במכשירים עם Android מגרסה 8.0 (API ברמה 26) ומעלה, ההתאמה של מכשיר משני מבצעת סריקת Bluetooth או Wi-Fi של מכשירים בקרבת מקום בשם האפליקציה שלכם, בלי לדרוש את ההרשאה ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. כך אפשר למקסם את ההגנה על פרטיות המשתמשים. משתמשים בשיטה הזו כדי לבצע את ההגדרה הראשונית של המכשיר הנלווה, כמו שעון חכם עם תמיכה ב-BLE. בנוסף, כדי לבצע שיוך של מכשיר משלים, צריך להפעיל את שירותי המיקום.
התאמה של מכשיר משני לא יוצרת חיבורים בעצמה ולא מאפשרת סריקה רציפה. אפליקציות יכולות להשתמש בממשקי API של קישוריות Bluetooth או Wi-Fi כדי ליצור חיבורים.
אחרי שהמכשיר יותאם, הוא יוכל להשתמש בהרשאות REQUEST_COMPANION_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND ו-REQUEST_COMPANION_USE_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND כדי להפעיל את האפליקציה ברקע. אפליקציות יכולות גם להשתמש בהרשאה
REQUEST_COMPANION_START_FOREGROUND_SERVICES_FROM_BACKGROUND
כדי להפעיל שירות שפועל בחזית מהרקע.
משתמש יכול לבחור מכשיר מרשימה ולהעניק לאפליקציה הרשאות גישה למכשיר. ההרשאות האלה מבוטלות אם מסירים את האפליקציה או מתקשרים אל disassociate().
האחריות לביטול השיוכים של האפליקציה הנלווית מוטלת עליה, אם המשתמש לא צריך אותם יותר, למשל כשהוא יוצא מהחשבון או מסיר מכשירים מקושרים.
הטמעה של התאמת מכשיר נלווה
בקטע הזה מוסבר איך להשתמש ב-CompanionDeviceManager כדי להתאים את האפליקציה למכשירים נלווים באמצעות Bluetooth, BLE ו-Wi-Fi.
ציון מכשירים נלווים
בדוגמת הקוד הבאה אפשר לראות איך מוסיפים את הדגל <uses-feature> לקובץ מניפסט. ההגדרה הזו אומרת למערכת שהאפליקציה שלכם מתכוונת להגדיר מכשירים נלווים.
<uses-feature android:name="android.software.companion_device_setup"/>
רשימת מכשירים לפי DeviceFilter
אפשר להציג את כל המכשירים הנלווים שנמצאים בטווח ומתאימים לDeviceFilter שסיפקתם (כמו שמוצג באיור 1). אם רוצים להגביל את הסריקה למכשיר אחד בלבד, אפשר setSingleDevice() ל-true (כמו שמוצג באיור 2).
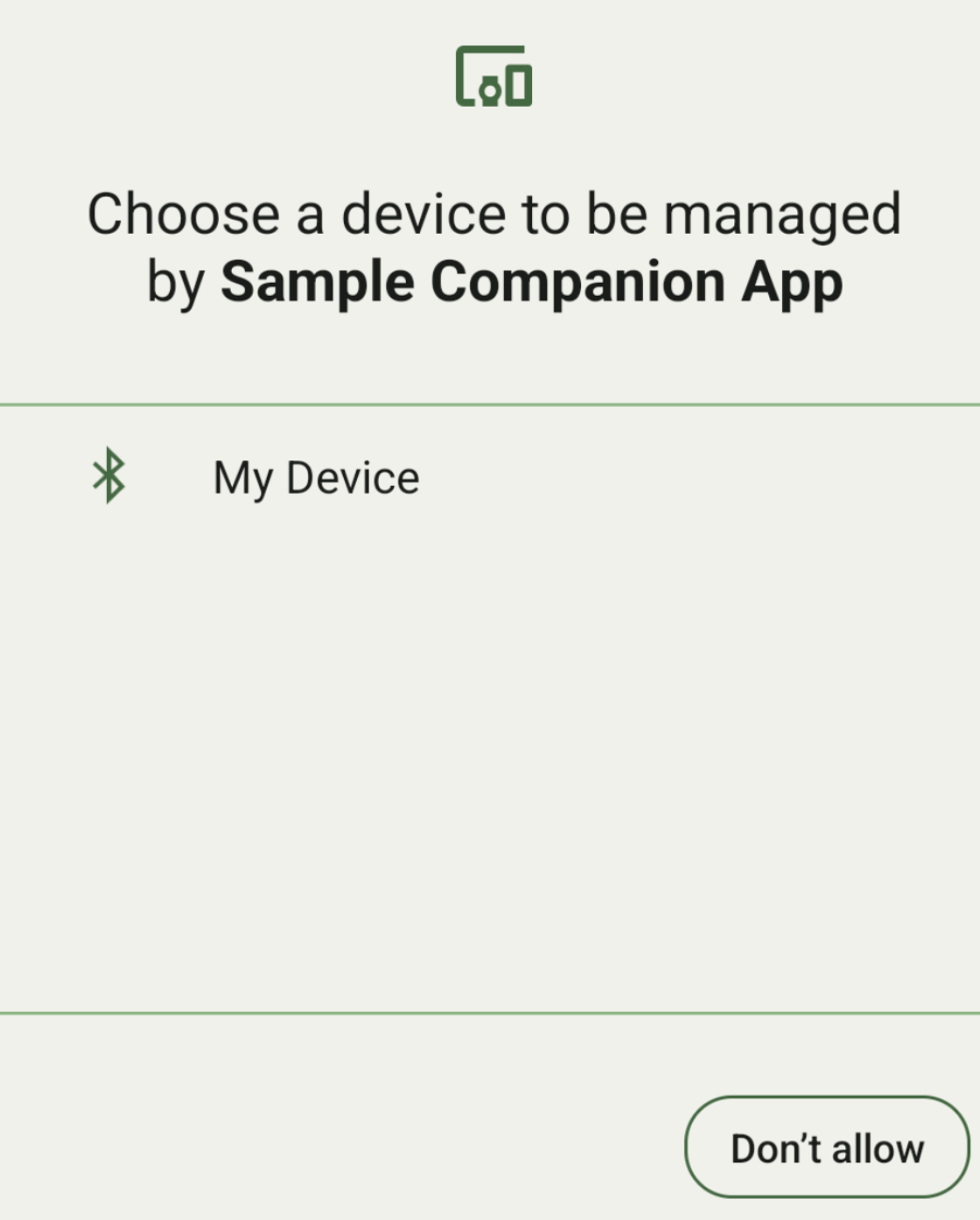
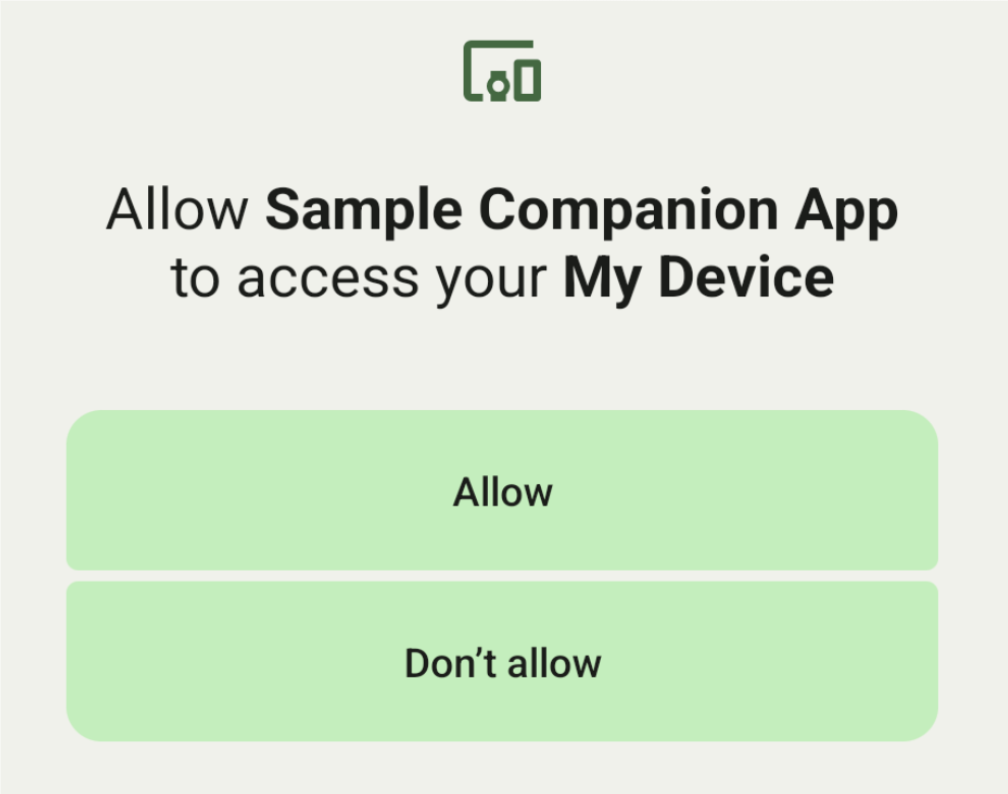
אלה תתי-המחלקות של DeviceFilter שאפשר לציין ב-AssociationRequest:
לכל שלוש המחלקות המשניות יש builders שמייעלים את הגדרת המסננים.
בדוגמה הבאה, מכשיר סורק מכשיר Bluetooth עם BluetoothDeviceFilter.
Kotlin
val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build()
Java
BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() // Match only Bluetooth devices whose name matches the pattern. .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) // Match only Bluetooth devices whose service UUID matches this pattern. .addServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build();
מגדירים DeviceFilter לAssociationRequest כדי ש-CompanionDeviceManager יוכל לקבוע איזה סוג מכשירים לחפש.
Kotlin
val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build()
Java
AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() // Find only devices that match this request filter. .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) // Stop scanning as soon as one device matching the filter is found. .setSingleDevice(true) .build();
אחרי שהאפליקציה מאתחלת AssociationRequest, מריצים את הפונקציה associate() ב-CompanionDeviceManager. הפונקציה associate() מקבלת AssociationRequest וCallback.
הפונקציה Callback מחזירה IntentSender ב-onAssociationPending כשהפונקציה CompanionDeviceManager מאתרת מכשיר והוא מוכן להצגת תיבת דו-שיח לבקשת הסכמה מהמשתמש.
אחרי שהמשתמש מאשר את המכשיר, מחזירים את AssociationInfo של המכשיר ב-onAssociationCreated.
אם האפליקציה לא מוצאת מכשירים, הקריאה החוזרת מחזירה את הערך onFailure עם הודעת שגיאה.
במכשירים שמותקנת בהם גרסת Android 13 (API ברמה 33) ומעלה:
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // An association is created. } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } })
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // An association is created. } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // To handle the failure. });
במכשירים שמותקנת בהם גרסת Android 12L (API ברמה 32) או גרסה קודמת (הוצאה משימוש):
Kotlin
val deviceManager = requireContext().getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // To handle the failure. } }, null)
Java
CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE); deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // To handle the failure. } }, null);
התוצאה של בחירת המשתמש נשלחת בחזרה אל הפעילות שלכם בקטע onActivityResult(). אחרי זה תוכלו לגשת למכשיר שנבחר.
כשמשתמש בוחר מכשיר Bluetooth, צפוי BluetoothDevice.
כשמשתמש בוחר מכשיר Bluetooth LE, צפוי android.bluetooth.le.ScanResult.
כשמשתמש בוחר מכשיר Wi-Fi, צפוי android.net.wifi.ScanResult.
Kotlin
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } }
Java
@Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // Continue to interact with the paired device. } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } }
דוגמה מלאה:
במכשירים שמותקנת בהם גרסת Android 13 (API ברמה 33) ומעלה:
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } val mBluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter by lazy { val java = BluetoothManager::class.java getSystemService(java)!!.adapter } val executor: Executor = Executor { it.run() } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, executor, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user // can select the device they want to pair with. override fun onAssociationPending(intentSender: IntentSender) { intentSender?.let { startIntentSenderForResult(it, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } } override fun onAssociationCreated(associationInfo: AssociationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. var associationId: int = associationInfo.id var macAddress: MacAddress = associationInfo.deviceMacAddress } override fun onFailure(errorMessage: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } ) override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; Executor executor = new Executor() { @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { runnable.run(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // do not include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { executor, // Called when a device is found. Launch the IntentSender so the user can // select the device they want to pair with. @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult( chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0 ); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { Log.e("MainActivity", "Failed to send intent"); } } @Override public void onAssociationCreated(AssociationInfo associationInfo) { // AssociationInfo object is created and get association id and the // macAddress. int associationId = associationInfo.getId(); MacAddress macAddress = associationInfo.getDeviceMacAddress(); } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence errorMessage) { // Handle the failure. }); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (resultCode != Activity.RESULT_OK) { return; } if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
במכשירים שמותקנת בהם גרסת Android 12L (API ברמה 32) או גרסה קודמת (הוצאה משימוש):
Kotlin
private const val SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0 class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private val deviceManager: CompanionDeviceManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE) as CompanionDeviceManager } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // To skip filters based on names and supported feature flags (UUIDs), // omit calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid() // respectively, as shown in the following Bluetooth example. val deviceFilter: BluetoothDeviceFilter = BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid(ParcelUuid(UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null) .build() // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of them appears. val pairingRequest: AssociationRequest = AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build() // When the app tries to pair with a Bluetooth device, show the // corresponding dialog box to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, object : CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { override fun onDeviceFound(chooserLauncher: IntentSender) { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0) } override fun onFailure(error: CharSequence?) { // Handle the failure. } }, null) } override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) { when (requestCode) { SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE -> when(resultCode) { Activity.RESULT_OK -> { // The user chose to pair the app with a Bluetooth device. val deviceToPair: BluetoothDevice? = data?.getParcelableExtra(CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE) deviceToPair?.let { device -> device.createBond() // Maintain continuous interaction with a paired device. } } } else -> super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data) } } }
Java
class MainActivityJava extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE = 0; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CompanionDeviceManager deviceManager = (CompanionDeviceManager) getSystemService( Context.COMPANION_DEVICE_SERVICE ); // To skip filtering based on name and supported feature flags, // don't include calls to setNamePattern() and addServiceUuid(), // respectively. This example uses Bluetooth. BluetoothDeviceFilter deviceFilter = new BluetoothDeviceFilter.Builder() .setNamePattern(Pattern.compile("My device")) .addServiceUuid( new ParcelUuid(new UUID(0x123abcL, -1L)), null ) .build(); // The argument provided in setSingleDevice() determines whether a single // device name or a list of device names is presented to the user as // pairing options. AssociationRequest pairingRequest = new AssociationRequest.Builder() .addDeviceFilter(deviceFilter) .setSingleDevice(true) .build(); // When the app tries to pair with the Bluetooth device, show the // appropriate pairing request dialog to the user. deviceManager.associate(pairingRequest, new CompanionDeviceManager.Callback() { @Override public void onDeviceFound(IntentSender chooserLauncher) { try { startIntentSenderForResult(chooserLauncher, SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE, null, 0, 0, 0); } catch (IntentSender.SendIntentException e) { // failed to send the intent } } @Override public void onFailure(CharSequence error) { // handle failure to find the companion device } }, null); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) { if (requestCode == SELECT_DEVICE_REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK && data != null) { BluetoothDevice deviceToPair = data.getParcelableExtra( CompanionDeviceManager.EXTRA_DEVICE ); if (deviceToPair != null) { deviceToPair.createBond(); // ... Continue interacting with the paired device. } } } else { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); } } }
פרופילים של מכשירים נלווים
ב-Android 12 (API ברמה 31) ומעלה, אפליקציות נלוות שמנהלות מכשירים כמו שעונים יכולות להשתמש בפרופילים של מכשירים נלווים כדי לייעל את תהליך ההגדרה על ידי מתן ההרשאות הנדרשות בזמן ההתאמה. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא פרופילים של מכשירים משלימים.
האפליקציות הנלוות לא יעברו למצב שינה
החל מ-Android 16 (רמת API 36),
המאפיינים CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence(String) ו-CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceAppeared() הוצאו משימוש.
מומלץ להשתמש ב-
CompanionDeviceManager.startObservingDevicePresence (ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)כדי לנהל באופן אוטומטי את הקישור שלCompanionDeviceServiceשהטמעתם.- מצב הקישור של
CompanionDeviceServiceמנוהל אוטומטית בהתאם לסטטוס הנוכחות של המכשיר הנלווה המשויך:- השירות מאוגד כשהמכשיר הנלווה נמצא בטווח BLE או מחובר באמצעות Bluetooth.
- השירות מפסיק להיות קשור כשהמכשיר הנלווה יוצא מטווח ה-BLE או כשחיבור ה-Bluetooth שלו מסתיים.
- מצב הקישור של
האפליקציה תקבל התקשרות חזרה על סמך מגוון של
DevicePresenceEvent.פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר
CompanionDeviceService.onDeviceEvent().
