Android 16 面向开发者引入了一些出色的新功能和 API。以下各部分总结了这些功能,可帮助您开始使用相关 API。
如需查看新增、修改和移除的 API 的详细列表,请参阅 API 差异报告。如需详细了解新的 API,请访问 Android API 参考文档,新 API 会突出显示以方便查看。您还应查看平台变更可能会在哪些方面影响您的应用。如需了解详情,请参阅以下页面:
核心功能
Android 包含一些新的 API,可扩展 Android 系统的核心功能。
2025 年发布了两个 Android API
- 此预览版适用于 Android 的下一个主要版本,计划于 2025 年第 2 季度发布。此版本与我们过去的所有 API 版本类似,我们可以进行计划性的行为更改,这些更改通常与 targetSdkVersion 相关联。
- 我们计划提前一个季度(2021 年第 2 季度,而非之前的第 3 季度)发布主要版本,以便更好地与整个生态系统中的设备发布时间表保持一致,让更多设备能够更早地搭载 Android 主要版本。由于主要版本将于第 2 季度发布,因此您需要比往年提前几个月进行年度兼容性测试,以确保您的应用已做好准备。
- 我们计划在 2025 年第 4 季度再发布一次,届时还将推出新的开发者 API。2025 年只有第二季度的主要版本包含可能影响应用的计划行为变更。
除了新的开发者 API 之外,第 4 季度次要版本还将包含功能更新、优化和 bug 修复;其中不会包含任何会影响应用的行为变更。
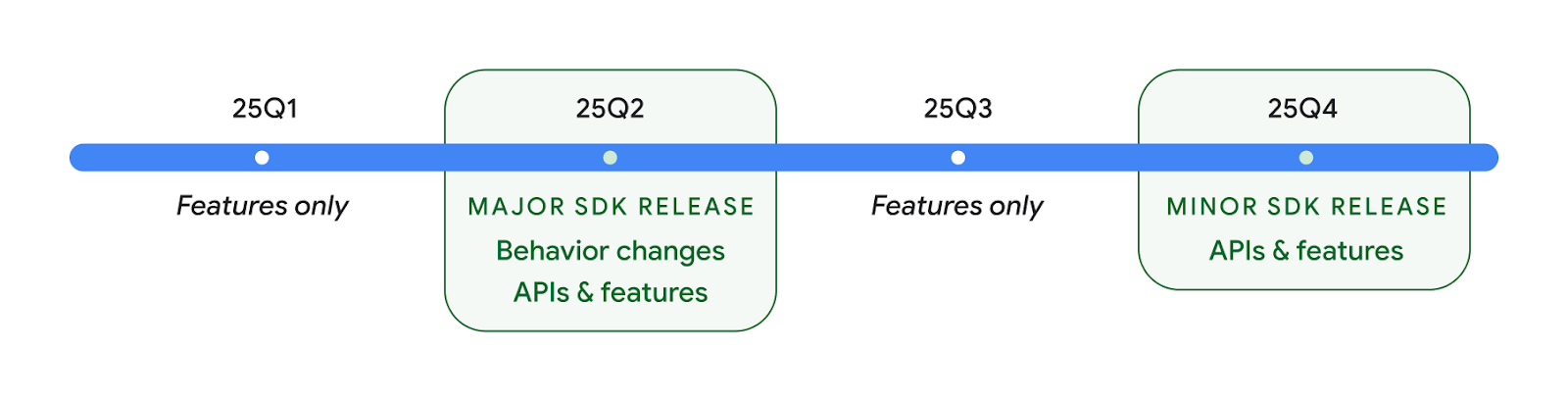
我们将继续每季度发布 Android 版本。在 API 版本之间,第 1 季度和第 3 季度的更新将提供增量更新,以帮助确保持续提供高质量的服务。我们正积极与设备合作伙伴合作,将 Q2 版本推广到尽可能多的设备。
在主要版本和次要版本中使用新 API
目前,使用 SDK_INT 常量与 VERSION_CODES 结合使用,即可通过检查 API 级别来保护代码块。我们将继续支持主要 Android 版本。
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
新的 SDK_INT_FULL 常量可用于针对主要版本和次要版本进行 API 检查,并使用新的 VERSION_CODES_FULL 枚举。
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
您还可以使用 Build.getMinorSdkVersion() 方法仅获取 SDK 次要版本。
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
这些 API 尚未最终确定,可能会发生变化,因此如果您有任何疑虑,请向我们发送反馈。
用户体验和系统界面
Android 16 为应用开发者和用户提供了更多控制权和灵活性,以便他们根据自己的需求配置设备。
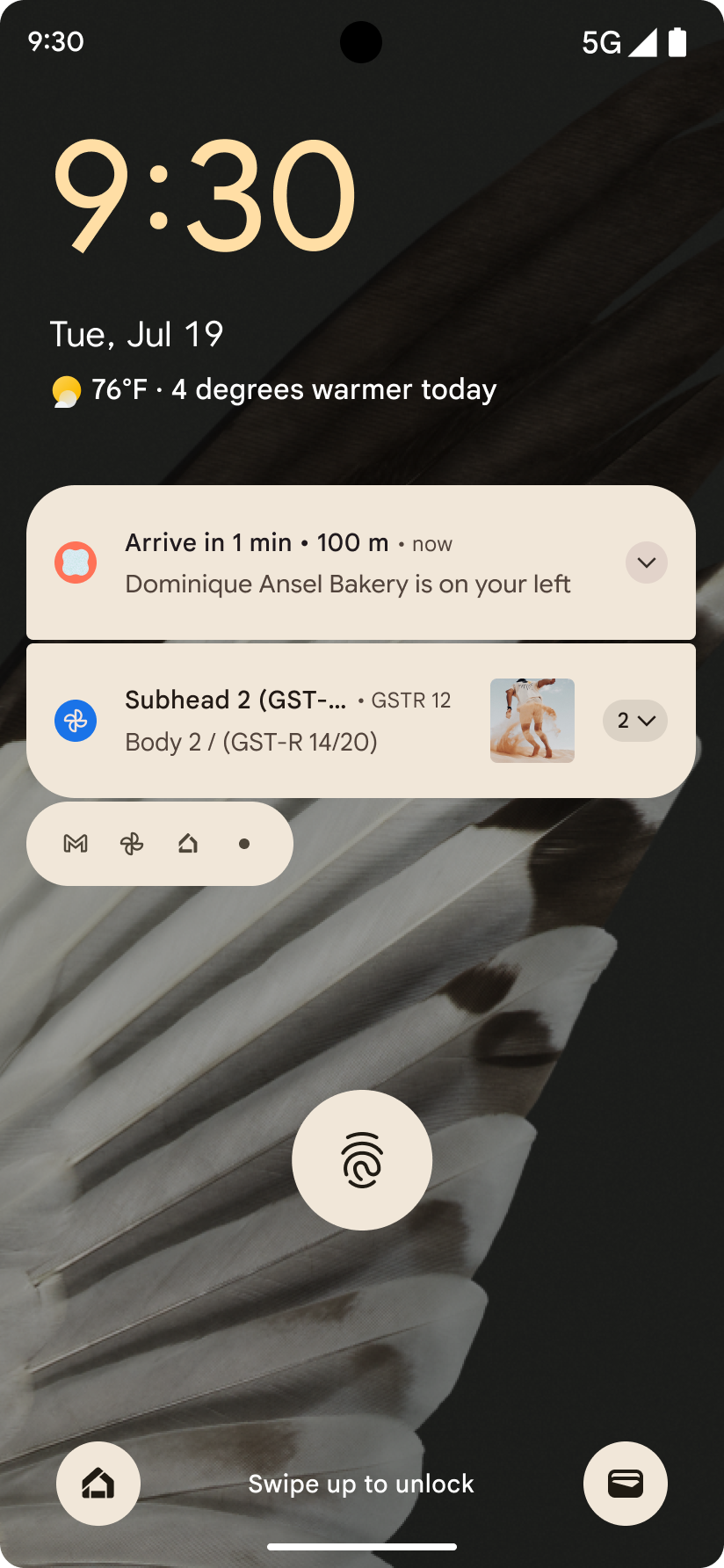
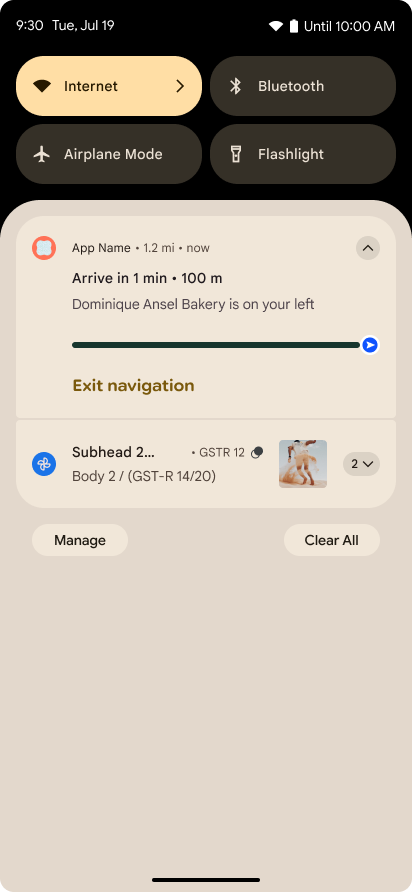
以进度为中心的通知
Android 16 引入了以进度为中心的通知,可帮助用户顺畅地跟踪用户发起的端到端历程。
Notification.ProgressStyle 是一种新的通知样式,可让您创建以进度为中心的通知。主要用例包括共享车辆、送货和导航。在 Notification.ProgressStyle 类中,您可以使用点和细分来表示用户体验历程中的状态和里程碑。
如需了解详情,请参阅以进度为中心的通知文档页面。
预测性返回更新
Android 16 添加了新 API,可帮助您在手势导航中启用预测性返回系统动画,例如“返回主屏幕”动画。通过使用新的 PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER 注册 onBackInvokedCallback,您的应用可以在系统处理返回导航时接收常规的 onBackInvoked 调用,而不会影响正常的返回导航流程。
Android 16 还添加了 finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() 和 moveTaskToBackCallback。通过向 OnBackInvokedDispatcher 注册这些回调,系统可以在调用返回手势时触发特定行为并播放相应的提前动画。
更丰富的触感反馈
自诞生之日起,Android 就提供了对触感反馈致动器的控制。
Android 11 添加了对更复杂的触感反馈效果的支持,更高级的致动器可以通过设备定义的语义基元 VibrationEffect.Compositions 支持这些效果。
Android 16 添加了触感反馈 API,让应用能够定义触感反馈效果的振幅和频率曲线,同时抽象出设备功能之间的差异。
开发者工作效率和工具
虽然我们的大部分工作都是围绕 Android Studio、Jetpack Compose 和 Android Jetpack 库等工具来提高您的工作效率,但我们始终在寻找平台中可帮助您实现愿景的方法。
动态壁纸的内容处理
在 Android 16 中,动态壁纸框架将获得一个新的 content API,以应对由用户驱动的动态壁纸带来的挑战。目前,包含用户提供的内容的实时壁纸需要复杂的服务专用实现。Android 16 引入了 WallpaperDescription 和 WallpaperInstance。借助 WallpaperDescription,您可以识别同一服务中的动态壁纸的不同实例。例如,如果某张壁纸同时在主屏幕和锁定屏幕上显示,则这两种情况下显示的内容可能各不相同。壁纸选择器和 WallpaperManager 会使用此元数据更好地向用户呈现壁纸,从而简化创建多样化个性化动态壁纸体验的过程。
性能和电池
Android 16 引入了可帮助您收集应用相关数据分析的 API。
系统触发的性能分析
ProfilingManager 在 Android 15 中添加,让应用能够在现场使用 Perfetto 请求收集性能数据。不过,由于此性能分析必须从应用启动,因此应用很难或根本无法捕获启动或 ANR 等关键流程。
为此,Android 16 向 ProfilingManager 引入了系统触发的性能分析。应用可以注册接收特定触发器(例如冷启动 reportFullyDrawn 或 ANR)轨迹的兴趣,然后系统会代表应用启动和停止轨迹。轨迹完成后,结果会传送到应用的数据目录。
ApplicationStartInfo 中的启动组件
ApplicationStartInfo 在 Android 15 中添加,可让应用查看进程启动原因、启动类型、启动时间、节流和其他实用诊断数据。Android 16 添加了 getStartComponent(),用于区分触发启动的组件类型,这有助于优化应用的启动流程。
更好地进行作业内省
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API 会返回作业可能处于待处理状态的原因。不过,作业处于待处理状态的原因可能有多种。
在 Android 16 中,我们引入了一个新 API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId),该 API 会返回作业处于待处理状态的多种原因,包括开发者设置的显式约束条件和系统设置的隐式约束条件。
我们还引入了 JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId),用于返回最新约束条件更改的列表。
我们建议您使用该 API 来调试作业可能无法执行的原因,尤其是在您发现某些任务的成功率降低或某些作业完成延迟存在 bug 时。例如,未能在后台更新微件,或在应用启动之前未能调用预加载作业。
这还有助于您更好地了解某些作业是否因系统定义的约束条件而无法完成,而不是因明确设置的约束条件而无法完成。
自动调节刷新率
Android 15 中引入的自适应刷新率 (ARR) 可让受支持硬件上的显示屏刷新率使用离散的 VSync 步长来适应内容帧速率。这不仅降低了功耗,还无需进行可能导致卡顿的模式切换。
Android 16 引入了 hasArrSupport() 和 getSuggestedFrameRate(int),同时恢复了 getSupportedRefreshRates(),以便您的应用更轻松地利用 ARR。RecyclerView 1.4 在从快速滑动或平滑滚动中稳定下来时会在内部支持 ARR,我们将继续努力,将 ARR 支持添加到更多 Jetpack 库中。这篇帧速率文章介绍了许多可用于设置帧速率的 API,以便您的应用可以直接使用 ARR。
ADPF 中的裕度 API
SystemHealthManager 引入了 getCpuHeadroom 和 getGpuHeadroom API,旨在为游戏和资源密集型应用提供可用 CPU 和 GPU 资源的估算值。通过这些方法,您可以评估应用或游戏如何以最佳方式改善系统运行状况,尤其是在与用于检测热节流的其他 Android 动态性能框架 (ADPF) API 搭配使用时。
在受支持的设备上使用 CpuHeadroomParams 和 GpuHeadroomParams,您可以自定义用于计算余量的时间范围,并在平均资源可用性或最低资源可用性之间进行选择。这有助于您相应地减少 CPU 或 GPU 资源用量,从而提升用户体验并延长电池续航时间。
无障碍
Android 16 新增了无障碍功能 API 和功能,可帮助您让所有用户都能使用您的应用。
改进了无障碍功能 API
Android 16 添加了其他 API 来增强界面语义,这有助于为依赖于无障碍服务(例如 TalkBack)的用户提高一致性。
为文字添加轮廓,以最大限度地提高文字对比度
视力较低的用户对对比度的敏感度通常较低,因此很难将对象与背景区分开来。为了帮助这些用户,Android 16 引入了轮廓文本,取代了高对比度文本,后者会在文本周围绘制较大的对比度区域,以大大提高可辨性。
Android 16 包含新的 AccessibilityManager API,可让您的应用检查或注册监听器,以查看此模式是否已启用。这主要适用于 Compose 等界面工具包,以提供类似的视觉体验。如果您维护界面工具包库,或者您的应用执行绕过 android.text.Layout 类的自定义文本渲染,则可以使用此方法来了解何时启用轮廓文本。
向 TtsSpan 添加了时长
Android 16 使用 TYPE_DURATION 扩展了 TtsSpan,其中包含 ARG_HOURS、ARG_MINUTES 和 ARG_SECONDS。这样,您就可以直接为时长添加注释,确保通过 TalkBack 等服务获得准确且一致的文本转语音输出。
支持具有多个标签的元素
Android 目前允许界面元素从其他元素派生其无障碍功能标签,现在还支持关联多个标签,这是 Web 内容中常见的情况。通过在 AccessibilityNodeInfo 中引入基于列表的 API,Android 可以直接支持这些多标签关系。在进行这项更改的过程中,我们已弃用 AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy 和 #getLabeledBy,改用 #addLabeledBy、#removeLabeledBy 和 #getLabeledByList。
改进了对可展开元素的支持
Android 16 添加了无障碍功能 API,可让您传达互动元素(例如菜单和展开式列表)的展开或收起状态。通过使用 setExpandedState 设置展开状态,并使用 CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED 内容更改类型调度 TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents,您可以确保 TalkBack 等屏幕阅读器会读出状态更改,从而提供更直观、更包容的用户体验。
不确定进度条
Android 16 添加了 RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE,让您可以为确定性和不确定性 ProgressBar 微件公开 RangeInfo,从而让 TalkBack 等服务能够更一致地为进度指示器提供反馈。
三态复选框
Android 16 中的新 AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked 和 setChecked(int) 方法现在除了“已选中”和“未选中”之外,还支持“部分选中”状态。此字段取代了已废弃的布尔值 isChecked 和 setChecked(boolean)。
补充说明
如果无障碍服务提供关于 ViewGroup 的说明,则会将来自其子视图的内容标签合并在一起。如果您为 ViewGroup 提供 contentDescription,无障碍服务会假定您还要覆盖不可聚焦的子视图的说明。如果您想为下拉菜单等内容添加标签(例如“字体系列”),同时保留当前的无障碍功能选择(例如“Roboto”),这可能会造成问题。Android 16 添加了 setSupplementalDescription,以便您提供用于提供 ViewGroup 相关信息的文本,而不会覆盖其子项中的信息。
必填表单字段
Android 16 向 AccessibilityNodeInfo 添加了 setFieldRequired,以便应用可以告知无障碍服务需要输入表单字段。对于填写各种类型表单的用户而言,这是一个重要的场景,即使是简单的必填条款及条件复选框,也能帮助用户始终如一地识别必填字段并在必填字段之间快速导航。
将手机作为 LEA 助听器的语音通话麦克风输入源
Android 16 新增了一项功能,让 LE Audio 助听器用户能够在助听器的内置麦克风和手机上的麦克风之间切换,以进行语音通话。在嘈杂的环境或助听器麦克风可能无法正常工作的其他情况下,这会很有帮助。
LEA 助听器的环境音量控制
Android 16 新增了一项功能,可让 LE Audio 助听器用户调节助听器麦克风接收的环境声音的音量。在背景噪音过大或过小的情况下,这可能会很有用。
相机
Android 16 增强了对专业相机用户的支持,允许进行混合自动曝光以及精确的色温和色调调整。新的夜间模式指示器可帮助应用了解何时切换到夜间模式相机会议,以及何时从夜间模式相机会议切换回来。新的 Intent 操作可让您更轻松地拍摄动态照片,并且我们还在不断改进 UltraHDR 图片,支持 HEIC 编码和 ISO 21496-1 草稿标准中的新参数。
混合自动曝光
Android 16 向 Camera2 添加了新的混合自动曝光模式,让您可以手动控制曝光的特定方面,同时让自动曝光 (AE) 算法处理其余部分。您可以控制 ISO + AE 和曝光时间 + AE,与当前方法(您要么完全手动控制,要么完全依赖自动曝光)相比,可提供更大的灵活性。
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
精确的色温和色调调整
Android 16 增加了对相机的精细色温和色调调整的支持,以更好地支持专业视频录制应用。在较低版本的 Android 中,您可以通过 CONTROL_AWB_MODE 控制白平衡设置,其中包含仅限于预设列表的选项,例如白炽灯、多云和黄昏。COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT 可让您使用 COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE 和 COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT 根据相关色温精确调整白平衡。
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
以下示例展示了应用不同色温和色调调整后的照片效果:





相机夜间模式场景检测
为了帮助应用了解何时切换到夜间模式相机会话以及何时从夜间模式相机会话切换出,Android 16 添加了 EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR。如果受支持,则可在 Camera2 内的 CaptureResult 中使用。
这是我们在Instagram 如何让用户拍出令人惊艳的低光照片博文中提到的即将推出的 API。该博文提供了有关如何实现夜间模式的实用指南,并附有一份案例研究,该案例研究将应用内夜间模式照片质量的提升与通过应用内相机分享的照片数量的增加联系起来。
动态照片拍摄 intent 操作
Android 16 添加了标准 intent 操作 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE 和 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE,用于请求相机应用拍摄动态照片并将其返回。
您必须传递额外的 EXTRA_OUTPUT 来控制将图片写入的位置,或者通过 Intent.setClipData(ClipData) 传递 Uri。如果您未设置 ClipData,系统会在调用 Context.startActivity(Intent) 时将其复制到该位置。
UltraHDR 图片增强功能

Android 16 继续致力于通过 UltraHDR 图片提供出色的图片质量。它添加了对 HEIC 文件格式的 UltraHDR 图片的支持。这些图片将获得 ImageFormat 类型 HEIC_ULTRAHDR,并包含类似于现有 UltraHDR JPEG 格式的嵌入式增益图。我们还在努力为 UltraHDR 添加 AVIF 支持,敬请期待。
此外,Android 16 在 UltraHDR 中实现了 ISO 21496-1 草稿标准中的其他参数,包括能够获取和设置应应用增益图算法的色彩空间,以及支持使用 SDR 增益图的 HDR 编码基础图片。
图形
Android 16 包含最新的图形改进,例如使用 AGSL 实现自定义图形效果。
使用 AGSL 实现自定义图形效果
Android 16 添加了 RuntimeColorFilter 和 RuntimeXfermode,让您可以创作阈值、Sepia 和 Hue Saturation 等复杂效果,并将其应用于绘制调用。从 Android 13 开始,您可以使用 AGSL 创建扩展 Shader 的自定义 RuntimeShader。新 API 反映了这一点,添加了由 AGSL 驱动的 RuntimeColorFilter(用于扩展 ColorFilter)和 Xfermode 效果,让您可以在源像素和目标像素之间实现基于 AGSL 的自定义合成和混合。
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
连接
Android 16 更新了平台,让您的应用能够使用通信和无线技术方面的最新进展。
测距(增强安全性)
Android 16 在搭载 Wi-Fi 6 的 802.11az 的受支持设备上为 Wi-Fi 位置信息添加了对强大的安全功能的支持,让应用能够将该协议的更高精确性、更高可伸缩性和动态调度与安全增强功能(包括基于 AES-256 的加密和防范中间人攻击)相结合。这样,在近距离使用情形(例如解锁笔记本电脑或车门)时,便可更安全地使用该功能。802.11az 与 Wi-Fi 6 标准集成,可利用其基础架构和功能实现更广泛的采用和更轻松的部署。
通用测距 API
Android 16 包含新的 RangingManager,它提供了在受支持的硬件上确定本地设备与远程设备之间的距离和角度的方法。RangingManager 支持使用各种测距技术,例如 BLE 信道声音探测、基于 BLE RSSI 的测距、超宽带和 Wi-Fi 往返时间。
配套设备管理器设备存在情况
Android 16 中引入了用于绑定配套应用服务的新 API。当 BLE 在范围内且蓝牙处于连接状态时,系统会绑定服务;当 BLE 不在范围内或蓝牙处于断开连接状态时,系统会解除绑定服务。应用将根据各种 DevicePresenceEvent 收到新的 'onDevicePresenceEvent()' 回调。如需了解详情,请参阅 'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'。
媒体
Android 16 包含多种可提升媒体体验的功能。
改进了照片选择器
照片选择器为用户提供了一种安全的内置授权方式,让用户可以向应用授予对本地存储空间和云端存储空间中所选图片和视频的访问权限,而不是对整个媒体库的访问权限。通过 Google 系统更新和 Google Play 服务组合使用模块化系统组件,该工具向后支持到 Android 4.4(API 级别 19)。只需几行代码即可与相关的 Android Jetpack 库集成。
Android 16 对照片选择器进行了以下改进:
- 嵌入式照片选择器:新 API,可让应用将照片选择器嵌入其视图层次结构中。这样,它就感觉像是应用中更为集成的一部分,同时仍可利用进程隔离功能,让用户能够选择媒体,而无需应用拥有过于宽泛的权限。为了最大限度地提高跨平台版本的兼容性并简化集成,如果您想集成嵌入式照片选择器,则需要使用即将推出的 Android Jetpack 库。
- 照片选择器中的云搜索:新的 API 可让 Android 照片选择器从云端媒体提供商中进行搜索。照片选择器中的搜索功能即将推出。
高级专业视频
Android 16 引入了对高级专业视频 (APV) 编解码器的支持,该编解码器专为专业级高品质视频录制和后期制作而设计。
APV 编解码器标准具有以下特点:
- 感知上无损的视频画质(接近原始视频画质)
- 复杂度低且吞吐量高的仅帧内编码(无像素域预测),以更好地支持编辑工作流
- 支持高比特率范围(最高几十 Gbps),适用于 2K、4K 和 8K 分辨率内容,由轻量级熵编码方案实现
- 帧平铺,用于沉浸式内容和启用并行编码和解码
- 支持各种色度采样格式和位深
- 支持多次解码和重新编码,且不会严重降低视觉质量
- 支持多视图视频和辅助视频,例如深度、Alpha 和预览
- 支持 HDR10/10+ 和用户定义的元数据
OpenAPV 项目提供了 APV 的参考实现。Android 16 将实现对 APV 422-10 配置文件的支持,该配置文件提供 YUV 422 色彩采样以及 10 位编码,并且目标比特率最高可达 2 Gbps。
隐私权
Android 16 包含多种有助于应用开发者保护用户隐私的功能。
健康数据共享更新
Health Connect 添加了 ACTIVITY_INTENSITY,这是一种根据世界卫生组织关于中等强度和剧烈强度活动的指南定义的数据类型。每个记录都需要提供开始时间、结束时间以及活动强度(中等或剧烈)。
Health Connect 还包含支持医疗记录的更新版 API。这样一来,应用便可在征得用户明确同意的情况下,读取和写入 FHIR 格式的医疗记录。
Privacy Sandbox on Android
Android 16 中集成了最新版本的 Privacy Sandbox on Android,这是我们持续致力于开发可让用户放心地知道其隐私受到保护的技术的一部分。您可以访问我们的网站,详细了解 Privacy Sandbox on Android 开发者 Beta 版计划,以便顺利上手。不妨了解 SDK 运行时,它可让 SDK 在与其所服务的应用分离的专用运行时环境中运行,从而为用户数据收集和共享提供更强的保护措施。
安全
Android 16 包含有助于增强应用安全性并保护应用数据的功能。
密钥共享 API
Android 16 添加了一些 API,这些 API 支持与其他应用共享对 Android Keystore 密钥的访问权限。新的 KeyStoreManager 类支持按应用 uid 授予和撤消对密钥的访问权限,并包含一个供应用访问共享密钥的 API。
设备规格
Android 16 为您的应用提供支持,让您充分利用 Android 的设备类型。
电视的标准化画质和音质框架
Android 16 中的新 MediaQuality 软件包公开了一组标准化 API,用于访问音频和图片配置文件以及与硬件相关的设置。这样,在线播放应用就可以查询配置文件并将其动态应用于媒体:
- 使用更大动态范围进行母版制作的电影需要更高的色彩准确度,才能看清阴影中的细微细节并根据环境光线进行调整,因此,最好使用色彩准确度优先于亮度的配置文件。
- 体育赛事直播通常采用较窄的动态范围进行母版制作,但通常是在白天观看,因此偏向亮度而非色彩准确度的配置文件可以获得更好的效果。
- 完全交互式内容需要尽可能减少处理以缩短延迟时间,并且需要更高的帧速率,因此许多电视都附带游戏配置文件。
借助此 API,应用可以在个人资料之间切换,用户可以享受调整支持的电视,以便尽可能适合其内容。
国际化
Android 16 添加了多项功能,可在设备以不同语言使用时提升用户体验。
竖排文字
Android 16 添加了对垂直渲染和测量文本的低级支持,以便为库开发者提供基本的垂直书写支持。这对于日语等通常使用竖向书写系统的语言特别有用。Paint 类中添加了一个新标志 VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG。使用 Paint.setFlags 设置此标志后,Paint 的文本测量 API 将报告垂直进度,而不是水平进度,并且 Canvas 将垂直绘制文本。
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
自定义度量制
用户现在可以在“设置”中的地区偏好设置中自定义测量系统。用户偏好设置包含在语言区域代码中,因此您可以在 ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED 上注册 BroadcastReceiver,以便在地区偏好设置发生更改时处理语言区域配置更改。
使用格式设置程序有助于提供符合当地体验的服务。例如,对于将手机设置为英语(丹麦)或将手机设置为英语(美国)并将公制作为首选测量系统的用户,“0.5 in”的英语(美国)对应于“12,7 mm”。
如需找到这些设置,请打开“设置”应用,然后依次前往系统 > 语言和地区。
