do Material 2 (
androidx.compose.material) no Compose, eles não vão processar encartes automaticamente. No entanto, você pode conseguir acesso aos encartes para fazer a aplicação manual. No androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 e versões mais recentes, use o parâmetrowindowInsetspara aplicar os encartes manualmente paraBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigationeNavigationRail. Da mesma forma, use o parâmetrocontentWindowInsetsparaScaffold. - Se o app usar views e componentes do Material
(
com.google.android.material), a maioria dos componentes do Material baseados em views, comoBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailViewouNavigationView, processa encartes e não exige mais trabalho. No entanto, você precisa adicionarandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"se estiver usandoAppBarLayout. - Para elementos combináveis personalizados, aplique os encartes manualmente como padding. Se o conteúdo estiver em um
Scaffold, você poderá consumir encartes usando os valores de padding Scaffold. Caso contrário, aplique o padding usando um dosWindowInsets. - Se o app estiver usando visualizações e
BottomSheet,SideSheetou contêineres personalizados, aplique padding usandoViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ParaRecyclerView, aplique padding usando esse listener e também adicioneclipToPadding="false".
O que verificar se o app precisa oferecer proteção de segundo plano personalizada
Se o app precisar oferecer proteção de plano de fundo personalizada para a navegação com três botões ou
a barra de status, ele deverá colocar um elemento combinável ou uma visualização atrás da barra de sistema
usando WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() para receber a altura da barra de navegação
com três botões ou WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Outros recursos de ponta a ponta
Consulte os guias Visualizações de ponta a ponta e Compose de ponta a ponta para mais considerações sobre a aplicação de encartes.
APIs descontinuadas
As APIs a seguir estão descontinuadas, mas não desativadas:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(para navegação com três botões, com alfa de 80%)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(para navegação com três botões, com alfa de 80%)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
As APIs a seguir estão descontinuadas e desativadas:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(para navegação por gestos)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(para navegação por gestos)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
Configuração estável
Se o app for direcionado ao Android 15 (API de nível 35) ou versões mais recentes, Configuration não vai mais excluir as barras de sistema. Se você usar o tamanho da tela na classe Configuration para cálculo de layout, substitua por alternativas melhores, como um ViewGroup, WindowInsets ou WindowMetricsCalculator adequado, dependendo da sua necessidade.
O Configuration está disponível desde a API 1. Normalmente, ele é obtido de
Activity.onConfigurationChanged. Ele fornece informações como densidade,
orientação e tamanhos da janela. Uma característica importante sobre os tamanhos de janela
retornados de Configuration é que ele excluía as barras de sistema.
O tamanho da configuração é usado normalmente para seleção de recursos, como
/res/layout-h500dp, e ainda é um caso de uso válido. No entanto, o uso para cálculo de layout sempre foi desencorajado. Se você estiver fazendo isso, pare agora. Substitua o uso de Configuration por algo mais adequado, dependendo do seu caso de uso.
Se você usar para calcular o layout, use um ViewGroup adequado, como
CoordinatorLayout ou ConstraintLayout. Se você usar para determinar a altura
da barra de navegação do sistema, use WindowInsets. Se quiser saber o tamanho atual
da janela do app, use computeCurrentWindowMetrics.
A lista a seguir descreve os campos afetados por essa mudança:
- Os tamanhos
Configuration.screenWidthDpescreenHeightDpnão excluem mais as barras de sistema. Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpé afetado indiretamente por mudanças emscreenWidthDpescreenHeightDp.- O
Configuration.orientationé afetado indiretamente por mudanças noscreenWidthDpe noscreenHeightDpem dispositivos quase quadrados. Display.getSize(Point)é afetado indiretamente pelas mudanças emConfiguration. Esse recurso foi descontinuado a partir do nível 30 da API.- O
Display.getMetrics()já funciona assim desde o nível 33 da API.
O atributo "elegantTextHeight" tem como padrão o valor "true".
Em apps destinados ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API), o atributo
elegantTextHeight TextView
passa a ser true por padrão, substituindo a fonte compacta usada por padrão por alguns
scripts com métricas verticais grandes por uma que é muito mais legível.
A fonte compacta foi introduzida para evitar a quebra de layouts. O Android 13 (nível
33 da API) evita muitas dessas quebras, permitindo que o layout de texto
estique a altura vertical usando o atributo
fallbackLineSpacing.
No Android 15, a fonte compacta ainda permanece no sistema. Assim, o app pode definir
elegantTextHeight como false para ter o mesmo comportamento de antes, mas é
improvável que haja suporte a ele nas próximas versões. Portanto, se o app oferecer suporte aos
seguintes scripts: árabe, lao, birmanês, tâmil, gujarati, canarês, malaiala,
odia, télugo ou tailandês, teste o app definindo elegantTextHeight como true.
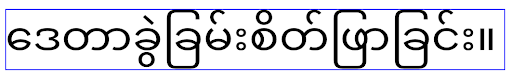
elegantTextHeight comportamento para apps destinados ao Android 14 (nível 34 da API) e versões anteriores.
elegantTextHeight para apps destinados ao Android 15.A largura da TextView muda para formas de letras complexas
在以前的 Android 版本中,某些具有复杂形状的手写字体或语言可能会在上一个或下一个字符的区域绘制字母。在某些情况下,此类字母会在开头或结尾处被剪裁。从 Android 15 开始,TextView 会分配宽度,以便为此类字母绘制足够的空间,并允许应用请求向左额外添加内边距以防止剪裁。
由于此更改会影响 TextView 确定宽度的方式,因此如果应用以 Android 15(API 级别 35)或更高版本为目标平台,TextView 会默认分配更多宽度。您可以通过对 TextView 调用 setUseBoundsForWidth API 来启用或停用此行为。
由于添加左内边距可能会导致现有布局未对齐,因此默认情况下不会添加内边距,即使以 Android 15 或更高版本为目标平台的应用也是如此。不过,您可以通过调用 setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang 添加额外的内边距以防止剪裁。
以下示例展示了这些更改如何改进某些字体和语言的文本布局。

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
Altura da linha padrão sensível à localidade para EditText
Nas versões anteriores do Android, o layout de texto estendia a altura do
texto para atender à altura da linha da fonte que correspondia à localidade atual. Por
exemplo, se o conteúdo estivesse em japonês, a altura da linha da fonte japonesa
seria um pouco maior do que a de uma fonte latina, e a altura do texto
ficaria um pouco maior. No entanto, apesar dessas diferenças nas alturas das linhas, o elemento
EditText foi dimensionado de maneira uniforme, independentemente
da localidade usada, conforme ilustrado na imagem a seguir:

EditText que
podem conter texto em inglês (en), japonês (ja) e birmanês (my). A
altura do EditText é a mesma, mesmo que esses idiomas
tenham alturas de linha diferentes.Para apps direcionados ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API), uma altura mínima de linha agora é
reservada para EditText para corresponder à fonte de referência da localidade especificada, conforme
mostrado na imagem a seguir:

EditText que
podem conter texto em inglês (en), japonês (ja) e birmanês (my). A
altura do EditText agora inclui espaço para acomodar a
altura da linha padrão das fontes desses idiomas.Se necessário, o app pode restaurar o comportamento anterior especificando o atributo
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum
para false e definir métricas verticais mínimas personalizadas usando a
API setMinimumFontMetrics em Kotlin e Java.
Câmera e mídia
O Android 15 faz as seguintes mudanças no comportamento de câmera e mídia para apps direcionados a ele ou a versões mais recentes.
Restrições ao solicitar o foco de áudio
Os apps direcionados ao Android 15 (nível 35 da API) precisam ser o app principal ou executar um
serviço em primeiro plano para solicitar o foco de áudio. Se um app
tentar solicitar o foco quando não atender a um desses requisitos, a
chamada vai retornar AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
Saiba mais sobre o foco de áudio em Gerenciar o foco de áudio.
Atualização das restrições não SDK
O Android 15 inclui listas atualizadas de interfaces não SDK restritas com base na colaboração com desenvolvedores Android e nos testes internos mais recentes. Antes de restringirmos interfaces não SDK, sempre que possível, garantimos que haja alternativas públicas disponíveis.
Caso seu app não seja destinado ao Android 15, é possível que algumas dessas mudanças não afetem você imediatamente. No entanto, embora seja possível que seu app acesse algumas interfaces não SDK dependendo do nível da API de destino do app, o uso de qualquer método ou campo não SDK sempre apresenta um alto risco de corromper o app.
Se você não souber se seu app usa interfaces não SDK, poderá testá-lo para descobrir. Se ele depende de interfaces não SDK, comece a planejar uma migração para alternativas SDK. No entanto, entendemos que alguns apps têm casos de uso válidos para interfaces não SDK. Se você não encontrar uma alternativa para deixar de usar uma interface não SDK em um recurso no seu app, solicite uma nova API pública.
如需详细了解此 Android 版本中的变更,请参阅 Android 15 中有关限制非 SDK 接口的更新。如需全面了解有关非 SDK 接口的详细信息,请参阅对非 SDK 接口的限制。

