הארכיטקטורה המועדפת לאפליקציית אודיו היא עיצוב לקוח/שרת. הלקוח הוא Activity באפליקציה שכולל MediaBrowser, בקר מדיה וממשק משתמש. השרת הוא MediaBrowserService שמכיל את הנגן ואת סשן המדיה.
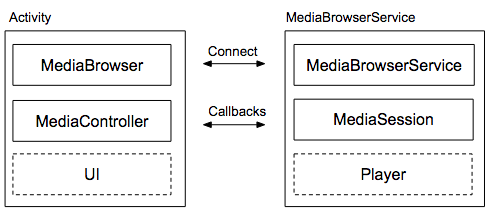
MediaBrowserService כולל שתי תכונות עיקריות:
- כשמשתמשים ב-
MediaBrowserService, רכיבים ואפליקציות אחרים עםMediaBrowserיכולים לגלות את השירות, ליצור בקר מדיה משלהם, להתחבר להפעלה של המדיה ולשלוט בנגן. כך אפליקציות ל-Wear OS ולאפליקציות ל-Android Auto מקבלות גישה לאפליקציית המדיה שלכם. - הוא כולל גם API לדפדפן אופציונלי. אפליקציות לא חייבות להשתמש בתכונה הזו. ה-API של הגלישה מאפשר ללקוחות לשלוח שאילתות לשירות ולבנות ייצוג של היררכיית התוכן שלו, שיכולה לייצג פלייליסטים, ספריית מדיה או סוג אחר של אוסף.
- פיתוח שירות של דפדפן מדיה
- איך יוצרים שירות דפדפן מדיה שמכיל סשן מדיה, מנהלים חיבורי לקוח והופכים לשירות שפועל בחזית בזמן הפעלת אודיו.
- יצירת לקוח של דפדפן מדיה
- איך ליצור פעילות של לקוח דפדפן מדיה שמכילה ממשק משתמש ובקר מדיה, ואיך להתחבר לשירות דפדפן מדיה ולתקשר איתו.
- התקשרות חוזרת (callback) של סשן מדיה
- מוסבר איך שיטות הקריאה החוזרת של סשן המדיה מנהלות את סשן המדיה, את שירות הדפדפן של המדיה ורכיבים אחרים של האפליקציה, כמו התראות ומקלט שידורים.
- Universal Android Music Player Sample
- בדוגמה הזו של GitHub מוסבר איך להטמיע אפליקציית מדיה שמאפשרת השמעת אודיו ברקע, ומספקת ספריית מדיה שחשופה לאפליקציות אחרות.
