يتضمّن الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android تغييرات في السلوك قد تؤثّر في تطبيقك.
تنطبق تغييرات السلوك التالية على جميع التطبيقات عند تشغيلها على الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android،
بغض النظر عن targetSdkVersion. عليك اختبار تطبيقك ثم تعديله حسب الحاجة ليتوافق مع هذه الميزات بشكل صحيح، حيثما ينطبق ذلك.
احرص أيضًا على مراجعة قائمة التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثّر فقط في التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android.
الوظيفة الأساسية
يعدّل نظام التشغيل Android 15 العديد من الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android أو يوسّع نطاقها.
التغييرات على حالة إيقاف الحزمة
The intention of the package FLAG_STOPPED state (which users
can engage in AOSP builds by long-pressing an app icon and selecting "Force
Stop") has always been to keep apps in this state until the user explicitly
removes the app from this state by directly launching the app or indirectly
interacting with the app (through the sharesheet or a widget, selecting the app
as live wallpaper, etc.). In Android 15, we've updated the behavior of the
system to be aligned with this intended behavior. Apps should only be removed
from the stopped state through direct or indirect user action.
To support the intended behavior, in addition to the existing restrictions, the
system also cancels all pending intents when the app enters the
stopped state on a device running Android 15. When the user's actions remove the
app from the stopped state, the ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED
broadcast is delivered to the app providing an opportunity to re-register any
pending intents.
You can call the new
ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped()
method to confirm whether the app was put into the stopped state.
التوافق مع صفحات بحجم 16 كيلوبايت
في السابق، كان نظام التشغيل Android يتيح فقط صفحات الذاكرة بحجم 4 كيلوبايت، ما ساعد في تحسين أداء ذاكرة النظام بما يتناسب مع إجمالي مساحة الذاكرة التي كانت تتوفّر عادةً في أجهزة Android. بدءًا من الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، يتيح مشروع Android مفتوح المصدر (AOSP) استخدام الأجهزة التي تم ضبطها لاستخدام حجم صفحة يبلغ 16 كيلوبايت (أجهزة 16 كيلوبايت). إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم أي مكتبات NDK، سواء بشكل مباشر أو غير مباشر من خلال حزمة تطوير برامج (SDK)، عليك إعادة إنشاء تطبيقك لكي يعمل على هذه الأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات ذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت.
مع استمرار الشركات المصنّعة للأجهزة في تصميم أجهزة تتضمّن كميات أكبر من الذاكرة الفعلية (RAM)، ستستخدم العديد من هذه الأجهزة أحجام صفحات تبلغ 16 كيلوبايت (وأكبر في النهاية) لتحسين أداء الجهاز. تتيح إضافة دعم للأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات بحجم 16 كيلوبايت تشغيل تطبيقك على هذه الأجهزة، كما تساعد تطبيقك في الاستفادة من التحسينات المرتبطة بالأداء. وبدون إعادة تجميع، لن تعمل التطبيقات على الأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات الذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت في إصدارات Android المستقبلية.
لمساعدتك في إضافة إمكانية استخدام تطبيقك، قدّمنا إرشادات حول كيفية التحقّق مما إذا كان تطبيقك سيتأثر، وكيفية إعادة إنشاء تطبيقك (إذا كان ذلك منطبقًا)، وكيفية اختبار تطبيقك في بيئة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت باستخدام المحاكيات (بما في ذلك صور نظام Android 15 لمحاكي Android).
Benefits and performance gains
تستهلك الأجهزة التي تم ضبطها على أحجام صفحات تبلغ 16 كيلوبايت مساحة أكبر قليلاً من الذاكرة في المتوسط، لكنها تُجري أيضًا تحسينات متنوعة في الأداء لكل من النظام والتطبيقات:
- أوقات تشغيل التطبيق أقل عندما يكون النظام تحت ضغط الذاكرة: 3.16% انخفاضًا في المتوسط، مع تحسينات أكثر أهمية (تصل إلى %30) لبعض التطبيقات التي اختبرناها
- انخفاض في استهلاك الطاقة أثناء تشغيل التطبيق: انخفاض بنسبة% 4.56 في المتوسّط
- تشغيل أسرع للكاميرا: عمليات تشغيل أسرع بنسبة 4.48% في المتوسط، وعمليات تشغيل على البارد أسرع بنسبة 6.60% في المتوسط
- مدة تشغيل النظام المحسَّنة: تحسّنت بنسبة %8 (950 ملي ثانية تقريبًا) في المتوسّط
تستند هذه التحسينات إلى اختبارنا الأوّلي، ومن المرجّح أن تختلف النتائج على الأجهزة الفعلية. وسنقدّم تحليلاً إضافيًا للفوائد المحتملة للتطبيقات أثناء مواصلة الاختبار.
Check if your app is impacted
إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم أي رموز برمجية أصلية، عليك إعادة إنشاء تطبيقك ليتوافق مع الأجهزة التي تستخدم صفحات ذاكرة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت. إذا لم تكن متأكدًا مما إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم رمزًا برمجيًا أصليًا، يمكنك استخدام "أداة تحليل حِزم APK" لتحديد ما إذا كان هناك أي رمز برمجي أصلي، ثم التحقّق من توافق أقسام ELF مع أي مكتبات مشتركة تجدها. يوفّر "استوديو Android" أيضًا ميزات تساعدك في رصد مشاكل المحاذاة تلقائيًا.
إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم فقط الرموز البرمجية المكتوبة بلغة البرمجة Java أو Kotlin، بما في ذلك جميع المكتبات أو حِزم تطوير البرامج (SDK)، يكون تطبيقك متوافقًا مع الأجهزة التي تبلغ سعتها 16 كيلوبايت. ومع ذلك، ننصحك باختبار تطبيقك في بيئة بحجم 16 كيلوبايت للتأكّد من عدم حدوث أي تراجع غير متوقّع في سلوك التطبيق.
التغييرات المطلوبة لكي تتوافق بعض التطبيقات مع المساحة الخاصّة
Private space is a new feature in Android 15 that lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. Because apps in the private space have restricted visibility, some types of apps need to take additional steps to be able to see and interact with apps in a user's private space.
All apps
Because apps in the private space are kept in a separate user profile, similar to work profiles, apps shouldn't assume that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile. If your app has logic related to work profile apps that make this assumption, you'll need to adjust this logic.
Medical apps
When a user locks the private space, all apps in the private space are stopped, and those apps can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications. This behavior might critically impact the use and function of medical apps installed in the private space.
The private space setup experience warns users that the private space is not suitable for apps that need to perform critical foreground or background activities, such as showing notifications from medical apps. However, apps can't determine whether or not they're being used in the private space, so they can't show a warning to the user for this case.
For these reasons, if you develop a medical app, review how this feature might impact your app and take appropriate actions—such as informing your users not to install your app in the private space—to avoid disrupting critical app capabilities.
Launcher apps
If you develop a launcher app, you must do the following before apps in the private space will be visible:
- Your app must be assigned as the default launcher app for the device—that
is, possessing the
ROLE_HOMErole. - Your app must declare the
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESnormal permission in your app's manifest file.
Launcher apps that declare the ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES permission must handle
the following private space use cases:
- Your app must have a separate launcher container for apps installed in the
private space. Use the
getLauncherUserInfo()method to determine which type of user profile is being handled. - The user must be able to hide and show the private space container.
- The user must be able to lock and unlock the private space container. Use
the
requestQuietModeEnabled()method to lock (by passingtrue) or unlock (by passingfalse) the private space. While locked, no apps in the private space container should be visible or discoverable through mechanisms such as search. Your app should register a receiver for the
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEandACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEbroadcasts and update the UI in your app when the locked or unlocked state of the private space container changes. Both of these broadcasts includeEXTRA_USER, which your app can use to refer to the private profile user.You can also use the
isQuietModeEnabled()method to check whether the private space profile is locked or not.
App store apps
The private space includes an "Install Apps" button that launches an implicit
intent to install apps into the user's private space. In order for your app to
receive this implicit intent, declare an <intent-filter>
in your app's manifest file with a <category> of
CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
تمت إزالة خط رموز الإيموجي المستند إلى PNG
The legacy, PNG-based emoji font file (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) has been
removed, leaving just the vector-based file. Beginning with Android 13 (API
level 33), the emoji font file used by the system emoji renderer changed from a
PNG-based file to a vector based file. The system retained
the legacy font file in Android 13 and 14 for compatibility reasons, so that
apps with their own font renderers could continue to use the legacy font file
until they were able to upgrade.
To check if your app is affected, search your app's code for references to the
NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf file.
You can choose to adapt your app in a number of ways:
- Use platform APIs for text rendering. You can render text to a bitmap-backed
Canvasand use that to get a raw image if necessary. - Add COLRv1 font support to your app. The FreeType open source library supports COLRv1 in version 2.13.0 and higher.
- As a last resort, you can bundle the legacy emoji font file
(
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) into your APK, although in that case your app will be missing the latest emoji updates. For more information, see the Noto Emoji GitHub project page.
زيادة الحد الأدنى لإصدار حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) المستهدَف من 23 إلى 24
Android 15 builds on the
the changes that were made in Android 14 and extends this
security further. In Android 15, apps with a
targetSdkVersion lower than 24 can't be installed.
Requiring apps to meet modern API levels helps to ensure better security and
privacy.
Malware often targets lower API levels in order to bypass security and privacy
protections that have been introduced in higher Android versions. For example,
some malware apps use a targetSdkVersion of 22 to avoid being subjected to the
runtime permission model introduced in 2015 by Android 6.0 Marshmallow (API
level 23). This Android 15 change makes it harder for malware to avoid security
and privacy improvements. Attempting to install an app targeting a lower API
level results in an installation failure, with a message like the following one
appearing in Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
On devices upgrading to Android 15, any apps with a targetSdkVersion lower
than 24 remain installed.
If you need to test an app targeting an older API level, use the following ADB command:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
الأمان والخصوصية
Android 15 引入了强大的措施来防范动态密码 (OTP) 欺诈并保护用户的敏感内容,重点是增强通知监听器服务和屏幕共享保护措施。主要增强功能包括从可供不可信应用访问的通知中隐去 OTP、在屏幕共享期间隐藏通知,以及在发布 OTP 时保护应用 activity。这些变更旨在保护用户的敏感内容,使其免受未经授权的操作者的侵害。
开发者需要注意以下事项,以确保其应用与 Android 15 中的变更兼容:
动态密码隐去
Android 会阻止实现 NotificationListenerService 的不受信任应用读取已检测到 OTP 的通知中的未隐去的内容。配套设备管理器关联等受信任应用不受这些限制。
屏幕共享保护
- 在屏幕共享会话期间,系统会隐藏通知内容,以保护用户的隐私。如果应用实现了
setPublicVersion(),Android 会显示通知的公开版本,该版本在不安全情境中用作替换通知。否则,系统会隐去通知内容,不提供任何其他背景信息。 - 系统会向远程观看者隐藏密码输入等敏感内容,以防止泄露用户的敏感信息。
- 如果在屏幕共享期间检测到动态密码,系统会隐藏在该时间段内发布通知的应用的活动。应用内容在启动时会向远程查看器隐藏。
- 除了 Android 自动识别敏感字段之外,开发者还可以使用
setContentSensitivity手动将应用的部分标记为敏感,在屏幕共享期间,这些敏感字段会对远程观看者隐藏。 - 开发者可以选择切换开发者选项下的停用屏幕共享防护选项,以便出于演示或测试目的豁免屏幕共享防护。默认的系统屏幕录制工具不受这些更改的影响,因为录制内容会保留在设备上。
الكاميرا والوسائط
يُجري نظام التشغيل Android 15 التغييرات التالية على سلوك الكاميرا والوسائط في جميع التطبيقات.
يؤدي تشغيل الصوت مباشرةً أو إيقافه إلى إبطال المقاطع الصوتية التي تم فتحها سابقًا مباشرةً أو إيقافها عند بلوغ حدود الموارد
Before Android 15, if an app requested direct or offload audio playback while
another app was playing audio and the resource limits were reached, the app
would fail to open a new AudioTrack.
Beginning with Android 15, when an app requests direct or offload
playback and the resource
limits are reached, the system invalidates any currently open
AudioTrack objects which prevent fulfilling the new track request.
(Direct and offload audio tracks are typically opened for playback of compressed audio formats. Common use-cases for playing direct audio include streaming encoded audio over HDMI to a TV. Offload tracks are typically used to play compressed audio on a mobile device with hardware DSP acceleration.)
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يتضمّن Android 15 بعض التغييرات التي تهدف إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر اتساقًا وسهولة.
تفعيل الصور المتحركة لإيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية للتطبيقات التي وافقت على استخدامها
Beginning in Android 15, the developer option for predictive back animations has been removed. System animations such as back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity now appear for apps that have opted in to the predictive back gesture either entirely or at an activity level. If your app is affected, take the following actions:
- Ensure that your app has been properly migrated to use the predictive back gesture.
- Ensure that your fragment transitions work with predictive back navigation.
- Migrate away from animation and framework transitions and use animator and androidx transitions instead.
- Migrate away from back stacks that
FragmentManagerdoesn't know about. Use back stacks managed byFragmentManageror by the Navigation component instead.
إيقاف التطبيقات المصغّرة عند إيقاف المستخدم تطبيقًا بالقوة
If a user force-stops an app on a device running Android 15, the system temporarily disables all the app's widgets. The widgets are grayed out, and the user cannot interact with them. This is because beginning with Android 15, the system cancels all an app's pending intents when the app is force-stopped.
The system re-enables those widgets the next time the user launches the app.
For more information, see Changes to package stopped state.
تنبّه شريحة شريط حالة عرض الوسائط المستخدمين إلى مشاركة الشاشة وإرسال المحتوى وتسجيله
تؤدي إساءة استخدام ميزة "إلقاء الشاشة" إلى تعريض بيانات المستخدمين الخاصة، مثل معلوماتهم المالية، لأنّ المستخدمين لا يدركون أنّه تتم مشاركة شاشة أجهزتهم.
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تعمل على الأجهزة التي تعمل بنظام التشغيل Android 15 QPR1 أو إصدار أحدث، يتم عرض شريحة ملف شخصي كبيرة ومميّزة في شريط الحالة لتنبيه المستخدمين بأي عملية بث شاشة جارية. يمكن للمستخدمين النقر على الشريحة لإيقاف مشاركة الشاشة أو بثها أو تسجيلها. ويتوقف أيضًا عرض الشاشة تلقائيًا عند قفل شاشة الجهاز.
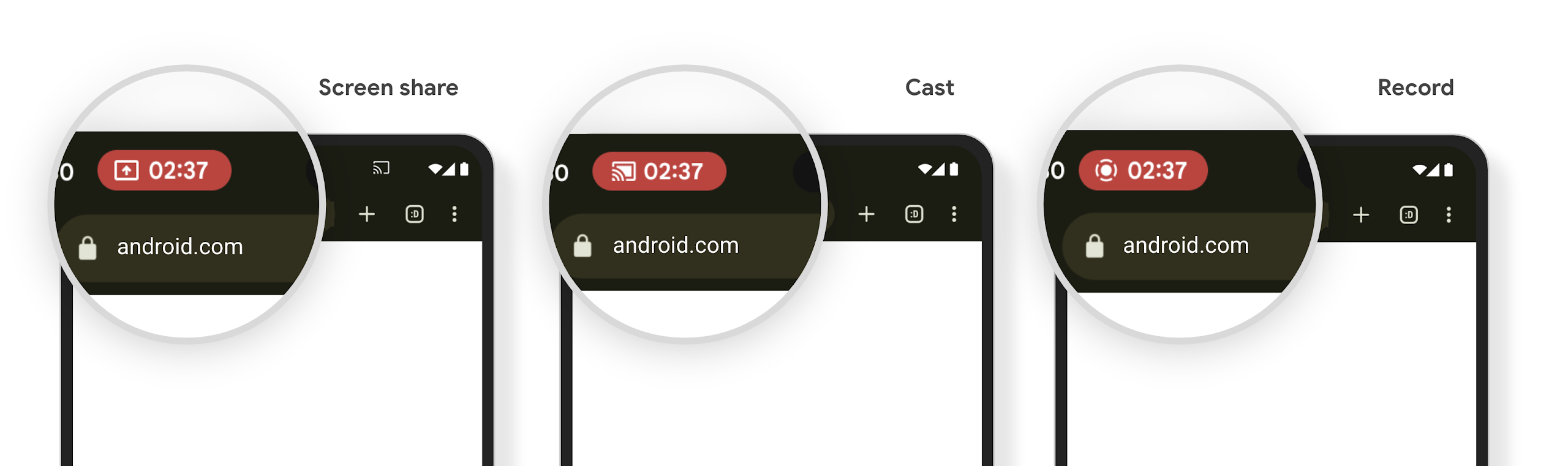
التحقّق مما إذا كان تطبيقك قد تأثّر
يتضمّن تطبيقك تلقائيًا شريحة شريط الحالة ويوقف تلقائيًا إرسال الشاشة عند تفعيل شاشة القفل.
للاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات عن كيفية اختبار تطبيقك لاستخدامات هذه الحالات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على شريحة "شريط الحالة" والإيقاف التلقائي.
قيود الوصول إلى الشبكة في الخلفية
在 Android 15 中,如果应用在有效的进程生命周期之外启动网络请求,则会收到异常。通常是 UnknownHostException 或其他与套接字相关的 IOException。在有效生命周期之外发生的网络请求通常是因为应用在不再活跃后,不知不觉地继续发出网络请求。
为缓解此异常,请使用生命周期感知型组件,确保您的网络请求具有生命周期感知功能,并在离开有效的进程生命周期时取消。如果您非常重视即使用户离开应用也要发出网络请求,请考虑使用 WorkManager 调度网络请求,或使用前台服务继续执行对用户可见的任务。
الميزات التي سيتم إيقافها نهائيًا
مع كل إصدار، قد تصبح واجهات برمجة تطبيقات معيّنة في Android قديمة أو تحتاج إلى إعادة تصميم لتوفير تجربة أفضل للمطوّرين أو إتاحة إمكانات جديدة على النظام الأساسي. في هذه الحالات، نوقف نهائيًا واجهات برمجة التطبيقات القديمة ونوجّه المطوّرين إلى استخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات بديلة.
يعني الإيقاف النهائي أنّنا أوقفنا الدعم الرسمي لواجهات برمجة التطبيقات، ولكن ستظل متاحة للمطوّرين. لمزيد من المعلومات حول عمليات الإيقاف النهائي المهمة في هذا الإصدار من Android، يمكنك الاطّلاع على صفحة عمليات الإيقاف النهائي.

