หากต้องการเข้าถึงโมเดล Gemini Pro และ Flash เราขอแนะนำให้นักพัฒนาแอป Android ใช้ Gemini Developer API โดยใช้ตรรกะ AI ของ Firebase ช่วยให้คุณเริ่มต้นใช้งานได้ โดยไม่ต้องใช้บัตรเครดิต และมีระดับฟรีที่ให้โควต้าอย่างมาก เมื่อ ตรวจสอบการผสานรวมกับฐานผู้ใช้ขนาดเล็กแล้ว คุณจะขยายขนาดได้โดยเปลี่ยนไปใช้ ระดับแบบชำระเงิน

เริ่มต้นใช้งาน
ก่อนที่จะโต้ตอบกับ Gemini API โดยตรงจากแอป คุณจะต้องทำสิ่งต่อไปนี้ก่อน ซึ่งรวมถึงการทำความคุ้นเคยกับการแจ้ง รวมถึง การตั้งค่า Firebase และแอปเพื่อใช้ SDK
ทดลองใช้พรอมต์
การทดลองใช้พรอมต์จะช่วยให้คุณค้นหาวลี เนื้อหา และรูปแบบที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับแอป Android ของคุณได้ Google AI Studio คือ IDE ที่คุณใช้สร้างต้นแบบและออกแบบพรอมต์สำหรับกรณีการใช้งานของแอปได้
การสร้างพรอมต์ที่เหมาะสมกับกรณีการใช้งานของคุณเป็นศิลปะมากกว่าวิทยาศาสตร์ ซึ่ง ทำให้การทดลองเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการแจ้งได้ในเอกสารประกอบของ Firebase
เมื่อพอใจกับพรอมต์แล้ว ให้คลิกปุ่ม "<>" เพื่อรับ ข้อมูลโค้ดที่คุณเพิ่มลงในโค้ดได้
ตั้งค่าโปรเจ็กต์ Firebase และเชื่อมต่อแอปกับ Firebase
เมื่อพร้อมที่จะเรียกใช้ API จากแอปแล้ว ให้ทําตามวิธีการใน "ขั้นตอนที่ 1" ของคู่มือเริ่มต้นใช้งานตรรกะ AI ของ Firebase เพื่อตั้งค่า Firebase และ SDK ในแอป
เพิ่มการขึ้นต่อกันของ Gradle
เพิ่มทรัพยากร Dependency ของ Gradle ต่อไปนี้ลงในโมดูลแอป
Kotlin
dependencies {
// ... other androidx dependencies
// Import the BoM for the Firebase platform
implementation(platform("com.google.firebase:firebase-bom:34.2.0"))
// Add the dependency for the Firebase AI Logic library When using the BoM,
// you don't specify versions in Firebase library dependencies
implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-ai")
}
Java
dependencies {
// Import the BoM for the Firebase platform
implementation(platform("com.google.firebase:34.2.0"))
// Add the dependency for the Firebase AI Logic library When using the BoM,
// you don't specify versions in Firebase library dependencies
implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-ai")
// Required for one-shot operations (to use `ListenableFuture` from Guava
// Android)
implementation("com.google.guava:guava:31.0.1-android")
// Required for streaming operations (to use `Publisher` from Reactive
// Streams)
implementation("org.reactivestreams:reactive-streams:1.0.4")
}
เริ่มต้นโมเดล Generative
เริ่มต้นด้วยการสร้างอินสแตนซ์ของ GenerativeModel และระบุชื่อโมเดล
Kotlin
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash")
Java
GenerativeModel firebaseAI = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash");
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(firebaseAI);
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโมเดลที่พร้อมใช้งานสำหรับใช้กับ Gemini Developer API นอกจากนี้ คุณยังดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์โมเดลได้ด้วย
โต้ตอบกับ Gemini Developer API จากแอป
เมื่อตั้งค่า Firebase และแอปให้ใช้ SDK แล้ว คุณก็พร้อมที่จะ โต้ตอบกับ Gemini Developer API จากแอป
สร้างข้อความ
หากต้องการสร้างคำตอบเป็นข้อความ ให้เรียกใช้ generateContent() พร้อมพรอมต์ของคุณ
Kotlin
scope.launch {
val response = model.generateContent("Write a story about a magic backpack.")
}
Java
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText("Write a story about a magic backpack.")
.build();
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
String resultText = result.getText();
[...]
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
สร้างข้อความจากรูปภาพและสื่ออื่นๆ
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังสร้างข้อความจากพรอมต์ที่มีข้อความและรูปภาพหรือสื่ออื่นๆ ได้ด้วย
เมื่อโทรหา generateContent() คุณจะส่งสื่อเป็นข้อมูลแบบอินไลน์ได้
เช่น หากต้องการใช้บิตแมป ให้ใช้ประเภทเนื้อหา image ดังนี้
Kotlin
scope.launch {
val response = model.generateContent(
content {
image(bitmap)
text("what is the object in the picture?")
}
)
}
Java
Content content = new Content.Builder()
.addImage(bitmap)
.addText("what is the object in the picture?")
.build();
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(content);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
String resultText = result.getText();
[...]
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
หากต้องการส่งไฟล์เสียง ให้ใช้inlineDataประเภทเนื้อหาต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
val contentResolver = applicationContext.contentResolver
val inputStream = contentResolver.openInputStream(audioUri).use { stream ->
stream?.let {
val bytes = stream.readBytes()
val prompt = content {
inlineData(bytes, "audio/mpeg") // Specify the appropriate audio MIME type
text("Transcribe this audio recording.")
}
val response = model.generateContent(prompt)
}
}
Java
ContentResolver resolver = getApplicationContext().getContentResolver();
try (InputStream stream = resolver.openInputStream(audioUri)) {
File audioFile = new File(new URI(audioUri.toString()));
int audioSize = (int) audioFile.length();
byte audioBytes = new byte[audioSize];
if (stream != null) {
stream.read(audioBytes, 0, audioBytes.length);
stream.close();
// Provide a prompt that includes audio specified earlier and text
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addInlineData(audioBytes, "audio/mpeg") // Specify the appropriate audio MIME type
.addText("Transcribe what's said in this audio recording.")
.build();
// To generate text output, call `generateContent` with the prompt
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
String text = result.getText();
Log.d(TAG, (text == null) ? "" : text);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to generate a response", t);
}
}, executor);
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Error getting input stream for file.");
// Handle the error appropriately
}
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read the audio file", e);
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Invalid audio file", e);
}
หากต้องการระบุไฟล์วิดีโอ ให้ใช้inlineDataประเภทเนื้อหาต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
val contentResolver = applicationContext.contentResolver
contentResolver.openInputStream(videoUri).use { stream ->
stream?.let {
val bytes = stream.readBytes()
val prompt = content {
inlineData(bytes, "video/mp4") // Specify the appropriate video MIME type
text("Describe the content of this video")
}
val response = model.generateContent(prompt)
}
}
Java
ContentResolver resolver = getApplicationContext().getContentResolver();
try (InputStream stream = resolver.openInputStream(videoUri)) {
File videoFile = new File(new URI(videoUri.toString()));
int videoSize = (int) videoFile.length();
byte[] videoBytes = new byte[videoSize];
if (stream != null) {
stream.read(videoBytes, 0, videoBytes.length);
stream.close();
// Provide a prompt that includes video specified earlier and text
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addInlineData(videoBytes, "video/mp4")
.addText("Describe the content of this video")
.build();
// To generate text output, call generateContent with the prompt
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
String resultText = result.getText();
System.out.println(resultText);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ในทำนองเดียวกัน คุณยังส่งเอกสาร PDF (application/pdf) และข้อความธรรมดา
(text/plain) ได้ด้วยการส่งประเภท MIME ที่เกี่ยวข้องเป็นพารามิเตอร์
แชทหลายรอบ
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังรองรับการสนทนาแบบหลายรอบได้ด้วย เริ่มต้นแชทด้วยฟังก์ชัน
startChat() คุณเลือกให้โมเดลมีประวัติข้อความได้
จากนั้นเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน sendMessage() เพื่อส่งข้อความแชท
Kotlin
val chat = model.startChat(
history = listOf(
content(role = "user") { text("Hello, I have 2 dogs in my house.") },
content(role = "model") { text("Great to meet you. What would you like to know?") }
)
)
scope.launch {
val response = chat.sendMessage("How many paws are in my house?")
}
Java
Content.Builder userContentBuilder = new Content.Builder();
userContentBuilder.setRole("user");
userContentBuilder.addText("Hello, I have 2 dogs in my house.");
Content userContent = userContentBuilder.build();
Content.Builder modelContentBuilder = new Content.Builder();
modelContentBuilder.setRole("model");
modelContentBuilder.addText("Great to meet you. What would you like to know?");
Content modelContent = userContentBuilder.build();
List<Content> history = Arrays.asList(userContent, modelContent);
// Initialize the chat
ChatFutures chat = model.startChat(history);
// Create a new user message
Content.Builder messageBuilder = new Content.Builder();
messageBuilder.setRole("user");
messageBuilder.addText("How many paws are in my house?");
Content message = messageBuilder.build();
// Send the message
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = chat.sendMessage(message);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
String resultText = result.getText();
System.out.println(resultText);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
สร้างรูปภาพ
โมเดลรูปภาพ Gemini 2.5 Flash (หรือที่เรียกว่า Nano Banana) สามารถสร้างและแก้ไข รูปภาพโดยใช้ความรู้และการให้เหตุผลเกี่ยวกับโลก โดยจะสร้างรูปภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องตามบริบท ผสานรวมหรือแทรกสลับเอาต์พุตข้อความและรูปภาพได้อย่างราบรื่น นอกจากนี้ยังสร้างภาพที่แม่นยำด้วยลำดับข้อความยาวๆ และรองรับการแก้ไขรูปภาพแบบสนทนาในขณะที่ยังคงบริบทไว้
คุณสามารถใช้โมเดล Imagen แทน Gemini ได้ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งสำหรับการสร้างรูปภาพคุณภาพสูงที่ต้องใช้ความสมจริงระดับภาพถ่าย รายละเอียดทางศิลปะ หรือสไตล์ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง อย่างไรก็ตาม สำหรับกรณีการใช้งานฝั่งไคลเอ็นต์ส่วนใหญ่สำหรับแอป Android นั้น Gemini จะมีประสิทธิภาพเพียงพอ
คู่มือนี้อธิบายวิธีใช้โมเดลรูปภาพ Gemini 2.5 Flash โดยใช้ Firebase AI Logic SDK สำหรับ Android ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการสร้างรูปภาพด้วย Gemini ได้ในเอกสารประกอบสร้างรูปภาพด้วย Gemini ใน Firebase หากสนใจใช้โมเดล Imagen โปรดดูเอกสารประกอบ
เริ่มต้นโมเดล Generative
สร้างอินสแตนซ์ของ GenerativeModel และระบุชื่อโมเดล
gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview ตรวจสอบว่าคุณกำหนดค่า responseModalities
ให้มีทั้ง TEXT และ IMAGE
Kotlin
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview",
// Configure the model to respond with text and images (required)
generationConfig = generationConfig {
responseModalities = listOf(ResponseModality.TEXT,
ResponseModality.IMAGE)
}
)
Java
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
"gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview",
// Configure the model to respond with text and images (required)
new GenerationConfig.Builder()
.setResponseModalities(Arrays.asList(ResponseModality.TEXT, ResponseModality.IMAGE))
.build()
);
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
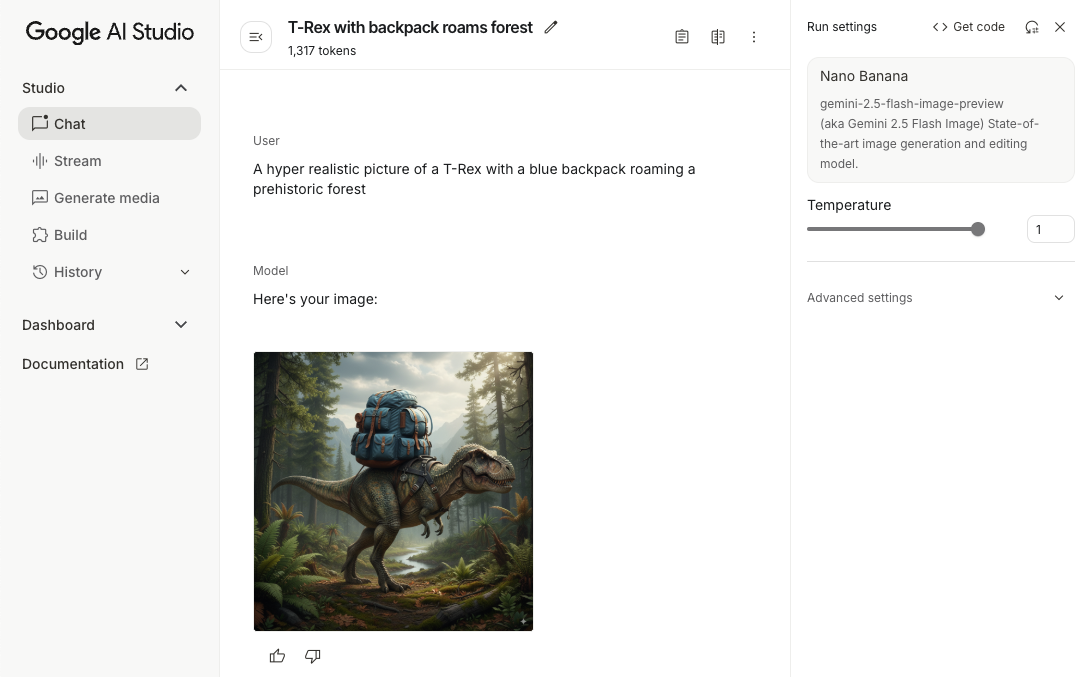
สร้างรูปภาพ (ป้อนข้อความเท่านั้น)
คุณสั่งให้โมเดล Gemini สร้างรูปภาพได้โดยระบุพรอมต์ที่เป็นข้อความเท่านั้น
Kotlin
// Provide a text prompt instructing the model to generate an image
val prompt = "A hyper realistic picture of a t-rex with a blue bag pack roaming a pre-historic forest."
// To generate image output, call `generateContent` with the text input
val generatedImageAsBitmap = model.generateContent(prompt)
.candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>()
.firstOrNull()?.image
Java
// Provide a text prompt instructing the model to generate an image
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText("Generate an image of the Eiffel Tower with fireworks in the background.")
.build();
// To generate an image, call `generateContent` with the text input
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
// iterate over all the parts in the first candidate in the result object
for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) {
if (part instanceof ImagePart) {
ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part;
// The returned image as a bitmap
Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage();
break;
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
แก้ไขรูปภาพ (ข้อความและรูปภาพที่ป้อน)
คุณขอให้โมเดล Gemini แก้ไขรูปภาพที่มีอยู่ได้โดยระบุทั้งข้อความและ รูปภาพอย่างน้อย 1 รูปในพรอมต์
Kotlin
// Provide an image for the model to edit
val bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.resources, R.drawable.scones)
// Provide a text prompt instructing the model to edit the image
val prompt = content {
image(bitmap)
text("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon")
}
// To edit the image, call `generateContent` with the prompt (image and text input)
val generatedImageAsBitmap = model.generateContent(prompt)
.candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image
// Handle the generated text and image
Java
// Provide an image for the model to edit
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, R.drawable.scones);
// Provide a text prompt instructing the model to edit the image
Content promptcontent = new Content.Builder()
.addImage(bitmap)
.addText("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon")
.build();
// To edit the image, call `generateContent` with the prompt (image and text input)
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(promptcontent);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
// iterate over all the parts in the first candidate in the result object
for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) {
if (part instanceof ImagePart) {
ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part;
Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage();
break;
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
ทำซ้ำและแก้ไขรูปภาพผ่านการแชทแบบหลายรอบ
หากต้องการใช้การแก้ไขรูปภาพแบบสนทนา คุณสามารถใช้แชทหลายรอบได้ ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ส่งคำขอติดตามเพื่อปรับแต่งการแก้ไขได้โดยไม่ต้องส่งรูปภาพต้นฉบับอีกครั้ง
ก่อนอื่น ให้เริ่มต้นแชทกับ startChat() โดยอาจระบุประวัติการแชทด้วย
จากนั้นใช้ sendMessage() สำหรับข้อความถัดไป
Kotlin
// Provide an image for the model to edit
val bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.resources, R.drawable.scones)
// Create the initial prompt instructing the model to edit the image
val prompt = content {
image(bitmap)
text("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon")
}
// Initialize the chat
val chat = model.startChat()
// To generate an initial response, send a user message with the image and text prompt
var response = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
// Inspect the returned image
var generatedImageAsBitmap = response
.candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image
// Follow up requests do not need to specify the image again
response = chat.sendMessage("But make it old-school line drawing style")
generatedImageAsBitmap = response
.candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image
Java
// Provide an image for the model to edit
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, R.drawable.scones);
// Initialize the chat
ChatFutures chat = model.startChat();
// Create the initial prompt instructing the model to edit the image
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.setRole("user")
.addImage(bitmap)
.addText("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon")
.build();
// To generate an initial response, send a user message with the image and text prompt
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = chat.sendMessage(prompt);
// Extract the image from the initial response
ListenableFuture<@Nullable Bitmap> initialRequest = Futures.transform(response,
result -> {
for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) {
if (part instanceof ImagePart) {
ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part;
return imagePart.getImage();
}
}
return null;
}, executor);
// Follow up requests do not need to specify the image again
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync(
initialRequest,
generatedImage -> {
Content followUpPrompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText("But make it old-school line drawing style")
.build();
return chat.sendMessage(followUpPrompt);
}, executor);
// Add a final callback to check the reworked image
Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) {
if (part instanceof ImagePart) {
ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part;
Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage();
break;
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำและข้อจำกัด
- รูปแบบเอาต์พุต: ระบบจะสร้างรูปภาพเป็น PNG โดยมีขนาดสูงสุด 1024 พิกเซล
- ประเภทอินพุต: โมเดลไม่รองรับอินพุตเสียงหรือวิดีโอสำหรับการสร้างรูปภาพ
- การรองรับภาษา: เพื่อให้ได้ประสิทธิภาพสูงสุด ให้ใช้ภาษาต่อไปนี้
อังกฤษ (
en), สเปน (เม็กซิโก) (es-mx), ญี่ปุ่น (ja-jp), จีนตัวย่อ (zh-cn) และฮินดี (hi-in) - ปัญหาการสร้าง
- การสร้างรูปภาพอาจไม่ทำงานเสมอไป และบางครั้งอาจแสดงผลเป็นข้อความเท่านั้น ลองขอเอาต์พุตรูปภาพอย่างชัดเจน (เช่น "สร้างรูปภาพ" "ใส่รูปภาพไปเรื่อยๆ" "อัปเดตรูปภาพ")
- โมเดลอาจหยุดสร้างกลางคัน ลองอีกครั้งหรือลองใช้พรอมต์อื่น
- โมเดลอาจสร้างข้อความเป็นรูปภาพ ลองขอเอาต์พุตข้อความ อย่างชัดเจน (เช่น "สร้างข้อความบรรยายพร้อมภาพ")
ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมได้ในเอกสารประกอบของ Firebase
ขั้นตอนถัดไป
- ดูแอปตัวอย่างของ Firebase สำหรับการเริ่มต้นใช้งาน Android อย่างรวดเร็วและ แคตตาล็อกตัวอย่าง AI ของ Android ใน GitHub
- เตรียมแอปสำหรับการใช้งานจริง รวมถึงตั้งค่า Firebase App Check เพื่อปกป้อง Gemini API จากการละเมิดโดย ไคลเอ็นต์ที่ไม่ได้รับอนุญาต
- ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับตรรกะ AI ของ Firebase ในเอกสารประกอบของ Firebase

