和先前版本一樣,Android 16 也包含可能會影響應用程式的行為變更。以下行為變更僅適用於指定 Android 16 以上版本的應用程式。如果您的應用程式指定 Android 16 以上版本,建議您視情況修改應用程式,以支援這些行為。
此外,無論應用程式的 targetSdkVersion 為何,請務必查看對所有 Android 16 應用程式有影響的行為變更清單。
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列變更,旨在打造更一致、直覺的使用者體驗。
無邊框設計停用選項即將移除
Android 15 對以 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 為目標版本的應用程式強制執行無邊框設計,但您的應用程式可以將 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 設為 true,選擇不採用這項設計。如果應用程式指定 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 為目標版本,系統會淘汰並停用 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement,且應用程式無法選擇不採用無邊框設計。
- 如果應用程式指定 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 版本為目標,且在 Android 15 裝置上執行,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement仍可正常運作。 - 如果應用程式指定 Android 16 (API 級別 36),且在 Android 16 裝置上執行,系統會停用
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement。
如要在 Android 16 中進行測試,請確保應用程式支援無邊框設計,並移除所有 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 的使用情形,讓應用程式在 Android 15 裝置上也能支援無邊框設計。如要支援無邊框設計,請參閱 Compose 和 Views 指南。
如要使用預測返回手勢,必須遷移或選擇停用
如果應用程式指定 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 以上版本,且在搭載 Android 16 以上版本的裝置上執行,系統會預設啟用預測返回系統動畫 (返回首頁、跨工作和跨活動)。此外,系統不會再呼叫 onBackPressed,也不會再分派 KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK。
如果應用程式會攔截返回事件,且您尚未遷移至預測返回手勢,請更新應用程式以使用支援的返回導覽 API,或在應用程式 AndroidManifest.xml 檔案的 <application> 或 <activity> 標記中,將 android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback 屬性設為 false,暫時停用這項功能。
已淘汰並停用 Elegant 字型 API
指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 的應用程式會預設將 elegantTextHeight
TextView 屬性設為 true,以更易於閱讀的字型取代精簡字型。您可以將 elegantTextHeight 屬性設為 false,藉此覆寫這項設定。
Android 16 會淘汰 elegantTextHeight 屬性,應用程式指定 Android 16 後,系統就會忽略該屬性。這些 API 控制的「UI 字型」即將停用,因此請調整所有版面配置,確保阿拉伯文、寮文、緬甸文、泰米爾文、古吉拉特文、卡納達文、馬拉雅拉姆文、奧里亞文、泰盧固文或泰文的文字顯示方式一致,且日後不會出錯。
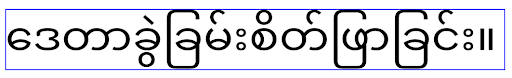 針對指定 Android 14 (API 級別 34) 以下版本的應用程式,或指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 但將
針對指定 Android 14 (API 級別 34) 以下版本的應用程式,或指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 但將 elegantTextHeight 屬性設為 false,藉此覆寫預設行為的應用程式,elegantTextHeight 行為如下: 如果應用程式指定 Android 16 (API 級別 36),或指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 但未將
如果應用程式指定 Android 16 (API 級別 36),或指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 但未將 elegantTextHeight 屬性設為 false 來覆寫預設值,則會採用 elegantTextHeight 行為。核心功能
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列變更,可修改或擴充 Android 系統的各種核心功能。
固定費率工作排程最佳化
在指定 Android 16 之前,如果 scheduleAtFixedRate 因不在有效的程序生命週期中而錯過執行工作,則應用程式返回有效生命週期時,所有錯過的執行作業會立即執行。
針對 Android 16 進行指定時,應用程式返回有效生命週期時,最多會立即執行 一次遺漏的 scheduleAtFixedRate 執行作業。這項行為異動預計可改善應用程式效能。在應用程式中測試這項行為,確認應用程式是否受到影響。您也可以使用應用程式相容性架構,並啟用 STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS 相容性標記來進行測試。
裝置板型規格
在大型螢幕裝置上顯示時,Android 16 (API 級別 36) 會對應用程式進行下列變更。
自動調整式版面配置
Android 應用程式現在可在各種裝置上執行 (例如手機、平板電腦、折疊式裝置、桌機、車輛和電視),並支援大螢幕上的視窗模式 (例如分割畫面和電腦視窗),因此開發人員應建構可配合任何螢幕和視窗大小調整的 Android 應用程式,無論裝置螢幕方向為何。在現今多裝置的世界中,限制螢幕方向和大小調整等範例過於嚴苛。
忽略螢幕方向、是否可調整大小和顯示比例限制
如果應用程式指定 Android 16 (API 級別 36),螢幕方向、大小調整和螢幕比例限制將不再適用於最小寬度 >= 600 dp 的螢幕。無論顯示比例或使用者偏好的螢幕方向為何,應用程式都會填滿整個顯示視窗,且不會出現側邊黑邊。
這項異動會導入新的標準平台行為。Android 正在朝向某種模式發展,預計應用程式將能適應各種螢幕方向、顯示大小和顯示比例。如果應用程式設有固定螢幕方向或大小調整限制,就無法適應各種裝置。讓應用程式具備適應性,提供最佳使用者體驗。
您也可以使用應用程式相容性架構,並啟用 UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT 相容性標記,測試這項行為。
常見的破壞性變更
忽略方向、可調整大小和長寬比限制,可能會影響應用程式在某些裝置上的 UI,尤其是專為鎖定直向的小版面配置設計的元素,例如版面配置遭到延展,以及動畫和元件超出螢幕範圍等問題。如果對顯示比例或螢幕方向做出任何假設,可能會導致應用程式出現視覺問題。請參閱這篇文章,進一步瞭解如何避免這類問題,並改善應用程式的適應性行為。
允許裝置旋轉會導致更多活動重建,如果未妥善保留,可能會導致使用者狀態遺失。如要瞭解如何正確儲存 UI 狀態,請參閱「儲存 UI 狀態」。
導入作業詳細資料
在全螢幕和多視窗模式下,大型螢幕裝置會忽略下列資訊清單屬性和執行階段 API:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
系統會忽略 screenOrientation、setRequestedOrientation() 和 getRequestedOrientation() 的下列值:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
就螢幕大小調整功能而言,android:resizeableActivity="false"、android:minAspectRatio 和 android:maxAspectRatio 不會產生任何影響。
如果應用程式以 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 為目標,系統預設會忽略大螢幕上的應用程式方向、大小調整和長寬比限制,但每個尚未完全準備就緒的應用程式都可以暫時選擇停用這項行為 (這會導致應用程式進入相容性模式)。
例外狀況
在下列情況中,Android 16 的螢幕方向、大小調整和長寬比限制不適用:
- 遊戲 (根據
android:appCategory旗標) - 使用者在裝置的顯示比例設定中,明確選擇採用應用程式的預設行為
- 小於
sw600dp的螢幕
暫時退出
如要停用特定活動,請宣告 PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY 資訊清單屬性:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
如果應用程式有太多部分尚未支援 Android 16,您可以在應用程式層級套用相同屬性,完全停用這項功能:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
健康與健身
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列與健康和健身資料相關的變更。
健康與健身權限
如果應用程式是以 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 以上版本為目標,BODY_SENSORS 權限會使用 android.permissions.health 底下更精細的權限,健康資料同步也會使用這些權限。自 Android 16 起,凡是先前需要 BODY_SENSORS 或 BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND 的 API,現在都需要對應的 android.permissions.health 權限。這會影響下列資料類型、API 和前景服務類型:
HEART_RATE_BPM從 Wear OS 上的健康照護服務Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE(來自 Android 感應器管理員)heartRateAccuracy和heartRateBpm從 Wear OS 上的ProtoLayout移除FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH,必須使用相應的android.permission.health權限,而非BODY_SENSORS
如果應用程式使用這些 API,就應要求對應的精細權限:
- 如要監控使用中的心率、血氧濃度或皮膚溫度:
請要求
android.permissions.health下的精細權限,例如READ_HEART_RATE,而非BODY_SENSORS。 - 如要存取背景感應器,請要求
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND,而非BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND。
這些權限與保護「健康資料同步」資料讀取權限相同,後者是 Android 的健康、健身和保健資料儲存空間。
行動應用程式
如果行動應用程式改用 READ_HEART_RATE 和其他細部權限,也必須宣告活動,才能顯示應用程式的隱私權政策。這與健康資料同步的規定相同。
連線能力
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含藍牙堆疊的下列變更,可提升與周邊裝置的連線能力。
處理債券遺失和加密變更的新意圖
除了改善連結遺失處理功能,Android 16 也推出了 2 個新的意圖,讓應用程式更能察覺連結遺失和加密變更。
鎖定 Android 16 的應用程式現在可以:
- 在偵測到遠端連結中斷時接收
ACTION_KEY_MISSING意圖,以便提供更有用的使用者意見回饋,並採取適當行動。 - 每當連結的加密狀態變更時,就會收到
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE意圖。包括加密狀態變更、加密演算法變更和加密金鑰大小變更。如果應用程式稍後收到ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE意圖,且連結已成功加密,則必須考慮恢復連結。
因應不同原始設備製造商 (OEM) 實作
雖然 Android 16 推出了這些新意圖,但不同裝置製造商 (OEM) 的實作和廣播方式可能有所不同。為確保應用程式可在所有裝置上提供一致且可靠的體驗,開發人員應設計連結中斷處理機制,以便妥善因應這些潛在的變化。
我們建議您採用下列應用程式行為:
如果廣播
ACTION_KEY_MISSING意圖:系統會中斷 ACL (非同步無連結) 連結,但會保留裝置的連結資訊 (如這裡所述)。
應用程式應使用這個意圖做為偵測連結中斷的主要信號,並在啟動裝置忘記或重新配對功能前,引導使用者確認遠端裝置是否在範圍內。
如果裝置在收到
ACTION_KEY_MISSING後中斷連線,應用程式應謹慎重新連線,因為裝置可能已不再與系統綁定。如果
ACTION_KEY_MISSING意圖未廣播:ACL 連結會保持連線狀態,系統會移除裝置的連結資訊,這與 Android 15 的行為相同。
在這種情況下,應用程式應繼續使用與先前 Android 版本相同的現有連結失效處理機制,以偵測及管理連結失效事件。
移除藍牙配對的新方式
所有以 Android 16 為目標版本的應用程式,現在都能使用 CompanionDeviceManager 中的公開 API 解除配對藍牙裝置。如果隨附裝置是以 CDM 關聯方式管理,應用程式可以在關聯裝置上使用新的 removeBond(int) API 觸發藍牙連結移除作業。應用程式可以監控連結狀態變更,方法是監聽藍牙裝置廣播事件 ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED。
安全性
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列安全性異動。
MediaStore 版本鎖定
針對指定 Android 16 以上版本的應用程式,MediaStore#getVersion() 現已成為每個應用程式的專屬值。這麼做可移除版本字串中的識別屬性,以免遭到濫用,並防止用於指紋辨識技術。應用程式不應對此版本的格式做出任何假設。應用程式在使用此 API 時應已處理版本變更,且在大多數情況下,不必變更目前的行為,除非開發人員嘗試推斷超出此 API 預期範圍的其他資訊。
更安全的意圖
「更安全的意圖」功能是一項多階段安全防護計畫,旨在提升 Android 意圖解析機制的安全性。目標是在意圖處理期間新增檢查,並篩除不符合特定條件的意圖,藉此保護應用程式免於惡意行為。
Android 15 的這項功能著重於傳送應用程式,現在 Android 16 則將控制權轉移至接收應用程式,讓開發人員使用應用程式資訊清單選擇加入嚴格的 Intent 解析。
我們將實施兩項重大變更:
明確意圖必須符合目標元件的意圖篩選器:如果意圖明確指定元件,就應符合該元件的意圖篩選器。
沒有動作的意圖無法與任何意圖篩選器相符:如果意圖未指定動作,就不應解析至任何意圖篩選器。
這些變更只會在涉及多個應用程式時生效,不會影響單一應用程式內的意圖處理程序。
影響
由於這項功能採選擇啟用制,開發人員必須在應用程式資訊清單中明確啟用,才會生效。因此,這項功能只會影響開發人員符合下列條件的應用程式:
- 瞭解 Safer Intents 功能及其優點。
- 主動選擇在應用程式中採用更嚴格的意圖處理做法。
這種選擇加入的做法可盡量避免現有應用程式中斷運作,因為這些應用程式可能依賴目前安全性較低的意圖解析行為。
雖然 Safer Intents 計畫在 Android 16 的初期影響可能有限,但我們已規劃好發展藍圖,未來將在 Android 版本中擴大影響力。我們最終會將嚴格意圖解析設為預設行為。
Safer Intents 功能可讓惡意應用程式更難以利用意圖解析機制中的漏洞,因此有助於大幅提升 Android 生態系統的安全性。
不過,為解決現有應用程式的潛在相容性問題,我們必須謹慎管理停用和強制執行的過渡期。
實作
開發人員必須在應用程式資訊清單中使用 intentMatchingFlags 屬性,明確啟用更嚴格的意圖比對。以下範例說明如何為整個應用程式啟用這項功能,但對接收器停用/停用這項功能:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
支援的旗標詳細資訊:
| 旗標名稱 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | 對傳入的意圖強制執行更嚴格的比對作業 |
| none | 停用所有傳入意圖的特殊比對規則。指定多個旗標時,系統會優先採用「none」旗標,解決值衝突的問題 |
| allowNullAction | 放寬比對規則,允許比對沒有動作的意圖。這個旗標應與「enforceIntentFilter」搭配使用,以達成特定行為 |
測試與偵錯
強制執行機制啟動後,如果意圖呼叫端已正確填入意圖,應用程式應可正常運作。不過,遭封鎖的意圖會觸發警告記錄訊息,例如 "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" 和 "Access blocked:",並附上 "PackageManager." 標記。這表示可能存在影響應用程式的問題,需要特別注意。
Logcat 篩選器:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU 系統呼叫篩選
為強化 Mali GPU 介面,我們已在正式版中封鎖已淘汰或僅供 GPU 開發使用的 Mali GPU IOCTL。此外,用於 GPU 分析的 IOCTL 已限制為僅供殼層程序或可偵錯的應用程式使用。如要進一步瞭解平台層級政策,請參閱 SAC 更新。
這項異動會影響使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 裝置 (Pixel 6 到 Pixel 9)。Arm 已在 Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst 的 r54p2 版本中,提供 IOCTL 的官方分類。我們會在日後發布的驅動程式版本中,持續維護這份清單。
這項異動不會影響支援的繪圖 API (包括 Vulkan 和 OpenGL),預計也不會影響開發人員或現有應用程式。Streamline Performance Analyzer 和 Android GPU 檢查器等 GPU 剖析工具不會受到影響。
測試
如果看到類似以下的 SELinux 拒絕訊息,表示您的應用程式可能受到這項異動影響:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
如果應用程式需要使用遭封鎖的 IOCTL,請回報錯誤並指派給 android-partner-security@google.com。
常見問題
這項政策異動是否適用於所有原始設備製造商? 這項變更將採選擇加入制,但任何想使用這項強化方法的 OEM 都能選擇加入。如需實作變更的操作說明,請參閱實作說明文件。
是否必須變更 OEM 程式碼集才能實作這項功能,還是預設會隨附於新的 AOSP 版本? 根據預設,平台層級的變更會隨附於新的 Android 開放原始碼計畫版本。如要套用這項變更,供應商可以在程式碼集選擇啟用。
SoC 是否負責更新 IOCTL 清單?舉例來說,如果我的裝置使用 ARM Mali GPU,是否需要就任何變更與 ARM 聯絡? 個別 SoC 必須在驅動程式發布後,依據裝置更新 IOCTL 清單。 舉例來說,ARM 會在驅動程式更新時,更新已發布的 IOCTL 清單。 不過,原始設備製造商應確保將更新納入 SEPolicy,並視需要將所選自訂 IOCTL 新增至清單。
這項變更會自動套用至所有市售 Pixel 裝置嗎?還是使用者必須切換某些設定才能套用? 這項異動適用於所有使用 Mali GPU 的 Pixel 上市裝置 (Pixel 6 至 Pixel 9)。這項異動會自動生效,您不必採取任何行動。
使用這項政策會影響核心驅動程式的效能嗎? 這項政策已在 Mali GPU 上使用 GFXBench 進行測試,結果顯示 GPU 效能沒有明顯變化。
IOCTL 清單是否必須與目前的使用者空間和核心驅動程式版本一致? 是,允許的 IOCTL 清單必須與使用者空間和核心驅動程式支援的 IOCTL 同步。如果使用者空間或核心驅動程式中的 IOCTL 已更新,SEPolicy IOCTL 清單也必須更新,才能與之相符。
ARM 已將 IOCTL 分類為「受限」/「儀器」,但我們想在正式環境的使用案例中採用部分 IOCTL,並/或拒絕其他 IOCTL。 各個 OEM/SoC 負責根據使用者空間 Mali 程式庫的設定,決定如何分類所用的 IOCTL。ARM 的清單可協助您做出這些決定,但每個 OEM/SoC 的使用案例可能有所不同。
隱私權
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列隱私權異動。
區域網路權限
只要應用程式具備 INTERNET 權限,就能存取 LAN 上的裝置。
這項功能可讓應用程式輕鬆連線至本機裝置,但也會產生隱私權影響,例如形成使用者指紋,以及成為位置資訊的 Proxy。
「區域網路保護」專案的目標是透過新的執行階段權限,限制區域網路的存取權,進而保護使用者隱私權。
發布計畫
這項異動將在 2025 年第 2 季和 2026 年第 2 季之間推出。開發人員務必遵循 25Q2 的這項指引,並分享意見回饋,因為這些保護措施將在日後的 Android 版本中強制執行。此外,他們也需要按照下列指引更新依附於隱含本機網路存取的案例,並準備好因應使用者拒絕或撤銷新權限的情況。
影響
現階段,LNP 是選擇加入的功能,因此只有選擇加入的應用程式會受到影響。在選擇加入階段,應用程式開發人員的目標是瞭解應用程式的哪些部分依附於隱含的區域網路存取權,以便為下一個版本準備權限防護措施。
如果應用程式使用下列方式存取使用者的本機網路,就會受到影響:
- 直接或透過程式庫使用本機網路位址的原始通訊端 (例如 mDNS 或 SSDP 服務探索通訊協定)
- 使用可存取本機網路的架構層級類別 (例如 NsdManager)
傳送至和傳送自區域網路位址的流量,需要區域網路存取權。下表列出一些常見案例:
| 應用程式低層級網路作業 | 必須授予區域網路權限 |
|---|---|
| 建立外送 TCP 連線 | 是 |
| 接受傳入的 TCP 連線 | 是 |
| 傳送 UDP 單點傳播、多點傳播、廣播 | 是 |
| 接收傳入的 UDP 單點傳播、多點傳播、廣播 | 是 |
這些限制是在網路堆疊深處實作,因此適用於所有網路 API。包括以原生或受管理程式碼建立的通訊端、Cronet 和 OkHttp 等網路程式庫,以及在這些程式庫上實作的任何 API。如要解析區域網路上的服務 (即含有 .local 後置字元的服務),必須具備區域網路權限。
上述規則的例外狀況:
- 如果裝置的 DNS 伺服器位於區域網路上,則往返該伺服器的流量 (通訊埠 53) 不需要區域網路存取權。
- 如果應用程式使用 Output Switcher 做為應用程式內選取器,則不需要區域網路權限 (更多指引將於 2025 年第 4 季發布)。
開發人員指引 (選擇加入)
如要啟用區域網路限制,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 將裝置刷機為 25Q2 Beta 3 以上版本。
- 安裝要測試的應用程式。
在 adb 中切換 Appcompat 標記:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>重新啟動裝置
現在應用程式的區域網路存取權受到限制,任何存取區域網路的嘗試都會導致通訊端錯誤。如果您使用的 API 會在應用程式程序外部執行本機網路作業 (例如 NsdManager),在選擇加入階段不會受到影響。
如要還原存取權,您必須授予應用程式 NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES 權限。
- 確認應用程式在資訊清單中宣告了
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES權限。 - 依序前往「設定」>「應用程式」>「[應用程式名稱]」>「權限」>「鄰近裝置」>「允許」。
現在應用程式應該已恢復區域網路存取權,所有情境也應與應用程式加入測試前一樣運作。
區域網路保護措施開始強制執行後,應用程式網路流量會受到以下影響。
| 權限 | 傳出 LAN 要求 | 傳出/傳入網際網路要求 | 傳入 LAN 要求 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 已授權 | Works | Works | Works |
| 未授予 | 凸槌影片 | Works | 凸槌影片 |
使用下列指令切換關閉 App-Compat 旗標
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
錯誤
每當呼叫插座叫用 send 或 send 變數至本機網路位址時,系統就會將因這些限制而產生的錯誤傳回呼叫插座。
錯誤示例:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
區域網路定義
本專案中的本機網路是指使用具備廣播功能的網路介面 (例如 Wi-Fi 或乙太網路) 的 IP 網路,但不包括行動網路 (WWAN) 或 VPN 連線。
下列為本機網路:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // 連結本機
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- 連結本機
- 直接連線的路徑
- Thread 等存根網路
- 多個子網路 (待定)
此外,多點播送位址 (224.0.0.0/4、ff00::/8) 和 IPv4 廣播位址 (255.255.255.255) 都屬於本機網路位址。
應用程式擁有的相片
當指定 SDK 36 以上版本的應用程式在搭載 Android 16 以上版本的裝置上執行時,如果系統提示使用者授予相片和影片權限,選擇限制所選媒體存取權的使用者會在相片挑選器中看到應用程式預先選取的所有相片。使用者可以取消選取任何預先選取的項目,這樣一來,應用程式就無法存取這些相片和影片。

