בדומה לגרסאות קודמות, Android 16 כולל שינויים בהתנהגות שעשויים להשפיע על האפליקציה שלכם. שינויי ההתנהגות הבאים רלוונטיים רק לאפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 16 ואילך. אם האפליקציה שלכם מטרגטת את Android מגרסה 16 ואילך, אתם צריכים לשנות את האפליקציה כדי שהיא תתמוך בהתנהגויות האלה, במקרים הרלוונטיים.
חשוב גם לבדוק את רשימת השינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים על כל האפליקציות שפועלות ב-Android 16, בלי קשר ל-targetSdkVersion של האפליקציה.
חוויית המשתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים, שנועדו ליצור חוויית משתמש עקבית ואינטואיטיבית יותר.
האפשרות להסיר את התצוגה מקצה לקצה תבוטל
האפשרות 'מקצה לקצה' נאכפת ב-Android 15 באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35), אבל אפשר להשבית אותה באפליקציה על ידי הגדרת R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement ל-true. באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36), R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement הוצא משימוש ומושבת, ולא ניתן לבטל את ההגדרה של תצוגה מקצה לקצה באפליקציה.
- אם האפליקציה מיועדת ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36) והיא פועלת במכשיר עם Android 15, הפונקציה
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementממשיכה לפעול. - אם האפליקציה מטרגטת ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36) והיא פועלת במכשיר עם Android 16, התכונה
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementמושבתת.
כדי לבדוק ב-Android 16, מוודאים שהאפליקציה תומכת בתצוגה מקצה לקצה ומסירים את השימוש ב-R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement כדי שהאפליקציה תתמוך בתצוגה מקצה לקצה גם במכשיר Android 15. הוראות לגבי תמיכה בתצוגה מקצה לקצה מופיעות במאמרים יצירת מסמכים ותצוגות.
כדי להשתמש בתכונה "חיזוי החזרה", צריך לבצע העברה או לבטל את ההסכמה
באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36) ואילך ופועלות במכשיר עם Android 16 ואילך, מופעלות כברירת מחדל האנימציות של מערכת הניווט התחזיתי אחורה (חזרה למסך הבית, מעבר בין משימות ומעבר בין פעילויות).
בנוסף, לא מתבצעת קריאה ל-onBackPressed ולא מתבצעת יותר שליחה של KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK.
אם האפליקציה שלכם מיירטת את אירוע החזרה ואתם עדיין לא עברתם לניווט חזוי אחורה, עדכנו את האפליקציה כדי להשתמש בממשקי API נתמכים של ניווט אחורה, או השביתו את התכונה באופן זמני על ידי הגדרת המאפיין android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback לערך false בתג <application> או <activity> של קובץ AndroidManifest.xml של האפליקציה.
הוצאה משימוש והשבתה של ממשקי API אלגנטיים לגופנים
以 Android 15(API 级别 35)为目标平台的应用默认将 elegantTextHeight
TextView 属性设置为 true,从而将紧凑型字体替换为可读性更高的字体。您可以通过将 elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 来替换此设置。
Android 16 弃用了 elegantTextHeight 属性,当您的应用以 Android 16 为目标平台后,系统会忽略该属性。由这些 API 控制的“界面字体”即将停用,因此您应调整所有布局,以确保阿拉伯语、老挝语、缅甸语、泰米尔语、古吉拉特语、卡纳达语、马拉雅拉姆语、奥里亚语、泰卢固语或泰语文本的呈现效果一致且不受未来变化的影响。
elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 替换默认值的应用,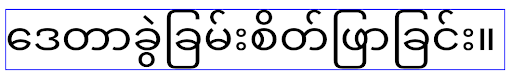
elegantTextHeight 行为。elegantTextHeight 属性设置为 false 来替换默认值的应用,其 elegantTextHeight 行为。
פונקציונליות עיקרית
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים, שמשנים או מרחיבים יכולות ליבה שונות של מערכת Android.
אופטימיזציה של תזמון פעולה בקצב קבוע
在以 Android 16 为目标平台之前,如果 scheduleAtFixedRate 因不在有效的进程生命周期内而错过了任务执行,则当应用返回到有效的生命周期时,所有错过的执行会立即执行。
以 Android 16 为目标平台时,当应用返回到有效的生命周期时,系统会立即执行最多 1 次未执行的 scheduleAtFixedRate 执行。此行为变更预计会提升应用性能。在您的应用中测试此行为,检查您的应用是否受到影响。您还可以使用应用兼容性框架并启用 STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS 兼容性标志进行测试。
גורמי צורה של מכשירים
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים באפליקציות כשהן מוצגות במכשירים עם מסך גדול.
פריסות מותאמות
现在,Android 应用可在各种设备(例如手机、平板电脑、可折叠设备、桌面设备、汽车和电视)上运行,并且在大屏设备上支持多种窗口模式(例如分屏和桌面窗口),因此开发者应构建能够适应任何屏幕和窗口尺寸的 Android 应用,无论设备方向如何。在当今多设备的世界中,限制屏幕方向和尺寸可调整性等范式过于严格。
忽略屏幕方向、尺寸可调整性和宽高比限制
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,屏幕方向、尺寸可调整性和宽高比限制不再适用于最小宽度 >= 600dp 的显示屏。无论宽高比或用户偏好的屏幕方向如何,应用都会填满整个显示窗口,且不会采用竖条模式。
此变更引入了新的标准平台行为。Android 正在向一种模型转变,在该模型中,应用需要适应各种屏幕方向、显示大小和宽高比。固定屏幕方向或有限的尺寸调整等限制会阻碍应用的适应性。使应用具有自适应性,以提供尽可能最佳的用户体验。
您还可以使用应用兼容性框架并启用 UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT 兼容性标志来测试此行为。
常见的重大更改
忽略屏幕方向、可调整大小性和宽高比限制可能会影响应用在某些设备上的界面,尤其是那些专为锁定为纵向的小布局设计的元素,例如布局拉伸、动画和组件超出屏幕等问题。任何关于宽高比或屏幕方向的假设都可能导致应用出现视觉问题。详细了解如何避免这些问题并改进应用的自适应行为。
允许设备旋转会导致更多 activity 重新创建,如果未正确保留,可能会导致用户状态丢失。如需了解如何正确保存界面状态,请参阅保存界面状态。
实现细节
在全屏模式和多窗口模式下,以下清单属性和运行时 API 会被大屏设备忽略:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
系统会忽略 screenOrientation、setRequestedOrientation() 和 getRequestedOrientation() 的以下值:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
对于显示屏可调整大小性,android:resizeableActivity="false"、android:minAspectRatio 和 android:maxAspectRatio 没有影响。
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)为目标平台的应用,默认情况下,大屏设备会忽略应用的屏幕方向、可调整尺寸性和宽高比限制,但尚未完全准备就绪的每个应用都可以选择停用此行为,从而暂时替换此行为(这会导致应用恢复到之前放置在兼容模式下的行为)。
异常
在以下情况下,Android 16 的屏幕方向、尺寸调整能力和宽高比限制不适用:
- 游戏(基于
android:appCategory标志) - 用户在设备的宽高比设置中明确选择启用应用的默认行为
- 小于
sw600dp的屏幕
暂时停用
如需选择停用特定 activity,请声明 PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY 清单属性:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
如果您的应用有太多部分尚未准备好支持 Android 16,您可以在应用级别应用相同的属性,从而完全选择不启用该功能:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
בריאות וכושר
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים שקשורים לנתוני בריאות וכושר.
הרשאות ל"בריאות וכושר"
对于以 Android 16(API 级别 36)或更高版本为目标平台的应用,BODY_SENSORS 权限使用 android.permissions.health 下更精细的权限,健康数据共享也使用这些权限。自 Android 16 起,凡是以前需要具有 BODY_SENSORS 或 BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND 权限的 API,现在都需要获取相应的 android.permissions.health 权限。这会影响以下数据类型、API 和前台服务类型:
- 从 Wear OS 上的健康服务中获取
HEART_RATE_BPM - 来自 Android Sensor Manager 的
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - 在 Wear OS 上,
ProtoLayout中的heartRateAccuracy和heartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH,其中需要使用相应的android.permission.health权限来代替BODY_SENSORS
如果您的应用使用这些 API,则应请求相应的精细权限:
- 对于使用期间的心率、血氧饱和度或体表温度监测:请求
android.permissions.health下的精细权限,例如READ_HEART_RATE,而不是BODY_SENSORS。 - 对于后台传感器访问权限:请求
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND而不是BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND。
这些权限与用于保护对 Health Connect(Android 健康、健身和身心状态数据存储区)中读取数据的访问权限相同。
移动应用
迁移到使用 READ_HEART_RATE 和其他精细权限的移动应用还必须声明 activity 以显示应用的隐私权政策。此要求与健康数据共享的要求相同。
קישוריות
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים במערך Bluetooth כדי לשפר את הקישוריות למכשירים היקפיים.
כוונה חדשה לטיפול באובדן של קשר ובשינויים בהצפנה
כחלק משיפור הטיפול באירועים של אובדן קישור, ב-Android 16 נוספו גם 2 כוונות חדשות כדי לספק לאפליקציות מודעוּת רבה יותר לאובדן קישור ולשינויים בהצפנה.
אפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 16 יכולות עכשיו:
- לקבל כוונה מסוג
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGכשמתגלה אובדן של אבטחה מרחוק, כדי לספק משוב מפורט יותר מהמשתמשים ולבצע פעולות מתאימות. - לקבל כוונה מסוג
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEבכל פעם שסטטוס ההצפנה של הקישור משתנה. זה כולל שינוי בסטטוס ההצפנה, שינוי באלגוריתם ההצפנה ושינוי בגודל מפתח ההצפנה. אפליקציות צריכות להתייחס לאיחוד כמשוחזר אם הקישור מוצפן בהצלחה לאחר קבלת הכוונהACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE.
התאמה להטמעות שונות של יצרני ציוד מקורי (OEM)
גרסת Android 16 כוללת את הכוונות החדשות האלה, אבל ההטמעה והשידור שלהן עשויים להשתנות בהתאם ליצרני המכשירים השונים (OEM). כדי לוודא שהאפליקציה מספקת חוויה עקבית ואמינה בכל המכשירים, המפתחים צריכים לתכנן את הטיפול באובדן הקשר כך שיתאים בצורה חלקה לשינויים הפוטנציאליים האלה.
מומלץ להשתמש בהתנהגויות הבאות באפליקציות:
אם המערכת משדרת את הכוונה
ACTION_KEY_MISSING:המערכת תנתק את הקישור של ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less), אבל פרטי הקישור של המכשיר יישמרו (כפי שמתואר כאן).
האפליקציה צריכה להשתמש בכוונה הזו כאות הראשי לזיהוי אובדן החיבור, ולהנחות את המשתמש לאשר שהמכשיר המרוחק נמצא בטווח לפני שהוא מתחיל למחוק את המכשיר או לבצע התאמה מחדש.
אם מכשיר מתנתק אחרי קבלת
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, האפליקציה צריכה להיזהר לפני שתנסה להתחבר מחדש, כי יכול להיות שהמכשיר כבר לא מקושר למערכת.אם הכוונה
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGלא משודרת:הקישור ל-ACL יישאר מחובר, ופרטי הקישור של המכשיר יוסרו על ידי המערכת, בדומה להתנהגות ב-Android 15.
בתרחיש הזה, האפליקציה צריכה להמשיך להשתמש במנגנונים הקיימים לטיפול באובדן אבטחה, כמו בגרסאות קודמות של Android, כדי לזהות אירועי אובדן אבטחה ולנהל אותם.
דרך חדשה להסרת שיוך Bluetooth
现在,以 Android 16 为目标平台的所有应用都可以使用 CompanionDeviceManager 中的公共 API 解除蓝牙设备配对。如果配套设备作为 CDM 关联进行管理,则应用可以在关联的设备上使用新的 removeBond(int) API 触发蓝牙配对的移除。该应用可以通过监听蓝牙设备广播事件 ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED 来监控配对状态变化。
אבטחה
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את שינויי האבטחה הבאים.
נעילת גרסה של MediaStore
对于以 Android 16 或更高版本为目标平台的应用,MediaStore#getVersion() 现在将是每个应用的唯一标识。这会从版本字符串中移除标识属性,以防止滥用和用于指纹识别技术。应用不应对此版本的格式做出任何假设。在使用此 API 时,应用应已处理版本变更,并且在大多数情况下无需更改其当前行为,除非开发者尝试推断超出此 API 预期范围的其他信息。
כוונות בטוחות יותר
“更安全的 intent”功能是一项多阶段安全计划,旨在提高 Android 的 intent 解析机制的安全性。目标是在 intent 处理期间添加检查,并过滤不符合特定条件的 intent,从而保护应用免受恶意操作的侵害。
在 Android 15 中,该功能侧重于发送应用,现在在 Android 16 中,控制权转移到了接收应用,允许开发者使用其应用清单选择加入严格的 intent 解析。
我们正在实施两项关键变更:
显式 intent 必须与目标组件的 intent 过滤器相匹配:如果 intent 显式定位到某个组件,则应与该组件的 intent 过滤器相匹配。
没有操作的 intent 无法匹配任何 intent 过滤器:未指定操作的 intent 不应解析为任何 intent 过滤器。
这些变更仅在涉及多个应用时适用,不会影响单个应用内的 intent 处理。
影响
选择启用性质意味着,开发者必须在应用清单中明确启用它,才能使其生效。 因此,此功能的影响将仅限于以下应用:
- 了解“更安全的 intent”功能及其优势。
- 主动选择在应用中采用更严格的 intent 处理实践。
这种选择性采用的方法可最大限度地降低破坏可能依赖于当前不太安全的 intent 解析行为的现有应用的风险。
虽然在 Android 16 中,初始影响可能有限,但“更安全的 intent”计划的路线图显示,未来 Android 版本的影响范围会更广。我们计划最终将严格的意图解析设为默认行为。
“更安全的 intent”功能可让恶意应用更难利用 intent 解析机制中的漏洞,从而有望显著提升 Android 生态系统的安全性。
不过,向选择退出和强制执行的过渡必须谨慎管理,以解决现有应用的潜在兼容性问题。
实现
开发者需要在应用清单中使用 intentMatchingFlags 属性明确启用更严格的 intent 匹配。
以下示例展示了如何为整个应用选择启用该功能,但在接收器上停用/选择停用该功能:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
有关支持的标志的更多信息:
| 标志名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | 对传入的 intent 强制执行更严格的匹配 |
| none | 停用针对传入 intent 的所有特殊匹配规则。指定多个标志时,系统会优先考虑“无”标志,以解决值冲突问题 |
| allowNullAction | 放宽了匹配规则,允许匹配没有操作的 intent。此标志与“enforceIntentFilter”结合使用可实现特定行为 |
测试和调试
在强制执行处于有效状态时,如果 intent 调用方已正确填充 intent,应用应能正常运行。
不过,被屏蔽的 intent 会触发警告日志消息(例如 "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" 和 "Access blocked:"),并带有标记 "PackageManager."。这表示存在可能会影响应用的潜在问题,需要引起注意。
Logcat 过滤条件:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
סינון של קריאות מערכת (syscall) ב-GPU
为了加固 Mali GPU 表面,在生产 build 中,已废弃或仅用于 GPU 开发的 Mali GPU IOCTL 已被屏蔽。此外,用于 GPU 性能分析的 IOCTL 已限制为 shell 进程或可调试的应用。如需详细了解平台级政策,请参阅 SAC 更新。
此更改适用于使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 设备(Pixel 6-9)。Arm 已在其 r54p2 版本的 Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst 中提供了 IOCTL 的官方分类。此列表将在未来的驱动程序版本中继续维护。
此项变更不会影响受支持的图形 API(包括 Vulkan 和 OpenGL),预计也不会影响开发者或现有应用。 Streamline Performance Analyzer 和 Android GPU 检查器等 GPU 性能剖析工具不会受到影响。
测试
如果您看到类似如下所示的 SELinux 拒绝,则说明您的应用可能受到了此变更的影响:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
如果您的应用需要使用被屏蔽的 IOCTL,请提交 bug 并将其分配给 android-partner-security@google.com。
常见问题解答
此政策变更是否适用于所有原始设备制造商 (OEM)? 此变更将采用选择启用模式,但任何想要使用此强化方法的 OEM 都可以使用。如需了解如何实现此变更,请参阅实现文档。
是否必须在 OEM 代码库中进行更改才能实现此功能,还是默认随新的 AOSP 版本提供? 平台级变更将默认随新的 AOSP 版本一起发布。如果供应商想要应用此变更,可以在其代码库中选择启用此变更。
SoC 是否负责使 IOCTL 列表保持最新状态?例如,如果我的设备使用 ARM Mali GPU,我是否需要就任何更改与 ARM 联系? 各个 SoC 必须在驱动程序发布后根据设备更新其 IOCTL 列表。 例如,ARM 会在驱动程序更新时更新其已发布的 IOCTL 列表。 不过,OEM 应确保在 SEPolicy 中纳入这些更新,并根据需要将任何选定的自定义 IOCTL 添加到列表中。
此变更是否会自动应用于所有在售 Pixel 设备,还是需要用户执行操作来切换某些设置才能应用此变更? 此变更适用于所有使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 在售设备(Pixel 6-9)。用户无需采取任何行动即可应用此变更。
使用此政策会影响内核驱动程序的性能吗? 我们使用 GFXBench 在 Mali GPU 上测试了此政策,未发现 GPU 性能有任何可衡量的变化。
IOCTL 列表是否需要与当前的用户空间和内核驱动程序版本保持一致? 是的,允许的 IOCTL 列表必须与用户空间和内核驱动程序支持的 IOCTL 同步。如果用户空间或内核驱动程序中的 IOCTL 发生更新,则必须更新 SEPolicy IOCTL 列表以保持一致。
ARM 已将 IOCTL 分类为“受限”/“检测”,但我们希望在生产用例中使用其中一些 IOCTL,并拒绝其他 IOCTL。 各个 OEM/SoC 负责根据其用户空间 Mali 库的配置来决定如何对其使用的 IOCTL 进行分类。ARM 的列表可用于帮助确定这些值,但每个 OEM/SoC 的使用情形可能有所不同。
פרטיות
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים שקשורים לפרטיות.
הרשאה לגישה לרשת המקומית
具有 INTERNET 权限的任何应用都可以访问局域网上的设备。
这使得应用可以轻松连接到本地设备,但也存在隐私影响,例如形成用户指纹,以及成为位置信息的代理。
本地网络保护项目旨在通过在新的运行时权限后限制对本地网络的访问,来保护用户的隐私。
发布计划
此变更将分别在 25Q2 和 26Q2 这两个版本之间部署。 开发者必须遵循 25Q2 的相关指南并分享反馈,因为这些保护措施将在后续 Android 版本中强制执行。此外,他们还需要按照以下指南更新依赖于隐式本地网络访问权限的场景,并为用户拒绝和撤消新权限做好准备。
影响
在当前阶段,LNP 是一项选择启用功能,这意味着只有选择启用的应用会受到影响。选择启用阶段的目标是让应用开发者了解应用的哪些部分依赖于隐式本地网络访问权限,以便他们可以为下一个版本做好权限保护准备。
如果应用使用以下方式访问用户的本地网络,则会受到影响:
- 在本地网络地址(例如 mDNS 或 SSDP 服务发现协议)上直接或通过库使用原始套接字
- 使用可访问本地网络的框架级类(例如 NsdManager)
向本地网络地址发送流量和从本地网络地址接收流量需要本地网络访问权限。下表列出了一些常见情况:
| 应用低级层网络操作 | 需要本地网络权限 |
|---|---|
| 建立出站 TCP 连接 | 是 |
| 接受传入的 TCP 连接 | 是 |
| 发送 UDP 单播、多播、广播 | 是 |
| 接收传入的 UDP 单播、多播、广播 | 是 |
这些限制是在网络堆栈深处实现的,因此适用于所有网络 API。这包括在原生代码或受管理代码中创建的套接字、Cronet 和 OkHttp 等网络库,以及基于这些库实现的任何 API。尝试解析本地网络上的服务(即带有 .local 后缀的服务)将需要本地网络权限。
上述规则的例外情况:
- 如果设备的 DNS 服务器位于本地网络上,则进出该服务器(位于端口 53)的流量不需要本地网络访问权限。
- 如果应用使用输出切换器作为其应用内选择器,则无需本地网络权限(更多指南将在 2025 年第 4 季度发布)。
开发者指南(选择启用)
如需选择启用本地网络限制,请执行以下操作:
- 将设备刷写到 25Q2 Beta 3 或更高版本的 build。
- 安装要测试的应用。
在 adb 中切换 Appcompat 标志:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>重启设备
现在,您的应用对本地网络的访问受到限制,任何访问本地网络的尝试都会导致套接字错误。如果您使用的 API 在应用进程之外执行本地网络操作(例如:NsdManager),在选择启用阶段,这些 API 不会受到影响。
如需恢复访问权限,您必须向应用授予 NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES 权限。
- 确保应用在其清单中声明了
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES权限。 - 依次前往设置 > 应用 > [应用名称] > 权限 > 附近的设备 > 允许。
现在,应用对本地网络的访问权限应该已恢复,并且所有场景都应像选择启用应用之前一样正常运行。
本地网络保护功能开始强制执行后,应用的网络流量将受到以下影响。
| 权限 | 出站 LAN 请求 | 出站/入站互联网请求 | 入站 LAN 请求 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 已授予 | Works | Works | Works |
| 未授予 | 最差排行榜 | Works | 最差排行榜 |
使用以下命令切换关闭应用兼容性标志
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
错误
每当调用套接字调用 send 或 send 变体向本地网络地址发送数据时,系统都会向该套接字返回因这些限制而产生的错误。
错误示例:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
本地网络定义
此项目中的本地网络是指使用支持广播的网络接口(例如 Wi-Fi 或以太网)的 IP 网络,但不包括移动网络 (WWAN) 或 VPN 连接。
以下网络被视为本地网络:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // 链路本地
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- 链路本地
- 直接连接的路线
- Thread 等桩网络
- 多个子网(待定)
此外,多播地址 (224.0.0.0/4、ff00::/8) 和 IPv4 广播地址 (255.255.255.255) 都归类为本地网络地址。
תמונות בבעלות האפליקציה
כשמוצגת בקשה להענקת הרשאות גישה לתמונות ולסרטונים מאפליקציה שתואמת ל-SDK מגרסה 36 ואילך במכשירים עם Android מגרסה 16 ואילך, משתמשים שבוחרים להגביל את הגישה למדיה שנבחרה יראו את כל התמונות שבבעלות האפליקציה שנבחרו מראש בבורר התמונות. המשתמשים יכולים לבטל את הבחירה של כל אחד מהפריטים שנבחרו מראש, וכך לבטל את הגישה של האפליקציה לתמונות ולסרטונים האלה.
