Android 14 มีฟีเจอร์และ API ที่ยอดเยี่ยมสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ความช่วยเหลือต่อไปนี้จะช่วย ให้คุณทราบเกี่ยวกับฟีเจอร์สำหรับแอปและเริ่มต้นใช้งาน API ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ดูรายการ API ที่เพิ่ม แก้ไข และนำออกโดยละเอียดได้ในรายงานความแตกต่างของ API ดูรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับ API ที่เพิ่มได้ที่เอกสารอ้างอิง Android API สำหรับ Android 14 ให้มองหา API ที่เพิ่มใน API ระดับ 34 หากต้องการดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับส่วนที่การเปลี่ยนแปลงของแพลตฟอร์มอาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ โปรดดูการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของ Android 14 สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 14 และสำหรับแอปทั้งหมด
การทำให้เป็นสากล
ค่ากำหนดภาษาที่ใช้ในแอป
Android 14 扩展了 Android 13(API 级别 33)中引入的按应用设定语言功能,并包含以下额外功能:
自动生成应用的
localeConfig:从 Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 和 AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 开始,您可以将应用配置为自动支持各应用语言偏好设定。Android Gradle 插件会根据您的项目资源生成LocaleConfig文件,并在最终清单文件中添加对该文件的引用,这样您就不再需要手动创建或更新该文件。AGP 使用应用模块的res文件夹中的资源以及任何库模块依赖项来确定要在LocaleConfig文件中添加的语言区域。动态更新应用的
localeConfig:使用LocaleManager方法中的setOverrideLocaleConfig()和getOverrideLocaleConfig()可以在设备的系统设置中动态更新应用的受支持语言列表。有了这种灵活性,您可以按区域自定义支持的语言列表、运行 A/B 实验,或者如果您的应用通过服务器端推送进行本地化,则可以提供更新后的语言区域列表。输入法 (IME) 的应用语言可见性:IME 可以利用
getApplicationLocales()方法查看当前应用的语言,并将 IME 语言与该语言进行匹配。
Grammatical Inflection API
有 30 亿人在使用区分性别的语言,此类语言的语法类别(例如名词、动词、形容词和介词)会根据您交谈所涉及的人或物的性别而变化。传统上,许多区分性别的语言使用阳性语法性别作为默认或通用性别。
以错误的语法性别来称呼用户,例如以阳性语法性别来称呼女性,可能会对她们的表现和态度产生负面影响。相比之下,界面语言如果能正确反映用户的语法性别,就可以提高用户互动度,并提供更个性化、更自然的用户体验。
为帮助您针对区分性别的语言构建以用户为中心的界面,Android 14 引入了 Grammatical Inflection API,让您无需重构应用便能添加对语法性别的支持。
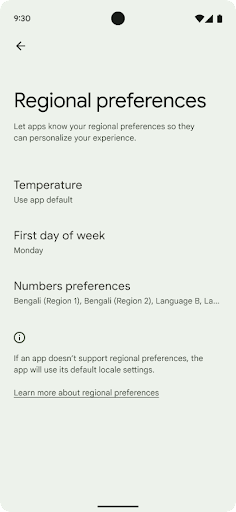
ค่ากำหนดตามพื้นที่
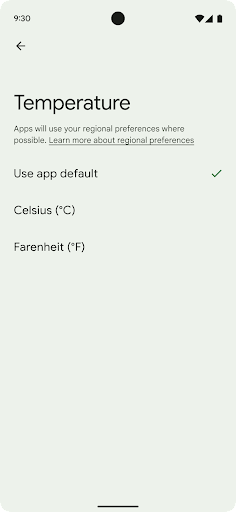
用户可通过地区偏好设置对温度单位、一周的第一天和编号系统进行个性化设置。居住在美国的欧洲用户可能更希望使用摄氏度,而不是华氏度,并且希望应用将星期一视为一周的开始,而不是像美国那样默认从星期日开始。
新 Android 设置菜单包含这些偏好设置,使用户能够在一个位置集中发现这些应用更改偏好设置。这些偏好设置在备份和恢复设备后也会保持不变。多个 API 和 intent(例如 getTemperatureUnit 和 getFirstDayOfWeek)会为您的应用授予读取权限来访问用户偏好设置,因此您的应用可以调整其显示信息的方式。您还可以在 ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED 上注册 BroadcastReceiver,以便在地区偏好设置发生更改时处理语言区域配置更改。
如需找到这些设置,请打开“设置”应用,然后依次前往系统 > 语言和输入法 > 地区偏好设置。
การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ
การปรับขนาดแบบอักษรที่ไม่ใช่แบบเชิงเส้นเป็น 200%
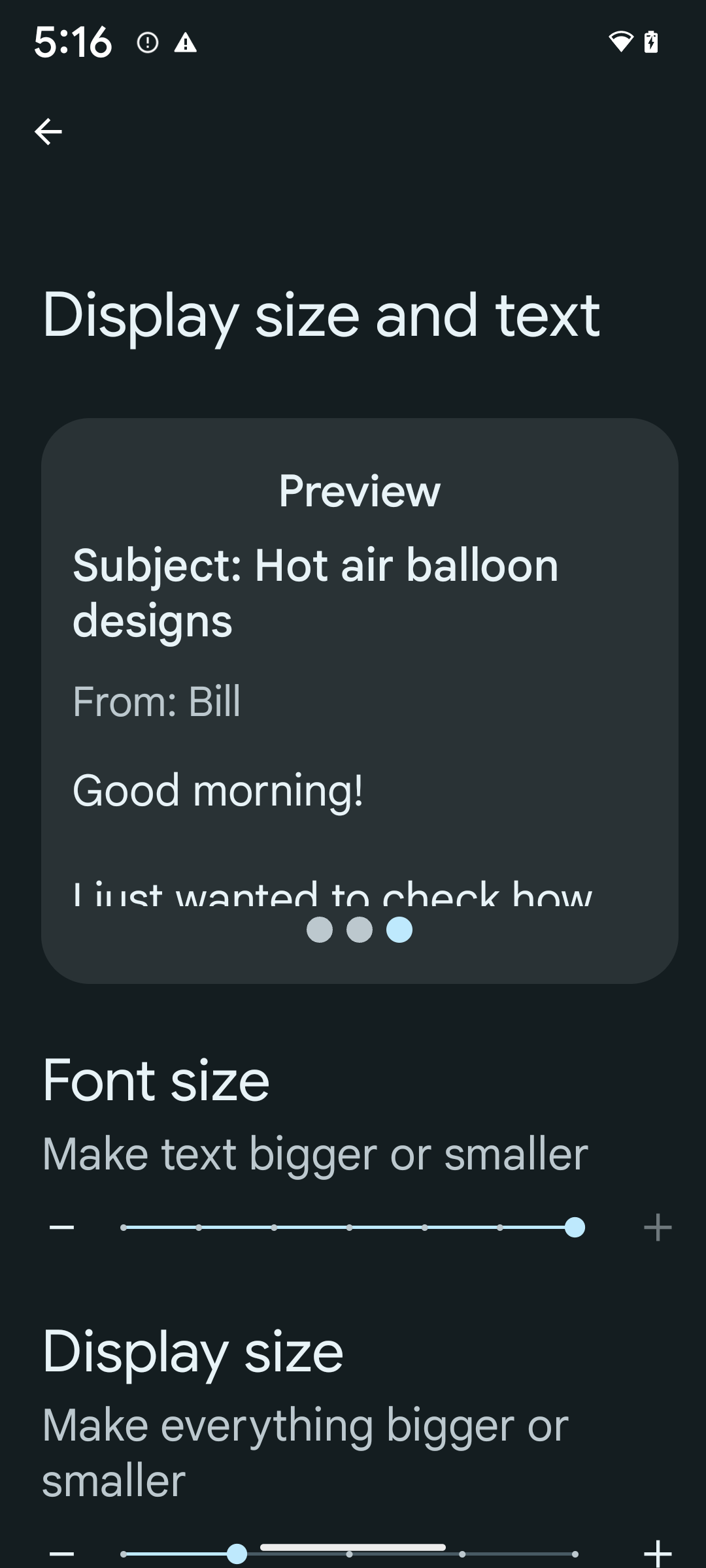
从 Android 14 开始,系统支持字体放大高达 200%,为弱视用户提供了符合网络内容无障碍指南 (WCAG) 的其他无障碍功能选项。
为防止屏幕上的大文本元素放大放大, 应用非线性缩放曲线。这种放大策略意味着大号文本的放大比例不会与较小的文本相同。非线性字体放大有助于保持不同大小元素之间的比例层次结构,同时缓解高级别线性文本放大存在的问题(例如文本被截断或文本因非常大的显示大小而难以阅读)。
使用非线性字体放大测试应用
如果您已使用放大像素 (sp) 单位来定义文字大小,那么这些 其他选项和扩缩方面的改进会自动应用到 。不过,您仍应使用 启用字体大小 (200%),以确保应用采用 且可以适应较大字号,并且不会影响易用性。
要启用 200% 字号,请按以下步骤操作:
- 打开“设置”应用,然后依次前往无障碍 > 显示大小和文字。
- 在字号选项中,点按加号 (+) 图标,直到启用最大字号设置,如本部分随附的图片所示。
针对文本大小使用放大像素 (sp) 单位
请务必始终以 sp 为单位指定文字大小。当应用使用 sp 单位时,Android 可以应用用户的首选文本大小,并相应地进行缩放。
请勿为内边距使用 sp 单位,也不要假定内边距来定义视图高度:使用非线性字体放大 sp 尺寸可能并不成比例,因此 4sp + 20sp 可能并不等于 24sp。
转换放大像素 (sp) 单位
使用 TypedValue.applyDimension() 从 sp 单位转换为像素,并使用 TypedValue.deriveDimension() 将像素转换为 sp。这些方法会自动应用适当的非线性放大曲线。
避免对公式进行硬编码,使用以下代码
Configuration.fontScale 或
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity。因为字体缩放
非线性的,则 scaledDensity 字段不再准确。fontScale
字段应仅用于提供信息,
使用单个标量值进行扩缩。
为 lineHeight 使用 sp 单位
始终使用 sp 单位定义 android:lineHeight
dp 为 dp,因此行高会随文本一起缩放。否则,如果文本使用 sp,但 lineHeight 使用 dp 或 px,则文本不会缩放,并且看起来很拥挤。TextView 会自动更正 lineHeight,以便实现您的目标
比例会得到保留,但前提是 textSize 和 lineHeight
以 sp 为单位进行定义。
กล้องและสื่อ
Ultra HDR สำหรับรูปภาพ

Android 14 新增了对高动态范围 (HDR) 图片的支持,可在拍摄照片时保留更多来自传感器的信息,从而实现鲜艳的色彩和更高的对比度。Android 使用 Ultra HDR 格式,该格式与 JPEG 图片完全向后兼容,可让应用与 HDR 图片无缝互操作,并根据需要以标准动态范围 (SDR) 显示这些图片。
当您的应用选择为其 activity 窗口使用 HDR 界面(通过清单条目或通过在运行时调用 Window.setColorMode())时,框架会自动在界面中以 HDR 格式渲染这些图片。您还可以在受支持的设备上拍摄压缩的 Ultra HDR 静态图片。从传感器中恢复的颜色越多,后期编辑的灵活性就越高。与 Ultra HDR 图片关联的 Gainmap 可用于使用 OpenGL 或 Vulkan 渲染这些图片。
ซูม โฟกัส ดูตัวอย่างหลังถ่าย และอื่นๆ ในส่วนขยายกล้อง
Android 14 升级并改进了相机扩展程序,让应用能够处理更长的处理时间,从而支持在受支持的设备上使用计算密集型算法(例如弱光摄影)来改善图片。这些功能可让用户在使用相机扩展功能时获得更出色的体验。这些改进的示例包括:
- 动态静态拍摄处理延迟时间估算功能可根据当前场景和环境条件提供更准确的静态拍摄延迟时间估算值。调用
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()可获取具有两种延迟时间估算方法的StillCaptureLatency对象。getCaptureLatency()方法会返回onCaptureStarted和onCaptureProcessStarted()之间的估算延迟时间,而getProcessingLatency()方法会返回onCaptureProcessStarted()和可用的最终处理帧之间的估算延迟时间。 - 支持拍摄进度回调,以便应用可以显示长时间运行的静态拍摄处理操作的当前进度。您可以检查
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable是否支持此功能,如果支持,则实现onCaptureProcessProgressed()回调,并将进度(从 0 到 100)作为参数传入。 扩展程序专用元数据,例如用于调节扩展程序效果(例如背景虚化程度)的
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTH和EXTENSION_BOKEH。相机扩展程序中的静态图片拍摄预览功能,该功能比最终图片更快地提供经过较少处理的图片。如果扩展程序的处理延迟时间增加,可以提供 postview 图片作为占位符以提升用户体验,并在稍后改用最终图片。您可以使用
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable检查此功能是否可用。然后,您可以将OutputConfiguration传递给ExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration。支持
SurfaceView,可实现更优化且能效更高的预览渲染路径。支持在使用扩展程序时点按对焦和缩放。
การซูมในเซ็นเซอร์
当 CameraCharacteristics 中的 REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE 包含 SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW 时,您的应用可以使用高级传感器功能,将剪裁后的 RAW 数据流的像素与全视野范围相同,方法是将 CaptureRequest 与将数据流用例设置为 CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW 的 RAW 目标搭配使用。通过实现请求替换控件,更新后的相机可让用户在其他相机控件准备就绪之前使用缩放控件。
เสียง USB แบบไม่สูญเสียข้อมูล
Android 14 支持无损音频格式,可通过 USB 有线耳机提供发烧友级体验。您可以查询 USB 设备的首选混音器属性,注册监听器以监听首选混音器属性的更改,以及使用 AudioMixerAttributes 类配置混音器属性。此类表示音频混音器的格式,例如声道掩码、采样率和行为。该类允许直接发送音频,而无需混音、调节音量或处理效果。
ประสิทธิภาพการทำงานและเครื่องมือสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์
Credential Manager
Android 14 เพิ่ม Credential Manager เป็น API ของแพลตฟอร์ม โดยรองรับอุปกรณ์ Android 4.4 (API ระดับ 19) เพิ่มเติมผ่านคลัง Jetpack โดยใช้บริการ Google Play Credential Manager มีเป้าหมายเพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ได้ง่ายขึ้นด้วย API ที่ดึงข้อมูลและจัดเก็บข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบด้วยผู้ให้บริการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบที่ผู้ใช้กําหนดค่าไว้ Credential Manager รองรับวิธีการลงชื่อเข้าใช้หลายวิธี รวมถึงชื่อผู้ใช้และรหัสผ่าน พาสคีย์ และโซลูชันการลงชื่อเข้าใช้แบบรวมศูนย์ (เช่น ฟีเจอร์ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ด้วย Google) ใน API เดียว
พาสคีย์มีข้อดีหลายประการ เช่น พาสคีย์สร้างขึ้นตามมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรม ทำงานได้กับระบบปฏิบัติการและระบบนิเวศของเบราว์เซอร์ต่างๆ รวมถึงใช้ได้กับทั้งเว็บไซต์และแอป
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์และบล็อกโพสต์เกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์
Health Connect
Health Connect 是用户健康与健身数据的设备端仓库。借助该功能,用户可以在一个位置控制要与这些应用共享哪些数据,并在自己喜爱的应用之间共享数据。
在搭载 Android 14 之前的 Android 版本的设备上,Health Connect 可作为应用从 Google Play 商店下载。从 Android 14 开始,Health Connect 将成为 Android 平台的一部分,并通过 Google Play 系统更新接收更新,而无需单独下载。这样一来,Health Connect 就可以频繁更新,您的应用可以依赖于搭载 Android 14 或更高版本的设备上提供的 Health Connect。用户可以通过设备的“设置”访问 Health Connect,隐私控制功能集成到系统设置中。
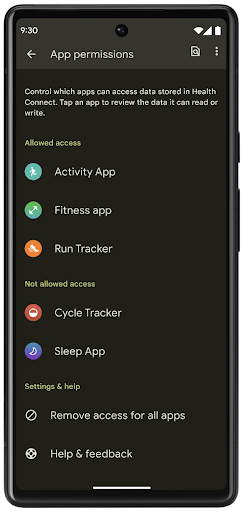
Health Connect 在 Android 14 中包含多项新功能,例如锻炼路线,可让用户分享可在地图上直观呈现的锻炼路线。路线定义为在一定时间范围内保存的位置列表,您的应用可以将路线插入锻炼时段,将它们关联起来。为确保用户能够完全控制此类敏感数据,用户必须允许与其他应用共享单个路线。
如需了解详情,请参阅 Health Connect 文档以及有关 Android Health 中的新功能的博文。
การอัปเดต OpenJDK 17
Android 14 ยังคงปรับปรุงไลบรารีหลักของ Android ให้สอดคล้องกับฟีเจอร์ใน OpenJDK LTS เวอร์ชันล่าสุด ซึ่งรวมถึงทั้งการอัปเดตไลบรารีและการรองรับภาษา Java 17 สําหรับนักพัฒนาแอปและแพลตฟอร์ม
ฟีเจอร์และการปรับปรุงต่อไปนี้จะรวมอยู่ด้วย
- อัปเดตคลาส
java.baseประมาณ 300 คลาสให้รองรับ Java 17 - บล็อกข้อความ ซึ่งจะนําสตริงตัวอักษรหลายบรรทัดมาสู่ภาษาโปรแกรม Java
- การจับคู่รูปแบบสำหรับ instanceof ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบถือว่าออบเจ็กต์มีประเภทที่เฉพาะเจาะจงใน
instanceofโดยไม่ต้องมีตัวแปรเพิ่มเติม - คลาสที่ปิด ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณจำกัดคลาสและอินเทอร์เฟซที่ขยายหรือนำไปใช้ได้
การอัปเดตระบบ Google Play (Project Mainline) ช่วยให้อุปกรณ์กว่า 600 ล้านเครื่องสามารถรับการอัปเดต Android Runtime (ART) ล่าสุดที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ ซึ่งเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของความมุ่งมั่นของเราที่จะมอบสภาพแวดล้อมที่ปลอดภัยและสอดคล้องกันมากขึ้นให้แก่แอปในอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ รวมถึงมอบฟีเจอร์และความสามารถใหม่ๆ ให้แก่ผู้ใช้โดยไม่ขึ้นอยู่กับรุ่นของแพลตฟอร์ม
Java และ OpenJDK เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าหรือเครื่องหมายการค้าจดทะเบียนของ Oracle และ/หรือบริษัทในเครือ
การปรับปรุงสำหรับ App Store
Android 14 เปิดตัว PackageInstaller API หลายรายการที่ช่วยปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้สำหรับ App Store
ขอการอนุมัติการติดตั้งก่อนดาวน์โหลด
การติดตั้งหรืออัปเดตแอปอาจต้องการอนุมัติของผู้ใช้
เช่น เมื่อผู้ติดตั้งที่ใช้สิทธิ์ REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES พยายามติดตั้งแอปใหม่ ใน Android เวอร์ชันก่อนๆ แอปสโตร์จะขอการอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้ได้หลังจากมีการเขียน APK ลงในเซสชันการติดตั้งและบันทึกเซสชันแล้วเท่านั้น
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป เมธอด requestUserPreapproval() จะอนุญาตให้ผู้ติดตั้งขอการอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้ก่อนยืนยันเซสชันการติดตั้ง การปรับปรุงนี้ช่วยให้ App Store เลื่อนการดาวน์โหลด APK ไว้ได้จนกว่าจะได้รับการอนุมัติการติดตั้งจากผู้ใช้ นอกจากนี้ เมื่อผู้ใช้อนุมัติการติดตั้งแล้ว แอปสโตร์จะดาวน์โหลดและติดตั้งแอปในเบื้องหลังได้โดยไม่รบกวนผู้ใช้
อ้างความรับผิดชอบสำหรับการอัปเดตในอนาคต
วิธีการ setRequestUpdateOwnership() ช่วยให้ผู้ติดตั้งระบุต่อระบบว่าตนตั้งใจที่จะรับผิดชอบต่อการอัปเดตแอปที่ติดตั้งในอนาคต ความสามารถนี้ช่วยให้สามารถบังคับใช้การเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตได้ ซึ่งหมายความว่ามีเพียงเจ้าของการอัปเดตเท่านั้นที่ได้รับอนุญาตให้ติดตั้งการอัปเดตอัตโนมัติในแอป การบังคับใช้การเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าผู้ใช้จะได้รับอัปเดตจาก App Store ที่คาดไว้เท่านั้น
โปรแกรมติดตั้งอื่นๆ รวมถึงโปรแกรมที่ใช้สิทธิ์ INSTALL_PACKAGES จะต้องได้รับอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้อย่างชัดเจนจึงจะติดตั้งการอัปเดตได้ หากผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจที่จะอัปเดตจากแหล่งที่มาอื่น ความเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตจะหายไป
อัปเดตแอปในเวลาที่รบกวนน้อยลง
โดยปกติแล้ว App Store ต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงการอัปเดตแอปที่ผู้ใช้กำลังใช้งานอยู่ เนื่องจากจะส่งผลให้กระบวนการที่ทำงานอยู่ของแอปหยุดลง ซึ่งอาจขัดจังหวะสิ่งที่ผู้ใช้กำลังทำอยู่
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป InstallConstraints API จะเปิดโอกาสให้ผู้ติดตั้งตรวจสอบว่าการอัปเดตแอปเกิดขึ้นในเวลาที่เหมาะสม ตัวอย่างเช่น แอปสโตร์สามารถเรียกใช้เมธอด commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าการอัปเดตจะดำเนินการต่อเมื่อผู้ใช้ไม่ได้โต้ตอบกับแอปที่เป็นปัญหาแล้ว
ติดตั้งส่วนแยกที่ไม่บังคับได้อย่างราบรื่น
เมื่อใช้ APK แบบแยก คุณจะส่งฟีเจอร์ของแอปเป็นไฟล์ APK แยกต่างหากได้ แทนที่จะส่งเป็น APK แบบรวม APK แบบแยกช่วยให้ App Store เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการนำส่งคอมโพเนนต์ต่างๆ ของแอปได้ เช่น แอปสโตร์อาจเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพตามพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ของอุปกรณ์เป้าหมาย PackageInstaller API รองรับการแยกตั้งแต่เปิดตัวใน API ระดับ 22
ใน Android 14 วิธีการ setDontKillApp() ช่วยให้ผู้ติดตั้งระบุได้ว่าไม่ควรหยุดกระบวนการที่ทำงานอยู่ของแอปเมื่อติดตั้งแยกใหม่ App Store สามารถใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้เพื่อติดตั้งฟีเจอร์ใหม่ของแอปได้อย่างราบรื่นขณะที่ผู้ใช้กำลังใช้แอปอยู่
App Bundle ข้อมูลเมตา
从 Android 14 开始,Android 软件包安装程序可让您指定应用元数据(例如数据安全做法),以在 Google Play 等应用商店页面上架。
ตรวจหาเวลาที่ผู้ใช้ถ่ายภาพหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์
为了打造更加标准化的屏幕截图检测体验,Android 14 引入了可保护隐私的屏幕截图检测 API。借助此 API,应用可以按 activity 注册回调。如果用户在该 activity 可见时截取屏幕截图,系统会调用这些回调并通知用户。
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้
การทำงานที่กำหนดเองของชีตการแชร์และการจัดอันดับที่ดียิ่งขึ้น
Android 14 更新了系统 Sharesheet,以便为用户提供自定义应用操作和信息更丰富的预览结果。
添加自定义操作
对于 Android 14,您的应用可以向其调用的系统 Sharesheet 添加自定义操作。
提高直接共享目标的排名
Android 14 根据来自应用的更多信号来确定直接共享目标的排名,以便为用户提供更实用的结果。为了提供最实用的排名信号,请遵循提高直接共享目标排名的准则。通讯应用还可以报告出站和入站消息的快捷方式使用情况。
รองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวในตัวและภาพเคลื่อนไหวที่กำหนดเองสำหรับท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา
Android 13 ได้เปิดตัวภาพเคลื่อนไหวแบบคาดเดาซึ่งนำผู้ใช้กลับไปยังหน้าจอหลักจากตัวเลือกของนักพัฒนาแอป เมื่อใช้ในแอปที่รองรับซึ่งเปิดใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป การปัดย้อนกลับจะแสดงภาพเคลื่อนไหวที่ระบุว่าท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับจะนำออกจากแอปกลับไปที่หน้าจอหลัก
Android 14 มีการปรับปรุงหลายอย่างและคำแนะนำใหม่สำหรับฟีเจอร์การย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์ ดังนี้
- คุณสามารถตั้งค่า
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueเพื่อเลือกใช้การเคลื่อนไหวของระบบสำหรับการย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดาต่อกิจกรรมแทนทั้งแอป - เราได้เพิ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวใหม่ของระบบเพื่อใช้ควบคู่ไปกับภาพเคลื่อนไหวของการเปลี่ยนกลับไปที่หน้าแรกจาก Android 13 ภาพเคลื่อนไหวของระบบแบบใหม่จะทำงานข้ามกิจกรรมและข้ามงาน ซึ่งคุณจะได้รับโดยอัตโนมัติหลังจากย้ายข้อมูลไปยังท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา
- เราได้เพิ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวใหม่สำหรับคอมโพเนนต์ Material สำหรับชีตด้านล่าง ชีตด้านข้าง และการค้นหา
- เราได้จัดทำคำแนะนำด้านการออกแบบสำหรับการสร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหวและทรานซิชันในแอปที่กำหนดเอง
- เราได้เพิ่ม API ใหม่เพื่อรองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวการเปลี่ยนภาพในแอปที่กําหนดเอง ดังนี้
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- ใช้
overrideActivityTransitionแทนoverridePendingTransitionสำหรับทรานซิชันที่ตอบสนองเมื่อผู้ใช้ปัดกลับ
ในรุ่นตัวอย่างของ Android 14 นี้ ฟีเจอร์ทั้งหมดของฟีเจอร์การกดย้อนกลับแบบคาดคะเนจะยังคงอยู่ในตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ดูคู่มือนักพัฒนาแอปเพื่อย้ายข้อมูลแอปไปใช้แบ็กเอนด์แบบคาดการณ์ รวมถึงคู่มือนักพัฒนาแอปในการสร้างทรานซิชันในแอปที่กําหนดเอง
การลบล้างต่อแอปของผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การลบล้างค่าแอปต่อแอปช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์เปลี่ยนลักษณะการทำงานของแอปในอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น การลบล้าง FORCE_RESIZE_APP จะสั่งให้ระบบปรับขนาดแอปให้พอดีกับขนาดการแสดงผล (หลีกเลี่ยงโหมดความเข้ากันได้ของขนาด) แม้ว่าจะมีการตั้งค่า resizeableActivity="false" ในไฟล์ Manifest ของแอปก็ตาม
การลบล้างมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้บนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ไฟล์ Manifest ใหม่ช่วยให้คุณปิดใช้การลบล้างผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์บางรายสำหรับแอปของคุณได้
การลบล้างต่อแอปสำหรับผู้ใช้หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
按应用替换项会更改应用在大屏设备上的行为。例如,无论应用的配置如何,OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE 设备制造商替换项都会将应用宽高比设置为 16:9。
借助 Android 14 QPR1,用户可以在大屏设备上通过新的设置菜单应用按应用替换项。
การแชร์หน้าจอแอป
借助应用界面共享功能,用户可以在录制屏幕内容时共享应用窗口,而不是整个设备屏幕。
在应用屏幕共享模式下,状态栏、导航栏、通知和其他系统界面元素会从共享显示屏中排除。系统只会分享所选应用的内容。
应用屏幕共享功能可让用户运行多个应用,但将内容共享限制为单个应用,从而提高工作效率并保护隐私。
ฟีเจอร์ช่วยตอบที่ทำงานด้วย LLM ใน Gboard บน Pixel 8 Pro
在搭载 12 月功能分块的 Pixel 8 Pro 设备上,开发者可以在 Gboard 中试用质量更高的智能回复,这些回复由在 Google Tensor 上运行的设备端大语言模型 (LLM) 提供支持。
此功能目前仅在 WhatsApp、Line 和 KakaoTalk 中以美式英语的形式提供给用户进行小范围测试。此功能需要使用 Pixel 8 Pro 设备,并将 Gboard 用作键盘。
如需试用此功能,请先依次前往设置 > 开发者选项 > AiCore 设置 > 启用 Aicore 持久性,启用该功能。
接下来,在受支持的应用中打开对话,即可在 Gboard 的建议栏中看到依托 LLM 的智能回复,以便回复收到的消息。
กราฟิก
เส้นทางจะค้นหาและประมาณค่าได้
Android 的 Path API 是一种强大且灵活的机制,可用于创建和渲染矢量图形,能够描边或填充路径、根据线段或二次曲线或立方曲线构建路径、执行布尔运算以获取更复杂的形状,或同时执行所有这些操作。但有一个限制是,您无法了解 Path 对象中实际包含的内容;该对象的内部信息在创建后对调用方是不透明的。
如需创建 Path,您可以调用 moveTo()、lineTo() 和 cubicTo() 等方法来添加路径段。但是,无法询问该路径有哪些片段,因此您必须在创建时保留该信息。
从 Android 14 开始,您可以查询路径以了解其内部内容。首先,您需要使用 Path.getPathIterator API 获取 PathIterator 对象:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
接下来,您可以调用 PathIterator 逐个遍历片段,并检索每个片段的所有必要数据。以下示例使用了 PathIterator.Segment 对象,它会为您打包数据:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator 还有一个非分配版 next(),您可以在其中传入缓冲区来保存点数据。
查询 Path 数据的一个重要用例是插值。例如,您可能想在两个不同的路径之间添加动画(或变形)。为了进一步简化该用例,Android 14 针对 Path 还包含 interpolate() 方法。假设两个路径具有相同的内部结构,interpolate() 方法会使用该插值结果创建一个新的 Path。以下示例返回了一个形状介于 path 和 otherPath 之间的一半(线性插值为 0.5)的路径:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Jetpack graphics-path 库也为早期版本的 Android 启用了类似的 API。
Custom meshes with vertex and fragment shaders
Android 长期以来一直支持使用自定义着色绘制三角网格,但输入网格格式仅限于一些预定义的属性组合。Android 14 增加了对自定义网格的支持,可将其定义为三角形或三角形条,并且可以选择是否编入索引。这些网格是使用自定义属性、顶点步长、可变以及使用 AGSL 编写的顶点着色器和片段着色器指定的。
顶点着色器定义了位置和颜色等变量,而片段着色器可以选择为像素定义颜色,通常是使用顶点着色器创建的变量。如果片段着色器提供颜色,则系统会使用绘制网格时选择的混合模式将其与当前 Paint 颜色混合。Uniform 可以传递到片段着色器和顶点着色器,以提高灵活性。
เครื่องมือแสดงผลบัฟเฟอร์ฮาร์ดแวร์สำหรับ Canvas
Android 14 เปิดตัว HardwareBufferRenderer เพื่อช่วยในการใช้ Canvas API ของ Android เพื่อวาดด้วย GPU ลงใน HardwareBuffer API นี้
ซึ่งจะเป็นประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งเมื่อกรณีการใช้งานของคุณเกี่ยวข้องกับการสื่อสารกับระบบ
Compositor ผ่าน SurfaceControl สำหรับเวลาในการตอบสนองต่ำ
ภาพวาด

