הרכיב Dialog מציג הודעות קופצות או מבקש קלט מהמשתמש בשכבה מעל תוכן האפליקציה הראשי. הוא יוצר חוויית ממשק משתמש מפריעה כדי למשוך את תשומת הלב של המשתמש.
תרחישים לדוגמה לשימוש בתיבת דו-שיח:
- אישור הפעולה של המשתמש, למשל כשמוחקים קובץ.
- בקשה לקלט של משתמש, למשל באפליקציה של רשימת משימות.
- הצגת רשימה של אפשרויות לבחירת המשתמש, כמו בחירת מדינה בהגדרת פרופיל.
בנושא הזה מפורטות ההטמעות הבאות:
תאימות גרסאות
כדי להטמיע את הקוד הזה, צריך להגדיר את minSDK של הפרויקט לרמת API 21 ואילך.
יחסי תלות
יצירת תיבת דו-שיח של התראה
הרכיב הניתן לקיבוץ AlertDialog מספק ממשק API נוח ליצירת תיבת דו-שיח בסגנון Material Design. בדוגמה הבאה מוטמעים שני לחצנים בתיבת דו-שיח של התראה, אחד לסגירת תיבת הדו-שיח והשני לאישור הבקשה:
ההטמעה הזו מתייחסת לרכיב קומפוזיציה הורה שמעביר ארגומנטים לרכיב הקומפוזיציה הצאצא באופן הבא:
תוצאות
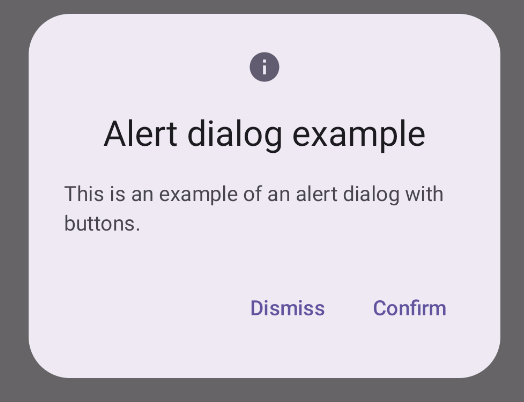
נקודות עיקריות
ל-AlertDialog יש פרמטרים ספציפיים לטיפול ברכיבים מסוימים של תיבת הדו-שיח. בין היתר:
title: הטקסט שמופיע בחלק העליון של תיבת הדו-שיח.text: הטקסט שמופיע במרכז תיבת הדו-שיח.icon: הגרפיקה שמופיעה בחלק העליון של תיבת הדו-שיח.onDismissRequest: הפונקציה שנקראת כשהמשתמש סוגר את תיבת הדו-שיח, למשל על ידי הקשה מחוץ אליה.dismissButton: רכיב מורכב שמשמש כלחצן הסגירה.confirmButton: רכיב מורכב שמשמש כלחצן אישור.כשהמשתמש לוחץ על אחד מהלחצנים, תיבת הדו-שיח נסגרת. כשהמשתמש לוחץ על 'אישור', מתבצעת קריאה לפונקציה שמטפלת גם באישור. בדוגמה הזו, הפונקציות האלה הן
onDismissRequest()ו-onConfirmRequest().במקרים שבהם תיבת הדו-שיח דורשת קבוצה מורכבת יותר של לחצנים, מומלץ להשתמש ב-
Dialogהניתן ליצירה ולהוסיף לו תוכן באופן חופשי יותר.
יצירת תיבת דו-שיח
Dialog הוא רכיב מורכב בסיסי שלא מספק עיצוב או משבצות מוגדרות מראש לתוכן. זהו מאגר פשוט שצריך לאכלס אותו במאגר כמו Card. ריכזנו כאן כמה מהפרמטרים העיקריים של תיבת דו-שיח:
onDismissRequest: פונקציית הלוגריתם הרגולרי (lambda) שנקראת כשהמשתמש סוגר את תיבת הדו-שיח.properties: מופע שלDialogPropertiesשמספק היקף נוסף של התאמה אישית.
יצירת תיבת דו-שיח בסיסית
הדוגמה הבאה היא הטמעה בסיסית של ה-composable Dialog. שימו לב שהוא משתמש ב-Card בתור הקונטיינר המשני. בלי Card, הרכיב Text יופיע לבד מעל לתוכן הראשי של האפליקציה.
התוצאה
חשוב לזכור שכשהתיבה נפתחת, תוכן האפליקציה הראשי שמתחתיה מופיע כהה ואפור:

יצירת תיבת דו-שיח מתקדמת
בהמשך מופיעה הטמעה מתקדמת יותר של ה-composable Dialog. במקרה הזה, הרכיב מטמיע באופן ידני ממשק דומה לדוגמה AlertDialog שלמעלה.
התוצאה
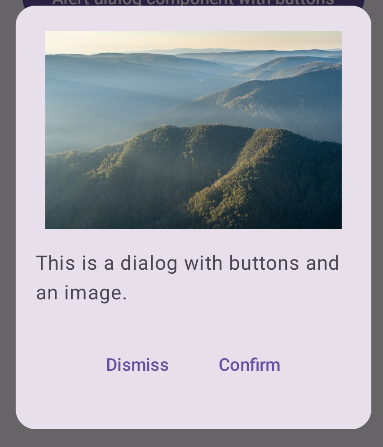
אוספים שמכילים את המדריך הזה
המדריך הזה הוא חלק מהאוספים הבאים של מדריכים מהירים, שמכסים יעדים רחבים יותר לפיתוח Android:
הטקסט שיוצג

בקשה להזנת משתמש




