通常,我们希望在应用不在前台时播放媒体内容。例如,音乐播放器通常会在用户锁定设备或使用其他应用时继续播放音乐。Media3 库提供了一系列接口,可让您支持后台播放。
使用 MediaSessionService
如需启用后台播放,您应将 Player 和 MediaSession 包含在单独的 Service 中。这样,即使您的应用不在前台,设备也能继续提供媒体服务。
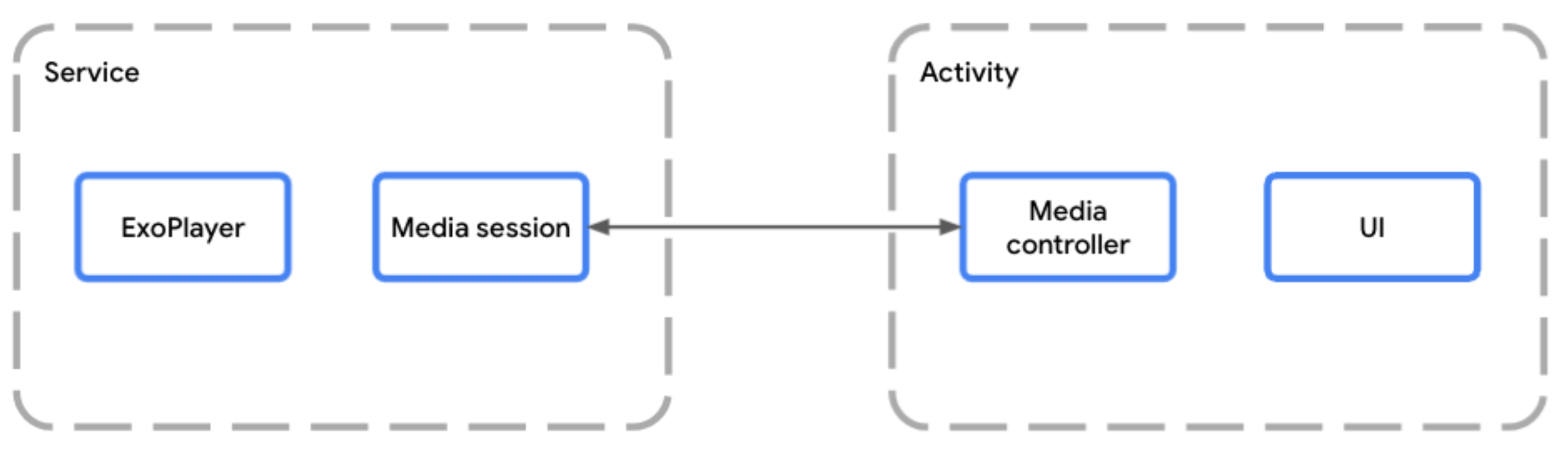
MediaSessionService 允许媒体会话独立于应用 activity 运行在服务中托管玩家时,您应使用 MediaSessionService。为此,请创建一个扩展 MediaSessionService 的类,并在其中创建媒体会话。
使用 MediaSessionService 可以让 Google 助理等外部客户端、系统媒体控件、外围设备上的媒体按钮或 Wear OS 等配套设备发现您的服务、连接到该服务并控制播放,而根本无需访问应用的界面 activity。事实上,可以有多个客户端应用同时连接到同一个 MediaSessionService,每个应用都有自己的 MediaController。
实现服务生命周期
您需要实现服务的两个生命周期方法:
- 当第一个控制器即将连接且服务已实例化并启动时,系统会调用
onCreate()。这里是打造Player和MediaSession的最佳场所。 - 当服务正在停止时,系统会调用
onDestroy()。需要释放所有资源,包括播放器和会话。
您可以选择替换 onTaskRemoved(Intent),以自定义当用户从“最近的任务”中关闭应用时发生的情况。默认情况下,如果正在播放,服务会保持运行状态;否则,服务会停止运行。
Kotlin
class PlaybackService : MediaSessionService() { private var mediaSession: MediaSession? = null // Create your player and media session in the onCreate lifecycle event override fun onCreate() { super.onCreate() val player = ExoPlayer.Builder(this).build() mediaSession = MediaSession.Builder(this, player).build() } // Remember to release the player and media session in onDestroy override fun onDestroy() { mediaSession?.run { player.release() release() mediaSession = null } super.onDestroy() } }
Java
public class PlaybackService extends MediaSessionService { private MediaSession mediaSession = null; // Create your Player and MediaSession in the onCreate lifecycle event @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); ExoPlayer player = new ExoPlayer.Builder(this).build(); mediaSession = new MediaSession.Builder(this, player).build(); } // Remember to release the player and media session in onDestroy @Override public void onDestroy() { mediaSession.getPlayer().release(); mediaSession.release(); mediaSession = null; super.onDestroy(); } }
除了在后台持续播放之外,您还可以选择在用户关闭应用时停止服务:
Kotlin
override fun onTaskRemoved(rootIntent: Intent?) { pauseAllPlayersAndStopSelf() }
Java
@Override public void onTaskRemoved(@Nullable Intent rootIntent) { pauseAllPlayersAndStopSelf(); }
对于 onTaskRemoved 的任何其他手动实现,您可以使用 isPlaybackOngoing() 检查播放是否被视为正在进行,以及前台服务是否已启动。
提供对媒体会话的访问权限
替换 onGetSession() 方法,以允许其他客户端访问在创建服务时构建的媒体会话。
Kotlin
class PlaybackService : MediaSessionService() { private var mediaSession: MediaSession? = null // [...] lifecycle methods omitted override fun onGetSession(controllerInfo: MediaSession.ControllerInfo): MediaSession? = mediaSession }
Java
public class PlaybackService extends MediaSessionService { private MediaSession mediaSession = null; // [...] lifecycle methods omitted @Override public MediaSession onGetSession(MediaSession.ControllerInfo controllerInfo) { return mediaSession; } }
在清单中声明服务
应用需要 FOREGROUND_SERVICE 和 FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MEDIA_PLAYBACK 权限才能运行播放前台服务:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_MEDIA_PLAYBACK" />
您还必须在清单中声明 Service 类,并使用 MediaSessionService 的 intent 过滤器和包含 mediaPlayback 的 foregroundServiceType。
<service
android:name=".PlaybackService"
android:foregroundServiceType="mediaPlayback"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.media3.session.MediaSessionService"/>
<action android:name="android.media.browse.MediaBrowserService"/>
</intent-filter>
</service>
使用 MediaController 控制播放
在包含播放器界面的 activity 或 fragment 中,您可以使用 MediaController 在界面和媒体会话之间建立关联。您的界面使用媒体控制器将命令从界面发送到会话中的播放器。如需详细了解如何创建和使用 MediaController,请参阅创建 MediaController 指南。
处理 MediaController 命令
MediaSession 通过其 MediaSession.Callback 接收来自控制器的命令。初始化 MediaSession 会创建 MediaSession.Callback 的默认实现,该实现会自动处理 MediaController 发送给播放器的所有命令。
通知
MediaSessionService 会自动为您创建 MediaNotification,在大多数情况下应该都能正常运行。默认情况下,发布的通知是 MediaStyle 通知,会根据媒体会话的最新信息保持更新,并显示播放控件。MediaNotification 知道您的会话,可用于控制连接到同一会话的任何其他应用的播放。
例如,使用 MediaSessionService 的音乐流媒体应用会创建一个 MediaNotification,其中显示当前播放的媒体内容的标题、音乐人和专辑封面,以及基于 MediaSession 配置的播放控件。
所需元数据可以在媒体中提供,也可以声明为媒体项的一部分,如以下代码段所示:
Kotlin
val mediaItem = MediaItem.Builder() .setMediaId("media-1") .setUri(mediaUri) .setMediaMetadata( MediaMetadata.Builder() .setArtist("David Bowie") .setTitle("Heroes") .setArtworkUri(artworkUri) .build() ) .build() mediaController.setMediaItem(mediaItem) mediaController.prepare() mediaController.play()
Java
MediaItem mediaItem = new MediaItem.Builder() .setMediaId("media-1") .setUri(mediaUri) .setMediaMetadata( new MediaMetadata.Builder() .setArtist("David Bowie") .setTitle("Heroes") .setArtworkUri(artworkUri) .build()) .build(); mediaController.setMediaItem(mediaItem); mediaController.prepare(); mediaController.play();
通知生命周期
当播放列表中的 Player 达到 MediaItem 个实例时,系统会立即创建通知。
所有通知更新都会根据 Player 和 MediaSession 状态自动进行。
前台服务运行时,无法移除通知。如需立即移除通知,您必须调用 Player.release() 或使用 Player.clearMediaItems() 清除播放列表。
如果播放器暂停、停止或失败的时间超过 10 分钟,且没有进一步的用户互动,服务会自动从前台服务状态转换出来,以便系统可以将其销毁。您可以实现播放恢复,以便用户在稍后时间点重启服务生命周期并恢复播放。
自定义通知
通过修改 MediaItem.MediaMetadata,可以自定义有关当前播放项的元数据。如果您想更新现有商品的元数据,可以使用 Player.replaceMediaItem 更新元数据,而不会中断播放。
您还可以通过为 Android 媒体控件设置自定义媒体按钮偏好设置,自定义通知中显示的部分按钮。 详细了解如何自定义 Android 媒体控件。
如需进一步自定义通知本身,请使用 DefaultMediaNotificationProvider.Builder 创建 MediaNotification.Provider,或创建提供器接口的自定义实现。使用 setMediaNotificationProvider 将提供商添加到 MediaSessionService。
继续播放
在 MediaSessionService 终止后,即使在设备重启后,也可以提供播放恢复功能,让用户重启服务并从上次停止播放的位置继续播放。默认情况下,播放恢复功能处于关闭状态。这意味着,当您的服务未运行时,用户无法恢复播放。如需选择启用此功能,您需要声明媒体按钮接收器并实现 onPlaybackResumption 方法。
声明 Media3 媒体按钮接收器
首先在清单中声明 MediaButtonReceiver:
<receiver android:name="androidx.media3.session.MediaButtonReceiver"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MEDIA_BUTTON" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
实现“继续播放”回调
当蓝牙设备或 Android 系统界面恢复功能请求恢复播放时,系统会调用 onPlaybackResumption() 回调方法。
Kotlin
override fun onPlaybackResumption( mediaSession: MediaSession, controller: ControllerInfo, isForPlayback: Boolean, ): ListenableFuture<MediaItemsWithStartPosition> { val settable = SettableFuture.create<MediaItemsWithStartPosition>() scope.launch { // Your app is responsible for storing the playlist, metadata (like title // and artwork) of the current item and the start position to use here. val resumptionPlaylist = restorePlaylist() settable.set(resumptionPlaylist) } return settable }
Java
@Override public ListenableFuture<MediaItemsWithStartPosition> onPlaybackResumption( MediaSession mediaSession, ControllerInfo controller, boolean isForPlayback ) { SettableFuture<MediaItemsWithStartPosition> settableFuture = SettableFuture.create(); settableFuture.addListener(() -> { // Your app is responsible for storing the playlist, metadata (like title // and artwork) of the current item and the start position to use here. MediaItemsWithStartPosition resumptionPlaylist = restorePlaylist(); settableFuture.set(resumptionPlaylist); }, MoreExecutors.directExecutor()); return settableFuture; }
如果您存储了其他参数(例如播放速度、重复播放模式或随机播放模式),那么 onPlaybackResumption() 是一个不错的选择,您可以在 Media3 准备播放器之前使用这些参数配置播放器,并在回调完成时开始播放。
在启动时调用此方法,以在设备重启且 isForPlayback 设置为 false 后创建 Android 系统界面恢复通知。对于富通知,建议使用本地可用的值填充当前项的 MediaMetadata、title 和 artworkData 或 artworkUri 等字段,因为网络访问可能尚未可用。您还可以向 MediaMetadata.extras 添加 MediaConstants.EXTRAS_KEY_COMPLETION_STATUS 和 MediaConstants.EXTRAS_KEY_COMPLETION_PERCENTAGE,以指示恢复播放位置。
高级控制器配置和向后兼容性
一个常见的使用场景是在应用界面中使用 MediaController 来控制播放和显示播放列表。与此同时,会话会向外部客户端公开,例如移动设备或电视上的 Android 媒体控件和 Google 助理、手表上的 Wear OS 以及汽车中的 Android Auto。Media3 会话演示应用是实现此类场景的应用示例。
这些外部客户端可能会使用旧版 AndroidX 库的 MediaControllerCompat 等 API 或 Android 平台的 android.media.session.MediaController 等 API。Media3 与旧版库完全向后兼容,并提供与 Android 平台 API 的互操作性。
识别可信控制器
任何应用都可以尝试连接到您的媒体会话或库。如果您想限制对系统控制器、具有媒体内容控制权限的控制器以及您自己的应用的访问权限,可以使用 ControllerInfo.isTrusted() 进行基本访问权限检查。或者,您也可以识别更具体的控制器,例如媒体通知控制器或 Android Auto 控制器,如以下部分所述。
使用媒体通知控制器
请务必了解,这些旧版控制器和平台控制器共享相同的状态,并且无法按控制器自定义可见性(例如可用的 PlaybackState.getActions() 和 PlaybackState.getCustomActions())。您可以使用媒体通知控制器来配置平台媒体会话中设置的状态,以实现与这些旧版控制器和平台控制器的兼容性。
例如,应用可以提供 MediaSession.Callback.onConnect() 的实现,以专门为平台会话设置可用的命令和媒体按钮偏好设置,如下所示:
Kotlin
override fun onConnect( session: MediaSession, controller: MediaSession.ControllerInfo ): ConnectionResult { if (session.isMediaNotificationController(controller)) { val playerCommands = ConnectionResult.DEFAULT_PLAYER_COMMANDS.buildUpon() .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_PREVIOUS) .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_PREVIOUS_MEDIA_ITEM) .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_NEXT) .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_NEXT_MEDIA_ITEM) .build() // Custom button preferences and commands to configure the platform session. return AcceptedResultBuilder(session) .setMediaButtonPreferences( listOf(seekBackButton, seekForwardButton) ) .setAvailablePlayerCommands(playerCommands) .build() } // Default commands with default button preferences for all other controllers. return AcceptedResultBuilder(session).build() }
Java
@Override public ConnectionResult onConnect( MediaSession session, MediaSession.ControllerInfo controller) { if (session.isMediaNotificationController(controller)) { Player.Commands playerCommands = ConnectionResult.DEFAULT_PLAYER_COMMANDS .buildUpon() .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_PREVIOUS) .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_PREVIOUS_MEDIA_ITEM) .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_NEXT) .remove(COMMAND_SEEK_TO_NEXT_MEDIA_ITEM) .build(); // Custom button preferences and commands to configure the platform session. return new AcceptedResultBuilder(session) .setMediaButtonPreferences( ImmutableList.of(seekBackButton, seekForwardButton)) .setAvailablePlayerCommands(playerCommands) .build(); } // Default commands with default button preferences for all other controllers. return new AcceptedResultBuilder(session).build(); }
授权 Android Auto 发送自定义命令
使用 MediaLibraryService 并通过移动应用支持 Android Auto 时,Android Auto 控制器需要提供适当的可用命令,否则 Media3 会拒绝来自该控制器的传入自定义命令:
Kotlin
override fun onConnect( session: MediaSession, controller: MediaSession.ControllerInfo ): ConnectionResult { val sessionCommands = ConnectionResult.DEFAULT_SESSION_AND_LIBRARY_COMMANDS.buildUpon() .add(customCommand) .build() if (session.isMediaNotificationController(controller)) { // [...] See above. } else if (session.isAutoCompanionController(controller)) { // Available session commands to accept incoming custom commands from Auto. return AcceptedResultBuilder(session) .setAvailableSessionCommands(sessionCommands) .build() } // Default commands for all other controllers. return AcceptedResultBuilder(session).build() }
Java
@Override public ConnectionResult onConnect( MediaSession session, MediaSession.ControllerInfo controller) { SessionCommands sessionCommands = ConnectionResult.DEFAULT_SESSION_COMMANDS .buildUpon() .add(customCommand) .build(); if (session.isMediaNotificationController(controller)) { // [...] See above. } else if (session.isAutoCompanionController(controller)) { // Available commands to accept incoming custom commands from Auto. return new AcceptedResultBuilder(session) .setAvailableSessionCommands(sessionCommands) .build(); } // Default commands for all other controllers. return new AcceptedResultBuilder(session).build(); }
此会话的演示应用具有汽车模块,可演示对需要单独 APK 的 Automotive OS 的支持。
