לחצן פעולה צף (FAB) הוא לחצן מודגש שמאפשר למשתמש לבצע פעולה ראשית באפליקציה. הוא מעודד פעולה אחת וממוקדת, שהיא הנתיב הנפוץ ביותר שמשתמש עשוי לעבור, ובדרך כלל הוא מוצג בפינה השמאלית התחתונה של המסך.
ריכזנו כאן שלושה תרחישים לדוגמה שבהם כדאי להשתמש בלחצן פעולה צף:
- יצירת פריט חדש: באפליקציה לסיכום פגישות, אפשר להשתמש ב-FAB כדי ליצור במהירות הערה חדשה.
- הוספת איש קשר חדש: באפליקציית צ'אט, לחצן ה-FAB יכול לפתוח ממשק שמאפשר למשתמש להוסיף מישהו לשיחה.
- מרכוז המיקום: בממשק מפה, לחצן FAB יכול למרכז את המפה במיקום הנוכחי של המשתמש.
ב-Material Design יש ארבעה סוגים של כפתורי פעולה צפים:
- FAB: לחצן פעולה צף בגודל רגיל.
- לחצן פעולה צף קטן: לחצן פעולה צף קטן יותר.
- לחצן פעולה צף גדול (FAB): לחצן פעולה צף גדול יותר.
- לחצן פעולה צף מורחב: לחצן פעולה צף שמכיל יותר מסמל.

פלטפורמת ה-API
אפשר להשתמש בכמה פונקציות קומפוזיציה כדי ליצור כפתורי פעולה צפים שתואמים לעיצוב Material Design, אבל הפרמטרים שלהן לא שונים בהרבה. הנה כמה מהפרמטרים החשובים שכדאי לזכור:
-
onClick: הפונקציה שמופעלת כשהמשתמש לוחץ על הלחצן. -
containerColor: צבע הכפתור. -
contentColor: הצבע של הסמל.
לחצן פעולה צף
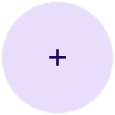
כדי ליצור לחצן פעולה צף כללי, משתמשים בקוד FloatingActionButton קומפוזבילי בסיסי. בדוגמה הבאה מוצגת הטמעה בסיסית של לחצן FAB:
@Composable fun Example(onClick: () -> Unit) { FloatingActionButton( onClick = { onClick() }, ) { Icon(Icons.Filled.Add, "Floating action button.") } }
ההטמעה הזו נראית כך:

כפתור קטן
כדי ליצור כפתור פעולה צף קטן, משתמשים בקוד SmallFloatingActionButton קומפוזבילי. בדוגמה הבאה אפשר לראות איך עושים את זה, עם הוספה של צבעים בהתאמה אישית.
@Composable fun SmallExample(onClick: () -> Unit) { SmallFloatingActionButton( onClick = { onClick() }, containerColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.secondaryContainer, contentColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.secondary ) { Icon(Icons.Filled.Add, "Small floating action button.") } }
ההטמעה הזו נראית כך:

כפתור גדול
כדי ליצור לחצן פעולה צף גדול, משתמשים בקוד LargeFloatingActionButton קומפוזבילי. הקומפוזיציה הזו לא שונה באופן משמעותי מהדוגמאות האחרות, מלבד העובדה שהיא יוצרת לחצן גדול יותר.
הנה הטמעה פשוטה של לחצן פעולה צף גדול.
@Composable fun LargeExample(onClick: () -> Unit) { LargeFloatingActionButton( onClick = { onClick() }, shape = CircleShape, ) { Icon(Icons.Filled.Add, "Large floating action button") } }
ההטמעה הזו נראית כך:
כפתור מורחב
אפשר ליצור לחצני פעולה צפים מורכבים יותר באמצעות ה-composable ExtendedFloatingActionButton. ההבדל העיקרי בינו לבין FloatingActionButton הוא שיש לו פרמטרים ייעודיים של icon ושל text. הם מאפשרים ליצור לחצן עם תוכן מורכב יותר שמשתנה בהתאם לתוכן שלו.
בקטע הקוד הבא אפשר לראות איך מטמיעים את ExtendedFloatingActionButton, עם ערכים לדוגמה שמועברים ל-icon ול-text.
@Composable fun ExtendedExample(onClick: () -> Unit) { ExtendedFloatingActionButton( onClick = { onClick() }, icon = { Icon(Icons.Filled.Edit, "Extended floating action button.") }, text = { Text(text = "Extended FAB") }, ) }
ההטמעה הזו נראית כך:

