設定使用 Android Game Development Extension 的專案。
Android 遊戲開發擴充功能會叫用 MSBuild,將 C/C++ 原始碼建構為共用程式庫 (.so) 和靜態程式庫 (.a)。在建構程序中,自訂 MSBuild 工作會叫用 Gradle 來編譯 Java 和 Kotlin 原始碼、封裝資產,並產生 APK 檔案供部署。設定專案時,您必須確認 MSBuild 包含為 Android 平台建構所需的資訊。
使用 MSBuild 建構 C/C++
一般 Android 專案是以 Gradle 建構,其中專案內的原生程式碼是以執行 CMake 或 ndk-build 的 Gradle 通道建構的。使用 Visual Studio 的 Android Game Development Extension 時,建構程序會按相反的順序執行。現在 MSBuild 是建構程序的起點。所有 C/C++ 原始碼都是先由 MSBuild 為您的系統上所安裝的新 Android 平台建構的,做為擴充功能的一部分 (例如「Android-x86_64」)。MSBuild 接著會叫用 Gradle,將含有 C/C++ 邏輯的共用資料庫檔案封裝至 APK。
請先在 MSBuild 內的 CMake 或 ndk-build 中複製專案現有的建構邏輯。將目標平台設為以下項目:
- Android-x86
- Android-x86_64
- Android-armeabi-v7a
- Android-arm64-v8a
這些平台都是由 Android Game Development Extension 提供。
設定編譯和連結選項
AGDE 會在建構應用程式的 C/C++ 部分時,使用您選取的 NDK 來判斷預設的編譯和連結選項。
如果您需要自訂這些編譯或連結選項,可以使用「專案屬性」進行設定。您可以在 C/C++ (用於編譯)、Librarian (用於靜態程式庫封存) 和 Linker (用於動態程式庫連結) 群組中找到最常見的選項。如果您需要傳遞任何其他自訂選項,可以將這些選項新增至「Command Line」部分。舉例來說,如果您使用的是 r28 以下版本的 NDK,建議您設定連結器標記,讓應用程式支援 16 KB 分頁大小。
新增 Android 平台
雖然茶壺範例專案包括 Android 平台,但您必須手動將 Android 平台新增至現有專案。如要新增平台,請在 Visual Studio 執行下列步驟:
- 依序選取「Build」>「Configuration Manager」。
- 在「Active solution platform」下方,選取「<New>」。
為新平台輸入下列其中一個值:
- Android-armeabi-v7a
- Android-arm64-v8a
- Android-x86
- Android-x86_64
在「Copy settings from」方塊中選取另一個現有 Android 平台。如果還沒有 Android 平台,則選取「<Empty>」。確認已啟用「Create new project platforms」。
新增 Android APK 項目
依序選取「Add」>「New Item」>「Visual C++」>「Android」>「Android APK」,然後按一下「Add」。請在下列對話方塊中設定 Android 應用程式。
- 「Application Name」:人類可讀的 Android 應用程式名稱。
- 「Application ID」:Android 應用程式的專屬 ID。
- 「Solution Explorer Location」:包含新增 Android 封裝支援檔案的虛擬資料夾位置。根據預設,這類檔案還位於名稱相同的資料夾的專案中。如要自訂位置,請勾選「Put support files in a custom location」核取方塊,並指定自訂位置。虛擬資料夾仍位於 Solution Explorer 的目前專案中。
讓 MSBuild 叫用 Gradle 建構 APK
除非 MSBuild 知道 Gradle 專案的位置,否則其無法叫用 Gradle。使用「Gradle Build Directory」屬性設定這個位置,如圖 1 所示。
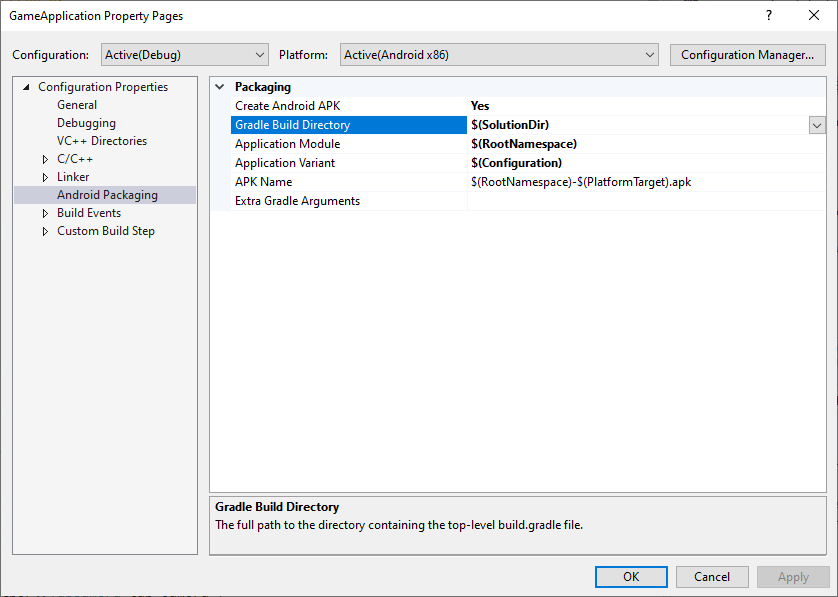
圖 1.「Gradle Build Directory」屬性
此外,請設定「Application Module」、「Application Variant」和「APK Name」屬性 (如上圖所示),以便 MSBuild 瞭解您要建構的內容。
- Application Module:Gradle 子專案的名稱。這是您在
settings.gradle檔案中設定的主要專案。對於使用 Android Studio 直接建立的專案,通常將其稱為app。 - 「Application Variant」:要建構的 Android 變化版本。這個值應根據 MSBuild 設定進行設定。舉例來說,偵錯版本應有一個設為偵錯變化版本的值。如果專案的 MSBuild 設定名稱與 Gradle 變化版本名稱相符,則請使用預設值
$(Configuration)。 - 「APK Name」:產生的 APK 檔案名稱,用於在開發電腦上偵錯和剖析。這個名稱會傳遞至 Gradle,且您的 Gradle 建構指令碼應遵循這點 (請參閱下一節的
MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME屬性)。
修改 Gradle 建構指令碼
在建構期間,MSBuild 會將下列資訊當做專案屬性傳遞至 Gradle 指令碼。變更專案現有的建構指令碼 (通常稱為 build.gradle) 以讀取這些屬性。
MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION:建構 APK 的最低 SDK 版本,以字串表示。在圖 2 所示的專案屬性頁面上,於「Minimum Android SDK Version」方塊中設定這個值。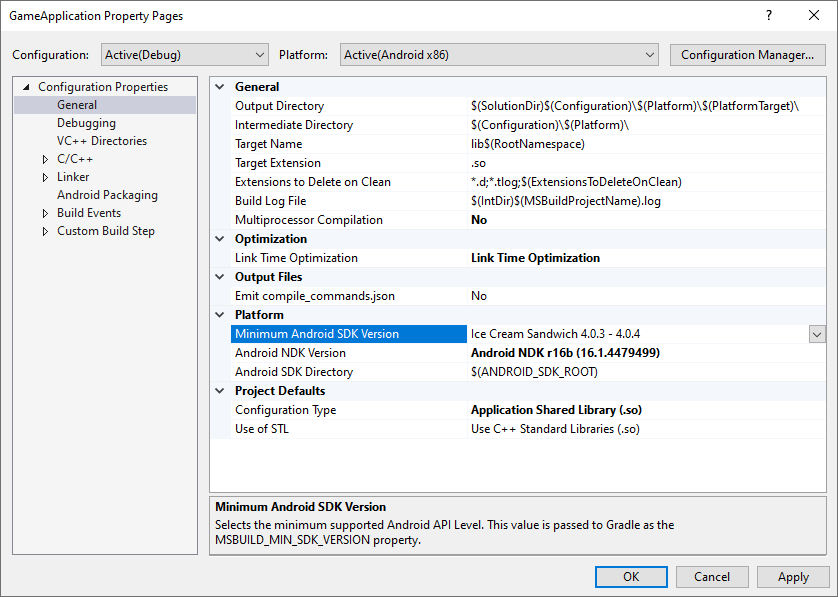
圖 2.「Minimum Android SDK Version」屬性Gradle 建構指令碼應將
minSdkVersion或minSdk設為這個字串值,並視需要進行toInteger()類型轉換。Groovy
android { // ... defaultConfig { applicationId "com.yourcompany.yourapp" minSdkVersion MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION // Or: minSdk MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION.toInteger() // ... } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... defaultConfig { applicationId = "com.yourcompany.yourapp" minSdkVersion(MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION) // Or: minSdk = MSBUILD_MIN_SDK_VERSION.toInteger() // ... } // ... }
MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME:Gradle 建構的 APK 預期名稱。Android Game Development Extension 功能會尋找與這個名稱相符的 APK,然後將其部署至已連結的裝置 (用於偵錯和剖析)。在圖 3 所示的專案屬性頁面的「APK Name」方塊中設定這個值。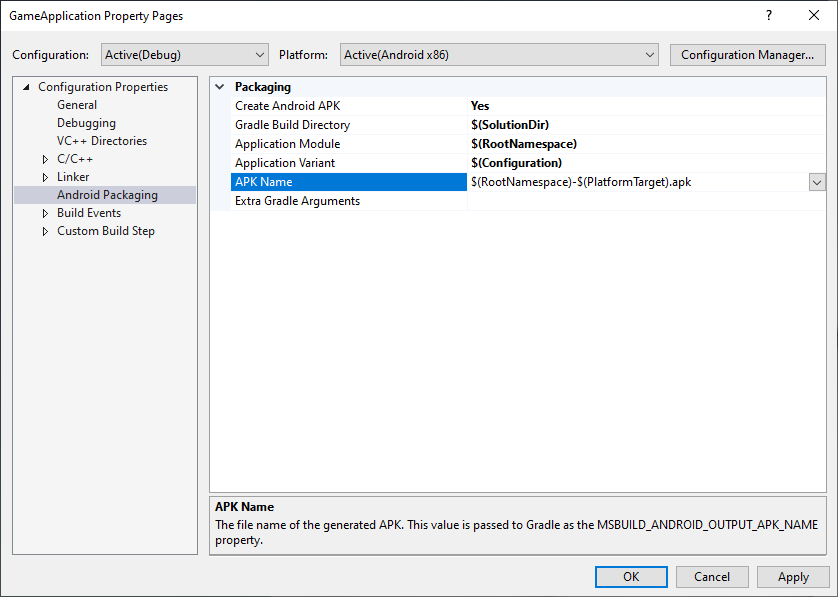
圖 3.「APK Name」屬性Gradle 建構指令碼必須遵守這項屬性。例如,以下範例會將所有變化版本的輸出 APK 名稱設為 MSBuild 選擇的名稱。
Groovy
android { // ... applicationVariants.all { variant -> variant.outputs.all { outputFileName = MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME } } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... applicationVariants.all { variant -> variant.outputs.all { outputFileName = MSBUILD_ANDROID_OUTPUT_APK_NAME } } // ... }
MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR:包含 MSBuild 建構的共用資料庫 (.so檔案) 的目錄。在下方所示的專案屬性頁面的「Output Directory」方塊中設定這個值。根據預設,這個值是 Visual Studio 專案的輸出目錄屬性,如圖 4 所示。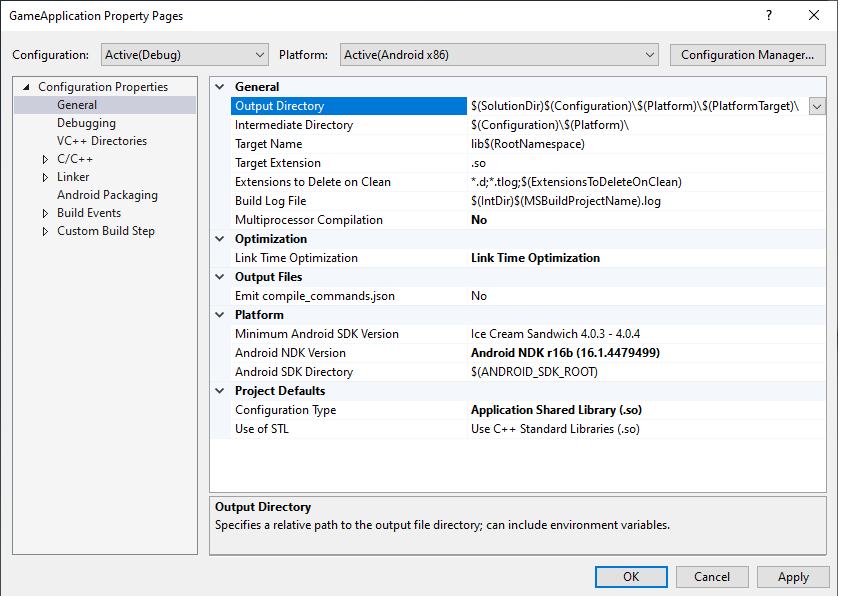
圖 4. 「Output Directory」屬性Gradle 應該將共用資料庫檔案封裝在 APK 中的資料夾中,以便 Android 應用程式在執行階段載入這些檔案。
Groovy
android { // ... sourceSets { main { jniLibs.srcDirs += [MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR] } } // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... sourceSets.getByName("main") { jniLibs.srcDir(MSBUILD_JNI_LIBS_SRC_DIR) } // ... }
此外,由於任何 C/C++ 程式碼現在是由 MSBuild 所建構,請移除 Gradle 建構指令碼中的
externalNativeBuild區段。這些區段用於叫用 CMake 或 ndk-build 來編譯 C/C++ 程式碼,但現在已不再需要。MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION:用於建構專案的 NDK 版本。在圖 5 所示的專案屬性頁面中,於「Android NDK Version」方塊中設定這個值。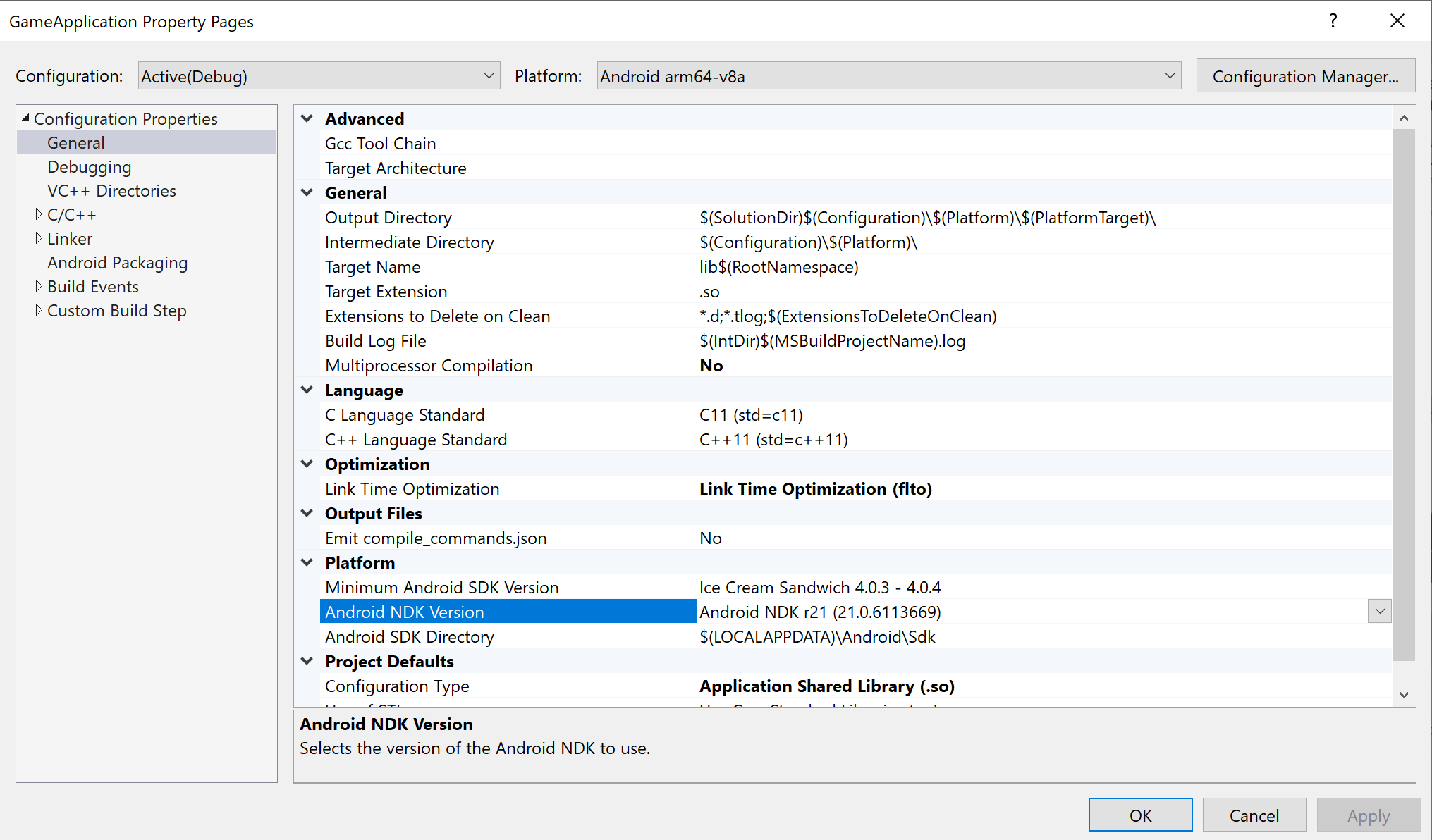
圖 5.「Android NDK Version」屬性Gradle 建構指令碼應將
ndkVersion設為這個值,如下所示:Groovy
android { // ... ndkVersion MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION // ... }
Kotlin
android { // ... ndkVersion = MSBUILD_NDK_VERSION // ... }
詳情請參閱 Android Studio 主題「安裝及設定 NDK 和 CMake」。
