Платформа Android 16 включает изменения в поведении, которые могут повлиять на ваше приложение. Следующие изменения в поведении применяются ко всем приложениям, работающим на Android 16, независимо от targetSdkVersion . Вам следует протестировать свое приложение, а затем внести в него необходимые изменения для поддержки этих изменений, где это применимо.
Обязательно ознакомьтесь также со списком изменений в поведении, которые затрагивают только приложения, ориентированные на Android 16 .
Основная функциональность
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения, которые модифицируют или расширяют различные основные возможности системы Android.
Оптимизация квот JobScheduler
Начиная с Android 16 мы корректируем квоту времени выполнения обычных и ускоренных заданий на основе следующих факторов:
- В каком контейнере ожидания приложения находится приложение : в Android 16 активные контейнеры ожидания начнут применяться принудительно с помощью щедрой квоты времени выполнения.
- Если выполнение задания начинается, когда приложение находится в верхнем состоянии : в Android 16 задания, запущенные, когда приложение видимо пользователю, и продолжающиеся после того, как приложение становится невидимым, будут соответствовать квоте времени выполнения задания.
- Если задание выполняется во время работы службы переднего плана : в Android 16 задания, выполняемые одновременно с службой переднего плана, будут соответствовать квоте времени выполнения задания. Если вы используете задания для передачи данных, инициированной пользователем, рассмотрите возможность использования заданий передачи данных, инициированных пользователем .
Это изменение влияет на задачи, запланированные с помощью WorkManager, JobScheduler и DownloadManager. Чтобы отладить причину остановки задания, рекомендуем зарегистрировать причину остановки, вызвав WorkInfo.getStopReason() (для заданий JobScheduler вызовите JobParameters.getStopReason() ).
Информацию о том, как состояние вашего приложения влияет на доступные ему ресурсы, см. в разделе «Ограничения ресурсов управления питанием» . Дополнительную информацию о передовых методах оптимизации расхода заряда батареи см. в руководстве по оптимизации использования батареи для API планирования задач .
Мы также рекомендуем использовать новый API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory представленный в Android 16, чтобы понять, почему задание не было выполнено.
Тестирование
Чтобы протестировать поведение вашего приложения, вы можете включить переопределение некоторых оптимизаций квот заданий, если приложение работает на устройстве Android 16.
Чтобы отключить принудительное соблюдение параметра «верхнее состояние будет соответствовать квоте времени выполнения задания», выполните следующую команду adb :
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Чтобы отключить принудительное выполнение параметра «Задания, которые выполняются одновременно с активной службой, будут придерживаться квоты времени выполнения задания», выполните следующую команду adb :
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Чтобы протестировать определенное поведение контейнера ожидания приложения, вы можете настроить контейнер ожидания приложения для своего приложения с помощью следующей команды adb :
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
Чтобы понять, в каком сегменте режима ожидания приложения находится ваше приложение, вы можете получить сегмент режима ожидания приложения с помощью следующей команды adb :
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Причина прекращения работы на заброшенных вакансиях
Прерванное задание происходит, когда объект JobParameters связанный с заданием, был удален, но JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters, boolean) не был вызван для сигнала о завершении задания. Это указывает на то, что задание может выполняться и перепланироваться без ведома приложения.
Приложения, использующие JobScheduler, не поддерживают строгую ссылку на объект JobParameters , и тайм-ауту теперь будет присвоена новая причина остановки задания STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED вместо STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT .
Если новые причины прерванной остановки возникают часто, система предпримет меры по смягчению последствий, чтобы снизить частоту выполнения заданий.
Приложения должны использовать новую причину остановки, чтобы обнаруживать и сокращать количество заброшенных заданий.
Если вы используете WorkManager, AsyncTask или DownloadManager, на вас это не повлияет, поскольку эти API управляют жизненным циклом задания от имени вашего приложения.
Полное прекращение поддержки JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
Метод JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) указывает на важность задания, когда приложение планирования находится на переднем плане или когда временно освобождено от фоновых ограничений.
Этот метод устарел с Android 12 (уровень API 31). Начиная с Android 16, он больше не работает эффективно, и вызов этого метода будет игнорироваться.
Это удаление функциональности также применимо к JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground() . Начиная с Android 16, при вызове метода метод возвращает false .
Область действия приоритета упорядоченной трансляции больше не является глобальной.
Приложениям Android разрешено определять приоритеты приемников вещания, чтобы контролировать порядок, в котором получатели получают и обрабатывают трансляцию. Для получателей, объявленных в манифесте, приложения могут использовать атрибут android:priority для определения приоритета, а для получателей, зарегистрированных в контексте, приложения могут использовать API IntentFilter#setPriority() для определения приоритета. При отправке широковещательной рассылки система доставляет ее получателям в порядке их приоритета, от самого высокого к самому низкому.
В Android 16 порядок широковещательной доставки с использованием атрибута android:priority или IntentFilter#setPriority() между различными процессами не гарантируется. Приоритеты вещания будут соблюдаться только в рамках одного и того же процесса подачи заявки, а не во всех процессах.
Кроме того, приоритеты вещания будут автоматически ограничены диапазоном ( SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY – 1). Только системным компонентам будет разрешено устанавливать SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY , SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY в качестве приоритета широковещания.
Ваше приложение может пострадать, если оно выполняет одно из следующих действий:
- Ваше приложение объявило несколько процессов с одним и тем же намерением широковещания и ожидает получения этих намерений в определенном порядке в зависимости от приоритета.
- Процесс вашего приложения взаимодействует с другими процессами и ожидает получения широковещательного намерения в определенном порядке.
Если процессам необходимо координировать друг друга, им следует взаимодействовать, используя другие каналы координации.
внутренние изменения ART
Android 16 включает последние обновления среды выполнения Android (ART), которые улучшают производительность среды выполнения Android (ART) и обеспечивают поддержку дополнительных функций Java. Благодаря обновлениям системы Google Play эти улучшения также доступны более чем миллиарду устройств под управлением Android 12 (уровень API 31) и выше .
После выхода этих изменений библиотеки и код приложений, использующие внутренние структуры ART, могут работать некорректно на устройствах под управлением Android 16, а также на более ранних версиях Android, которые обновляют модуль ART через обновления системы Google Play.
Использование внутренних структур (например, интерфейсов, отличных от SDK ) всегда может привести к проблемам совместимости, но особенно важно избегать использования кода (или библиотек, содержащих код), который использует внутренние структуры ART, поскольку изменения ART не привязаны к платформе. версию, на которой работает устройство, и они распространяются на более чем миллиард устройств через обновления системы Google Play.
Всем разработчикам следует проверить, не затронуто ли их приложение, путем тщательного тестирования своих приложений на Android 16. Кроме того, проверьте известные проблемы , чтобы узнать, зависит ли ваше приложение от каких-либо выявленных нами библиотек, которые полагаются на внутренние структуры ART. Если у вас есть код приложения или зависимости библиотеки, которые затронуты, по возможности ищите альтернативы общедоступным API и запросите общедоступные API для новых вариантов использования, создав запрос функции в нашем отслеживании проблем.
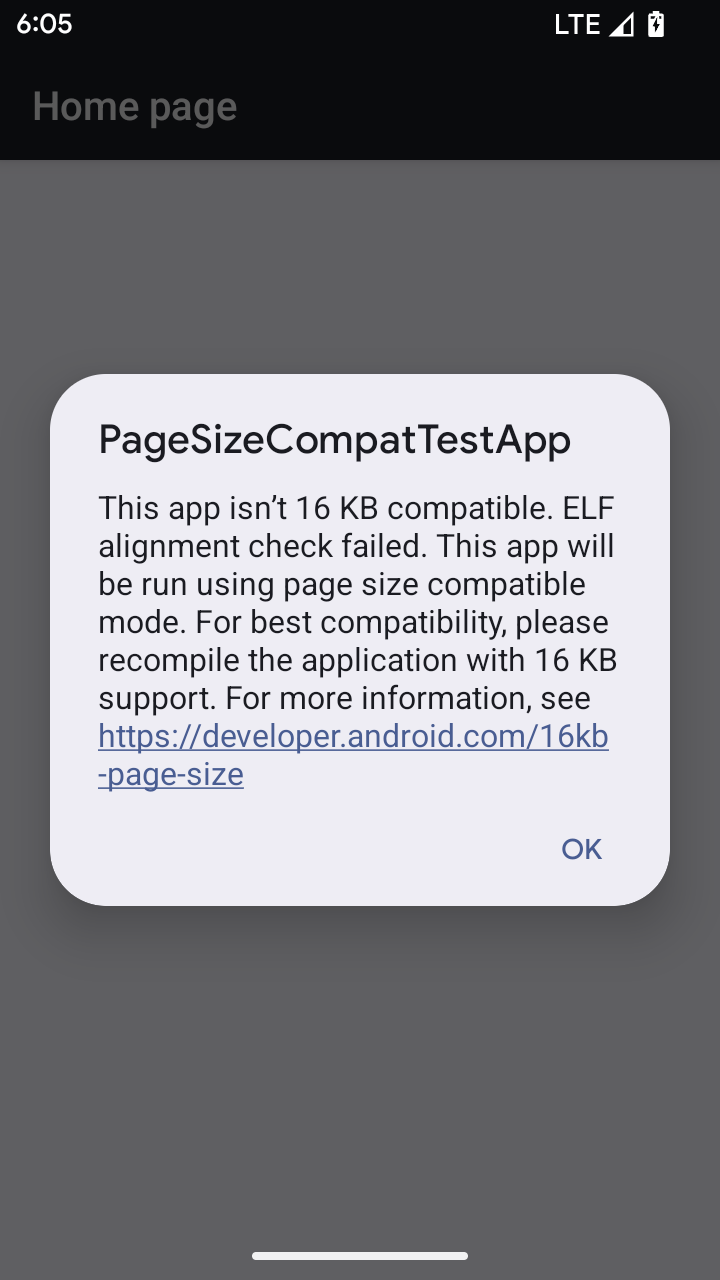
режим совместимости с размером страницы 16 КБ
В Android 15 появилась поддержка страниц памяти размером 16 КБ для оптимизации производительности платформы. В Android 16 добавлен режим совместимости , позволяющий запускать некоторые приложения, созданные для страниц памяти размером 4 КБ, на устройстве, настроенном для страниц памяти 16 КБ.
Когда ваше приложение работает на устройстве с Android 16 или более поздней версии, если Android обнаруживает, что ваше приложение имеет выровненные страницы памяти размером 4 КБ, оно автоматически использует режим совместимости и отображает диалоговое окно уведомления для пользователя. Установка свойства android:pageSizeCompat в AndroidManifest.xml для включения режима обратной совместимости предотвратит отображение диалогового окна при запуске вашего приложения. Чтобы использовать свойство android:pageSizeCompat , скомпилируйте приложение с помощью Android 16 SDK .
Для обеспечения максимальной производительности, надежности и стабильности размер вашего приложения по-прежнему должен составлять 16 КБ. Для получения более подробной информации ознакомьтесь с нашей недавней публикацией в блоге об обновлении ваших приложений для поддержки страниц памяти 16 КБ.
Пользовательский опыт и пользовательский интерфейс системы
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения, призванные обеспечить более согласованный и интуитивно понятный пользовательский интерфейс.
Отмена нежелательных объявлений, нарушающих доступность.
В Android 16 больше не поддерживаются объявления о специальных возможностях, характеризующиеся использованием announceForAccessibility или отправкой событий доступности TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT . Это может создать несогласованный пользовательский опыт для пользователей TalkBack и программы чтения с экрана Android, а альтернативы лучше удовлетворяют более широкий спектр потребностей пользователей в различных вспомогательных технологиях Android.
Примеры альтернатив:
- Для значительных изменений пользовательского интерфейса, таких как изменения окон, используйте
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)иsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). В Compose используйтеModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - Чтобы сообщить пользователю об изменениях в критическом пользовательском интерфейсе, используйте
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). В Compose используйтеModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. Их следует использовать с осторожностью, поскольку они могут генерировать объявления каждый раз при обновлении представления. - Чтобы уведомить пользователей об ошибках, отправьте
AccessibilityEventтипаAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORи установитеAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)или используйтеTextView#setError(CharSequence).
Справочная документация по устаревшему API announceForAccessibility содержит более подробную информацию о предлагаемых альтернативах.
Поддержка навигации с помощью 3 кнопок
В Android 16 добавлена поддержка прогнозного возврата в трехкнопочную навигацию для приложений, которые правильно перешли на интеллектуальный возврат . Длительное нажатие кнопки «Назад» запускает прогнозирующую анимацию возврата, давая вам предварительный просмотр того, куда вас приведет смахивание назад.
Такое поведение применимо ко всем областям системы, которые поддерживают прогнозирующую анимацию возврата, включая системную анимацию (возврат домой, перекрестные задачи и перекрестные действия).
Автоматические тематические значки приложений
Начиная с Android 16 QPR 2, Android автоматически применяет темы к значкам приложений для создания целостного интерфейса на главном экране. Это происходит, если приложение не предоставляет собственный тематический значок. Приложения могут управлять дизайном своего тематического значка, добавляя монохромный слой в адаптивный значок и предварительно просматривая, как будет выглядеть значок в Android Studio .
форм-факторы устройств
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения для приложений, проецируемых на экраны владельцами виртуальных устройств.
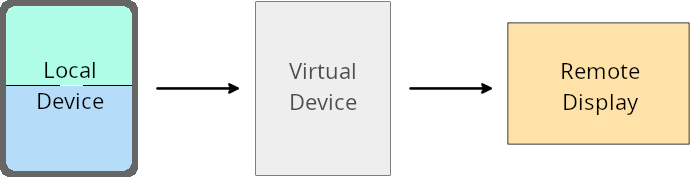
Владелец виртуального устройства вносит изменения по своему усмотрению.
Владелец виртуального устройства — это доверенное или привилегированное приложение, которое создает и управляет виртуальным устройством. Владельцы виртуальных устройств запускают приложения на виртуальном устройстве, а затем проецируют их на экран удаленного устройства, такого как персональный компьютер, устройство виртуальной реальности или автомобильная информационно-развлекательная система. Владелец виртуального устройства находится на локальном устройстве, например, на мобильном телефоне.
Переопределения для отдельных приложений
На устройствах под управлением Android 16 (уровень API 36) владельцы виртуальных устройств могут переопределять настройки приложений на отдельных виртуальных устройствах, которыми они управляют. Например, для улучшения компоновки приложения владелец виртуального устройства может игнорировать ограничения по ориентации, соотношению сторон и масштабируемости при проецировании приложений на внешний дисплей.
Распространенные изменения, нарушающие обратную связь
Особенности работы Android 16 могут повлиять на пользовательский интерфейс вашего приложения на больших экранах, таких как автомобильные дисплеи или Chromebook, особенно на макеты, разработанные для небольших экранов в портретной ориентации. Чтобы узнать, как адаптировать ваше приложение для всех форм-факторов устройств, см. раздел «Об адаптивных макетах» .
Ссылки
Потоковое вещание сопутствующего приложения
Безопасность
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены изменения, повышающие безопасность системы и помогающие защитить приложения и пользователей от вредоносных программ.
Повышена защита от атак с перенаправлением намерений.
Android 16 обеспечивает защиту от атак с использованием перенаправления Intent по умолчанию, требуя минимальных изменений для обеспечения совместимости и участия разработчиков.
Мы внедряем решения по усилению безопасности по умолчанию для защиты от уязвимостей, связанных с перенаправлением Intent . В большинстве случаев приложения, использующие Intent, обычно не испытывают проблем с совместимостью; мы собирали метрики на протяжении всего процесса разработки, чтобы отслеживать, какие приложения могут столкнуться с проблемами.
Перенаправление намерений в Android происходит, когда злоумышленник может частично или полностью контролировать содержимое намерения, используемого для запуска нового компонента в контексте уязвимого приложения, в то время как приложение-жертва запускает недоверенное намерение нижнего уровня в поле extras (название намерения верхнего уровня). Это может привести к тому, что приложение злоумышленника запустит приватные компоненты в контексте приложения-жертвы, запустит действия с привилегиями или получит доступ к конфиденциальным данным по URI, что потенциально может привести к краже данных и выполнению произвольного кода.
Отказаться от обработки перенаправлений Intent
В Android 16 представлен новый API, позволяющий приложениям отключать защиту при запуске. Это может быть необходимо в отдельных случаях, когда поведение системы безопасности по умолчанию мешает корректному использованию приложений.
Для приложений, компилируемых с использованием Android 16 (уровень API 36) SDK или выше.
Вы можете напрямую использовать метод removeLaunchSecurityProtection() объекта Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Для приложений, компилируемых под Android 15 (уровень API 35) или ниже.
Хотя это и не рекомендуется, вы можете использовать рефлексию для доступа к методу removeLaunchSecurityProtection() .
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Сопутствующие приложения больше не получают уведомления о превышении времени ожидания обнаружения.
Android 16 представляет новое поведение во время сопряжения сопутствующего устройства для защиты конфиденциальности местоположения пользователя от вредоносных приложений. Все сопутствующие приложения, работающие на Android 16, больше не уведомляются напрямую о тайм-ауте обнаружения с помощью RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT . Вместо этого пользователь уведомляется о событиях тайм-аута с помощью визуального диалога. Когда пользователь закрывает диалог, приложение оповещается об ошибке ассоциации с помощью RESULT_USER_REJECTED .
Продолжительность поиска также была увеличена с первоначальных 20 секунд, и обнаружение устройств может быть остановлено пользователем в любой момент поиска. Если хотя бы одно устройство было обнаружено в течение первых 20 секунд с начала поиска, CDM прекращает поиск дополнительных устройств.
Подключение
В Android 16 (уровень API 36) внесены следующие изменения в стек Bluetooth для улучшения связи с периферийными устройствами.
Улучшенная обработка убытков по облигациям
Начиная с Android 16, стек Bluetooth был обновлен для повышения безопасности и удобства работы пользователей при обнаружении потери удаленного соединения. Раньше система автоматически удаляла связь и инициировала новый процесс сопряжения, что могло привести к непреднамеренному повторному сопряжению. Мы видели во многих случаях приложения, которые не заботятся о событии потери облигаций должным образом.
Чтобы унифицировать этот опыт, в Android 16 улучшена обработка потерь по облигациям в системе. Если ранее подключенное устройство Bluetooth не могло быть аутентифицировано при повторном подключении, система отключит соединение, сохранит информацию о локальной связи и отобразит системное диалоговое окно, информирующее пользователей о потере соединения и предписывающее им выполнить повторное соединение.
,Начиная с Android 16, стек Bluetooth был обновлен для повышения безопасности и удобства работы пользователей при обнаружении потери удаленного соединения. Раньше система автоматически удаляла связь и инициировала новый процесс сопряжения, что могло привести к непреднамеренному повторному сопряжению. Мы видели во многих случаях приложения, которые не заботятся о событии потери облигаций должным образом.
Чтобы унифицировать этот опыт, в Android 16 улучшена обработка потерь по облигациям в системе. Если ранее подключенное устройство Bluetooth не могло быть аутентифицировано при повторном подключении, система отключит соединение, сохранит информацию о локальной связи и отобразит системное диалоговое окно, информирующее пользователей о потере соединения и предписывающее им выполнить повторное соединение.
,Начиная с Android 16, стек Bluetooth был обновлен для повышения безопасности и удобства работы пользователей при обнаружении потери удаленного соединения. Раньше система автоматически удаляла связь и инициировала новый процесс сопряжения, что могло привести к непреднамеренному повторному сопряжению. Мы видели во многих случаях приложения, которые не заботятся о событии потери облигаций должным образом.
Чтобы унифицировать этот опыт, в Android 16 улучшена обработка потерь по облигациям в системе. Если ранее подключенное устройство Bluetooth не могло быть аутентифицировано при повторном подключении, система отключит соединение, сохранит информацию о локальной связи и отобразит системное диалоговое окно, информирующее пользователей о потере соединения и предписывающее им выполнить повторное соединение.

